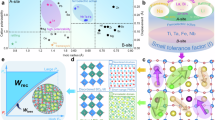
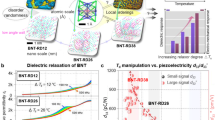
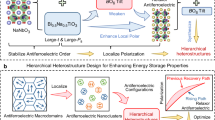
Abstract
Lead-free dielectric capacitors commonly rely on chemical disorder design to regulate relaxor behavior. In order to avoid the polarization sacrifice caused by non-ferroactive cations while maintaining a strong enough local random field, an oxygen octahedron tilt framework design strategy is introduced in this work. Based on the Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-AgNbO3 system with high-content ferroactive cations, slush-like heterogeneous polar nanoregions enable a large polarization response. Meanwhile, besides the local random electric and elastic fields caused by the heterovalence and different cation radii, the additional local random elastic field caused by the randomly disordered distribution of the BO6 tilt mode and angle not only slows polarization reorientation and growth but also provides a restoring force to reset polarization during charging, enabling the slim hysteresis loop with delayed polarization saturation as well as excellent energy storage properties. This work provides a feasible avenue for high-performance lead-free relaxors with low tolerance factor.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data supporting this study and its findings are available within the article and its Supplementary Information. Any data deemed relevant are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Wang, G. et al. Electroceramics for high-energy density capacitors: current status and future perspectives. Chem. Rev. 121, 6124–6172 (2021).
Yang, L. T. et al. Perovskite lead-free dielectrics for energy storage applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 102, 72–108 (2019).
Yao, F. Z., Yuan, Q. B., Wang, Q. & Wang, H. Multiscale structural engineering of dielectric ceramics for energy storage applications: from bulk to thin films. Nanoscale 12, 17165–17184 (2020).
Zhang, Y. et al. High-performance ferroelectric based materials via high-entropy strategy: Design, properties, and mechanism. Infomat 5, e12488 (2023).
Qi, H., Xie, A. X. & Zuo, R. Z. Local structure engineered lead-free ferroic dielectrics for superior energy-storage capacitors: a review. Energy Storage Mater. 45, 541–567 (2021).
Yan, F., Qian, J., Wang, S. & Zhai, J. W. Progress and outlook on lead-free ceramics for energy storage applications. Nano Energy 123, 109394 (2024).
Jayakrishnan, A. R. et al. Are lead-free relaxor ferroelectric materials the most promising candidates for energy storage capacitors? Prog. Mater Sci. 132, 101046 (2023).
Zhang, M. et al. Ultrahigh energy storage in high-entropy ceramic capacitors with polymorphic relaxor phase. Science 384, 185–189 (2024).
Chen, L. et al. Excellent energy storage and mechanical performance in hetero-structure BaTiO3-based relaxors. Chem. Eng. J. 452, 139222 (2023).
Fu, J. et al. A highly polarizable concentrated dipole glass for ultrahigh energy storage. Nat. Commun. 15, 7338 (2024).
Bokov, A. A. & Ye, Z. G. Recent progress in relaxor ferroelectrics with perovskite structure. J. Mater. Sci. 41, 31–52 (2006).
Smith, M., Khatiwada, R. & Li, P. Exploring ion polarizabilities and their correlation with van der Waals radii: a theoretical investigation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 20, 8505–8516 (2024).
Laulhé, C. et al. EXAFS study of lead-free relaxor ferroelectric BaTi1-xZrxO3 at the Zr K edge. Phys. Rev. B 74, 014106 (2006).
Li, D. et al. Atomic-scale high-entropy design for superior capacitive energy storage performance in lead-free ceramics. Adv. Mater. 37, 2409639 (2025).
Wei, T. et al. High-entropy assisted capacitive energy storage in relaxor ferroelectrics by chemical short-range order. Nat. Commun. 16, 807 (2025).
Qi, H. et al. Large (anti)ferrodistortive NaNbO3-based lead-free relaxors: Polar nanoregions embedded in ordered oxygen octahedral tilt matrix. Mater. Today 60, 91–97 (2022).
Li, F. et al. Superior electrocaloric performance enabled by highly robust monomorphic ferrodistortion in NaNbO3-based relaxor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 35, 2418534 (2024).
Duan, J. et al. High-entropy superparaelectrics with locally diverse ferroic distortion for high-capacitive energy storage. Nat. Commun. 15, 6754 (2024).
Liu, H. et al. Chemical design of Pb-free relaxors for giant capacitive energy storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 11764–11772 (2023).
Wang, Q. et al. Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-based relaxor-ferroelectric ceramics for low-electric-field dielectric energy storage via bidirectional optimization strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 452, 139422 (2023).
Luo, C. et al. Significantly enhanced energy-storage properties of Bi0.47Na0.47Ba0.06TiO3-CaHfO3 ceramics by introducing Sr0.7Bi0.2TiO3 for pulse capacitor application. Chem. Eng. J. 429, 132165 (2022).
Chen, L. et al. Large energy capacitive high-entropy lead-free ferroelectrics. Nano-Micro Lett 15, 65 (2023).
Qi, H. et al. Ultrahigh energy-storage density in nanbo3-based lead-free relaxor antiferroelectric ceramics with nanoscale domains. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1903877 (2019).
Dong, X. et al. (1-x)[0.90NN-0.10Bi(Mg2/3Nb1/3)O3]-x(Bi0.5Na0.5)0.7Sr0.3TiO3 ceramics with core-shell structures: a pathway for simultaneously achieving high polarization and breakdown strength. Nano Energy 101, 107577 (2022).
Chen, L. et al. Outstanding energy storage performance in high-hardness (Bi0.5K0.5)TiO3-based lead-free relaxors via multi-scale synergistic design. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2110478 (2021).
Sun, Z. et al. Superior capacitive energy-storage performance in Pb-free relaxors with a simple chemical composition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 6194–6202 (2023).
Chen, L. et al. Giant energy-storage density with ultrahigh efficiency in lead-free relaxors via high-entropy design. Nat. Commun. 13, 3089 (2022).
Li, D. et al. Improved energy storage properties achieved in (K, Na)NbO3‑based relaxor ferroelectric ceramics via a combinatorial optimization strategy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2111776 (2021).
Wu, J. et al. High energy storage performance in BiFeO3-based lead-free high-entropy ferroelectrics. Small 20, 2400997 (2024).
Lu, Z. et al. Superior energy density through tailored dopant strategies in multilayer ceramic capacitors. Energ. Environ. Sci. 13, 2938–2948 (2020).
Zhou, X. F. et al. Lead-free ferroelectrics with giant unipolar strain for high-precision actuators. Nat. Commun. 15, 6625 (2024).
Xiong, X. et al. Giant energy-storage in Pb-free relaxor ferroelectrics via atomic-level design. Adv. Mater. 9, e17815 (2025).
Tan, X. L., Ma, C., Frederick, J., Beckman, S. & Webber, K. G. The antiferroelectric ↔ ferroelectric phase transition in lead-containing and lead-free perovskite ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 4091–4107 (2011).
Luo, H. J. et al. Structural origin for the high piezoelectric performance of (Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3-BaTiO3-BiAlO3 lead-free ceramics. Acta Mater 218, 117202 (2021).
Qi, H., Xie, A. W., Fu, J. & Zuo, R. Z. Emerging antiferroelectric phases with fascinating dielectric, polarization and strain response in NaNbO3-(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 lead-free binary system. Acta Mater 208, 116710 (2021).
Su, F. Y. et al. Superior electrostatic storage energy under moderate electric field of superparaelectrics with highly polarizable clusters. Adv. Funct. Mater. 35, 2500988 (2025).
Liu, G. F., Chen, L. & Qi, H. Energy storage properties of NaNbO3-based lead-free superparaelectrics with large antiferrodistortion. Microstructures 3, 2023009 (2023).
Momma, K. & Izumi, F. VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 44, 1272–1276 (2011).
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2023YFB3508200 (H.Q.)), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52202127 (J.W.), 12404103 (H.L.) and 52462017 (H.L.)), the Outstanding Young Scientist Program of Beijing Colleges and Universities (JWZQ20240101015 (J.C.)), the Start-up Research Foundation of Hainan University (Grant No. XJ2500000599 (J.W.) and XJ2500000594 (Y.L.)), and the State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through the contributions of all authors. J.W. and H.Q. conceived this study. Y.L. performed this study with the supervision of J.W., H.Q., and J.C. Y.L. and H.L. fabricated the samples and carried out the electrical measurements. The XRD and dielectric spectra were collected by W.-S.F. and X.-S.M. The finite element simulation was processed by H.-F.Y. L.C. and S.-Q.D. conducted the microstructural SEM, TEM and STEM research. Y.C. conducted the in-situ XRD measurements for this work. J.W. conducted the PDF research. The manuscript was drafted by Y.L. and H.L., revised by J.W., H.Q., and J.C.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks Bastola Narayan, Thanapong Sareein and the other anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Li, H., Wu, J. et al. Oxygen octahedron framework design for large energy capacitive relaxors. Nat Commun (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-69282-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-69282-7