Abstract
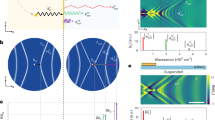
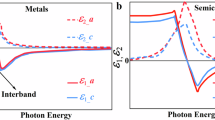
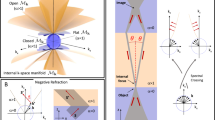
Hyperbolic media enable unique optical phenomena including hyperlensing, negative refraction, enhanced photonic density of states (PDOS), and highly confined polaritons. While most hyperbolic media are artificially engineered metamaterials, certain natural materials with extreme anisotropy can exhibit hyperbolic dispersion. Here, based on experimental evidence and theoretical fitting estimates to the experimental data, we suggest the presence of natural hyperbolic dispersion in hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) in the deep-ultraviolet (DUV) regime, induced by strong, anisotropic exciton resonances. Using all-optical imaging spectroscopic ellipsometry (ISE), we characterize the complex dielectric function along in-plane and out-of-plane directions down to 190 nm (6.53 eV), revealing a potential type-II hyperbolic window in the DUV regime. We predict that hyperbolicity supports hyperbolic exciton polaritons (HEP) with high directionality and slow group velocity, as confirmed by numerical calculations. Our findings suggest hBN as a platform for nanophotonic applications in the technologically significant DUV spectral range.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Relevant data supporting the key findings of this study are available within the article and the Supplementary Information file. All raw data generated during the current study are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
References
Sreekanth, K. V. et al. Extreme sensitivity biosensing platform based on hyperbolic metamaterials. Nat. Mater. 15, 621–627 (2016).
Sternbach, A. et al. Programmable hyperbolic polaritons in van der Waals semiconductors. Science 371, 617–620 (2021).
Liu, Z., Lee, H., Xiong, Y., Sun, C. & Zhang, X. Far-field optical hyperlens magnifying sub-diffraction-limited objects. Science 315, 1686–1686 (2007).
Poddubny, A., Iorsh, I., Belov, P. & Kivshar, Y. Hyperbolic metamaterials. Nat. Photonics 7, 948–957 (2013).
Krishnamoorthy, H. N., Jacob, Z., Narimanov, E., Kretzschmar, I. & Menon, V. M. Topological transitions in metamaterials. Science 336, 205–209 (2012).
Yang, X., Yao, J., Rho, J., Yin, X. & Zhang, X. Experimental realization of three-dimensional indefinite cavities at the nanoscale with anomalous scaling laws. Nat. Photonics 6, 450–454 (2012).
Lynch, J. et al. High-temperature-resilient hyperbolicity in a mixed-dimensional superlattice. Matter 8, 102290 (2025).
Salandrino, A. & Engheta, N. Far-field subdiffraction optical microscopy using metamaterial crystals: Theory and simulations. Phys. Rev. B. Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 74, 075103 (2006).
Jacob, Z., Alekseyev, L. V. & Narimanov, E. Optical hyperlens: far-field imaging beyond the diffraction limit. Opt. Express 14, 8247–8256 (2006).
Hoffman, A. J. et al. Negative refraction in semiconductor metamaterials. Nat. Mater. 6, 946–950 (2007).
Poddubny, A. N., Belov, P. A. & Kivshar, Y. S. Spontaneous radiation of a finite-size dipole emitter in hyperbolic media. Phys. Rev. A At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 84, 023807 (2011).
Choi, B. et al. Giant optical anisotropy in 2D metal–organic chalcogenates. ACS Nano 18, 25489–25498 (2024).
Zhang, H. et al. Cavity-enhanced linear dichroism in a van der Waals antiferromagnet. Nat. Photonics 16, 311–317 (2022).
Grudinin, D. et al. Hexagonal boron nitride nanophotonics: a record-breaking material for the ultraviolet and visible spectral ranges. Mater. Horiz. 10, 2427–2435 (2023).
Wang, H. et al. Planar hyperbolic polaritons in 2D van der Waals materials. Nat. Commun. 15, 69 (2024).
Ma, W. et al. In-plane anisotropic and ultra-low-loss polaritons in a natural van der Waals crystal. Nature 562, 557–562 (2018).
Giles, A. J. et al. Ultralow-loss polaritons in isotopically pure boron nitride. Nat. Mater. 17, 134–139 (2018).
Wang, C. et al. Van der Waals thin films of WTe2 for natural hyperbolic plasmonic surfaces. Nat. Commun. 11, 1158 (2020).
Wang, F. et al. Prediction of hyperbolic exciton-polaritons in monolayer black phosphorus. Nat. Commun. 12, 5628 (2021).
Ruta, F. L. et al. Hyperbolic exciton polaritons in a van der Waals magnet. Nat. Commun. 14, 8261 (2023).
Gershuni, Y. & Epstein, I. In-plane exciton polaritons versus plasmon polaritons: nonlocal corrections, confinement, and loss. Phys. Rev. B 109, L121408 (2024).
Eini, T. et al. Electrically tunable interband collective excitations in biased bilayer and trilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 134, 196903 (2025).
Kats, I., Eini, T. & Epstein, I. Monolayer semiconductor superlattices as hyperbolic materials at visible to near-infrared frequencies. Phys. Rev. B 111, L041302 (2025).
Dai, S. et al. Tunable phonon polaritons in atomically thin van der Waals crystals of boron nitride. Science 343, 1125–1129 (2014).
Venturi, G., Mancini, A., Melchioni, N., Chiodini, S. & Ambrosio, A. Visible-frequency hyperbolic plasmon polaritons in a natural van der Waals crystal. Nat. Commun. 15, 9727 (2024).
Watanabe, K., Taniguchi, T. & Kanda, H. Direct-bandgap properties and evidence for ultraviolet lasing of hexagonal boron nitride single crystal. Nat. Mater. 3, 404–409 (2004).
Cassabois, G., Valvin, P. & Gil, B. Hexagonal boron nitride is an indirect bandgap semiconductor. Nat. Photonics 10, 262–266 (2016).
Elias, C. et al. Flat bands and giant light-matter interaction in hexagonal boron nitride. Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 137401 (2021).
Zunger, A., Katzir, A. & Halperin, A. Optical properties of hexagonal boron nitride. Phys. Rev. B 13, 5560 (1976).
Tarrio, C. & Schnatterly, S. Interband transitions, plasmons, and dispersion in hexagonal boron nitride. Phys. Rev. B 40, 7852 (1989).
Cao, X., Clubine, B., Edgar, J., Lin, J. & Jiang, H. Two-dimensional excitons in three-dimensional hexagonal boron nitride. Appl. Phys.s Lett. 103, 191106 (2013).
Arnaud, B., Lebègue, S., Rabiller, P. & Alouani, M. Huge excitonic effects in layered hexagonal boron nitride. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 026402 (2006).
Wirtz, L., Marini, A. & Rubio, A. Excitons in boron nitride nanotubes: dimensionality effects. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 126104 (2006).
Caldwell, J. D. et al. Sub-diffractional volume-confined polaritons in the natural hyperbolic material hexagonal boron nitride. Nat. Commun. 5, 5221 (2014).
Sponza, L. et al. Direct and indirect excitons in boron nitride polymorphs: a story of atomic configuration and electronic correlation. Phys. Rev. B 98, 125206 (2018).
Artús, L. et al. Ellipsometry study of hexagonal boron nitride using synchrotron radiation: transparency window in the Far-UVC. Adv. Photonics Res. 2, 2000101 (2021).
Fujiwara, H. Spectroscopic Ellipsometry: Principles and Applications. (Wiley, 2007).
Dahal, R. et al. Anisotropic charge carrier transport in free-standing hexagonal boron nitride thin films. Appl. Phys. express 9, 065801 (2016).
Hoffman, T. B., Clubine, B., Zhang, Y., Snow, K. & Edgar, J. H. Optimization of Ni–Cr flux growth for hexagonal boron nitride single crystals. J. Cryst. growth 393, 114–118 (2014).
Scuri, G. et al. Large excitonic reflectivity of monolayer MoSe 2 encapsulated in hexagonal boron nitride. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 037402 (2018).
Epstein, I. et al. Near-unity light absorption in a monolayer WS2 van der Waals heterostructure cavity. Nano Lett. 20, 3545–3552 (2020).
Li, M., Biswas, S., Hail, C. U. & Atwater, H. A. Refractive index modulation in monolayer molybdenum diselenide. Nano Lett. 21, 7602–7608 (2021).
Horng, J. et al. Perfect absorption by an atomically thin crystal. Phys. Rev. Appl. 14, 024009 (2020).
Atash Kahlon, A. et al. Importance of pure dephasing in the optical response of excitons in high-quality van der Waals heterostructures. Phys. Rev. B 112, L041402 (2025).
Meshulam, M. et al. Temperature-dependent optical and polaritonic properties of excitons in HBN-encapsulated monolayer TMDs. Adv. Opt. Mater. 10, e02535 (2025).
Cannuccia, E., Monserrat, B. & Attaccalite, C. Theory of phonon-assisted luminescence in solids: application to hexagonal boron nitride. Phys. Rev. B 99, 081109 (2019).
Paleari, F., P C Miranda, H., Molina-Sánchez, A. & Wirtz, L. Exciton-phonon coupling in the ultraviolet absorption and emission spectra of bulk hexagonal boron nitride. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 187401 (2019).
Malitson, I. H. Interspecimen comparison of the refractive index of fused silica. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 55, 1205–1209 (1965).
Dodge, M. J. Refractive properties of magnesium fluoride. Appl. Opt. 23, 1980–1985 (1984).
Reshef, O., De Leon, I., Alam, M. Z. & Boyd, R. W. Nonlinear optical effects in epsilon-near-zero media. Nat. Rev. Mater. 4, 535–551 (2019).
Liberal, I. & Engheta, N. Zero-index structures as an alternative platform for quantum optics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 114, 822–827 (2017).
Chernikov, A. et al. Exciton binding energy and nonhydrogenic Rydberg series in monolayer WS 2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 076802 (2014).
Ishihara, T., Takahashi, J. & Goto, T. Optical properties due to electronic transitions in two-dimensional semiconductors (CnH2n+1NH3)2PbI4. Phys. Rev. B 42, 11099 (1990).
Epstein, I. et al. Highly confined in-plane propagating exciton-polaritons on monolayer semiconductors. 2D Mater. 7, 035031 (2020).
Song, B. et al. Determination of dielectric functions and exciton oscillator strength of two-dimensional hybrid perovskites. ACS Mater. Lett. 3, 148–159 (2020).
Kats, M. A., Blanchard, R., Genevet, P. & Capasso, F. Nanometre optical coatings based on strong interference effects in highly absorbing media. Nat. Mater. 12, 20–24 (2013).
Pettersson, L. A., Roman, L. S. & Inganäs, O. Modeling photocurrent action spectra of photovoltaic devices based on organic thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 86, 487–496 (1999).
Peumans, P., Yakimov, A. & Forrest, S. R. Small molecular weight organic thin-film photodetectors and solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 3693–3723 (2003).
Ma, E. Y. et al. The reststrahlen effect in the optically thin limit: a framework for resonant response in thin media. Nano Lett. 22, 8389–8393 (2022).
Basov, D., Fogler, M. & García de Abajo, F. Polaritons in van der Waals materials. Science 354, aag1992 (2016).
Jackson, E., Tischler, J., Ratchford, D. & Ellis, C. The role of losses in determining hyperbolic material figures of merit. Sci. Rep. 14, 25156 (2024).
Novotny, L. & Hecht, B. Principles of Nano-Optics. (Cambridge University Press, 2012).
Maier, S. A. Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications. Vol. 1 (Springer, 2007).
Wang, H. et al. Strain-tunable hyperbolic exciton polaritons in monolayer black arsenic with two exciton resonances. Nano Lett. 24, 2057–2062 (2024).
Eini, T., Asherov, T., Mazor, Y. & Epstein, I. Valley-polarized hyperbolic exciton polaritons in few-layer two-dimensional semiconductors at visible frequencies. Phys. Rev. B 106, L201405 (2022).
Low, T. et al. Polaritons in layered two-dimensional materials. Nat. Mater. 16, 182–194 (2017).
Fei, Z. et al. Nano-optical imaging of WS e2 waveguide modes revealing light-exciton interactions. Phys. Rev. B 94, 081402 (2016).
Pizzocchero, F. et al. The hot pick-up technique for batch assembly of van der Waals heterostructures. Nat. Commun. 7, 11894 (2016).
Malitson, I. H. & Dodge, M. J. Refractive index and birefringence of synthetic sapphire. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 62, 1405 (1972).
McPeak, K. M. et al. Plasmonic films can easily be better: rules and recipes. ACS Photonics 2, 326–333 (2015).
Hill, H. M. et al. Observation of excitonic Rydberg states in monolayer MoS2 and WS2 by photoluminescence excitation spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 15, 2992–2997 (2015).
He, K. et al. Tightly bound excitons in monolayer WSe2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 026803 (2014).
Wang, G. et al. Exciton states in monolayer MoSe2: impact on interband transitions. 2D Mater. 2, 045005 (2015).
Blancon, J.-C. et al. Extremely efficient internal exciton dissociation through edge states in layered 2D perovskites. Science 355, 1288–1292 (2017).
Jariwala, D., Davoyan, A. R., Wong, J. & Atwater, H. A. Van der Waals materials for atomically-thin photovoltaics: promise and outlook. ACS Photonics 4, 2962–2970 (2017).
Ahuja, R. et al. Electronic and optical properties of lead iodide. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 7219–7224 (2002).
Li, Y. et al. Measurement of the optical dielectric function of monolayer transition-metal dichalcogenides: MoS2, MoSe2, WS2, and WSe2. Phys. Rev. B 90, 205422 (2014).
Anantharaman, S. B. et al. Ultrastrong light–matter coupling in two-dimensional metal–organic chalcogenolates. Nat. Photonics 19, 322–328 (2025).
Beliaev, L. Y., Shkondin, E., Lavrinenko, A. V. & Takayama, O. Thickness-dependent optical properties of aluminum nitride films for mid-infrared wavelengths. J. Vacuum Sci. Technol. A 39, 043408 (2021).
Acknowledgements
D. J., B.C., and J.L. acknowledge support from the Office of Naval Research Young Investigator Award, Metamaterials Program (N00014-23−1-2037). This work was carried out in part at the Singh Center for Nanotechnology, which is supported by the NSF National Nanotechnology Coordinated Infrastructure Program under Grant NNCI-2025608. J.K. acknowledges the support from the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Korea under Project Code IBS-R014-A1 and the National Research Foundation of Korea grants (NRF-2023R1A2C2007998). N. E. acknowledges partial support from the US Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR) Multidisciplinary University Research Initiatives (MURI) program with grant # FA9550-21−1-0312 and AFOSR grant # FA9550-23-1-0307.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.J. supervised and acquired funding for the project. D.J. and B.C. conceived and designed the experiment. B.C. performed the ellipsometry measurements and conducted the data fitting. B.C. performed the optical simulations and calculations in discussion with D.J., N.E., and J.L. W.C. fit preliminary ellipsometry data. K.Y. fabricated samples. S. J. and H.C. performed the reflectance measurement under the supervision of J.K., B.C., and D.J. wrote the manuscript with inputs from all authors. All authors discussed the results and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, B., Lynch, J., Chen, W. et al. Natural hyperbolicity of hexagonal boron nitride in the deep ultraviolet. Nat Commun (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-69536-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-69536-4