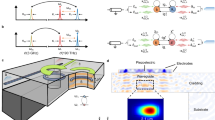
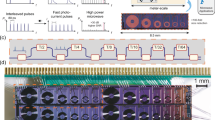
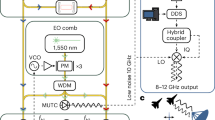
Abstract
Microwave sources are central to modern technologies ranging from radar and directed energy to medical applications, yet conventional electronic approaches face long-standing trade-offs between output power and tunability. Optoelectronic techniques offer a promising alternative by combining the broad bandwidth of optical systems with the high power-handling capability of wide-bandgap semiconductors. Here we show an optoelectronic microwave source based on fast-response silicon carbide, enabling picosecond-scale control of photogenerated carrier lifetime while sustaining power-handling capacities up to 55 MW. The system generates continuously tunable pulsed microwave emission across the P–L band, delivering peak output power exceeding 1 MW over the 0.25–1.3 GHz range and exhibiting stable nanosecond-scale pulse operation. The generated pulses exhibit low timing jitter and highly efficient power combining in array operation. These results demonstrate a scalable route toward high-power, broadband, and flexible microwave sources, enabling applications that demand simultaneous control over frequency, energy, and spatial distribution.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The source data generated in this study have been deposited in the Figshare database under accession code https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.30963374.
Code availability
All codes used in this study are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
References
Rumelhard, C., Algani, C., Billabert, A. L. Microwaves Photonic Links: Components and Circuits (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, 2017).
Andreas, B. et al. Lithium niobate photonics: unlocking the electromagnetic spectrum. Science 379, 40 (2023).
Guo, G. et al. Investigation and batch fabrication of G-band broadband and low-loss monocrystalline diamond window for vacuum electron devices. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 45, 1981–1984 (2024).
Casciati, A. et al. Effects of ultra-short pulsed electric field exposure on glioblastoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 3001 (2022).
Karunasagara, S. et al. Electrically-stimulated cellular and tissue events are coordinated through ion channel-mediated calcium influx and chromatin modifications across the cytosol-nucleus space. Biomaterials 314, 122854 (2025).
Wang, S. et al. Modeling and simulation of a multi-source microwave heating of soil based on PSO-BPNN. Appl. Therm. Eng. 257, 124148 (2024).
Yang, B. et al. The optimization of consensus decision-making for a multi-microwave source system based on composite leader-follower clustering for intelligent agent-based joint heating temperature field. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 66, 105668 (2025).
Yang, R. & Chen, J. Heating performance of dual-source microwave heating using different frequency shifting strategies in a solid-state system. Food Res. Int. 175, 113781 (2024).
Chen, C. et al. Dual-frequency microwave plasma source based on microwave coaxial transmission line. Appl. Sci. 11, 9873 (2021).
Sekiguchi, H. Experimental investigations of plasma-assisted ammonia combustion using rod-electrode-type microwave plasma source. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 65, 66–73 (2024).
Seeds, A. J. & Williams, K. J. Microwave photonics. J. Lightwave Technol. 24, 4628–4641 (2006).
Yao, J. Arbitrary waveform generation. Nat. Photonics 4, 79–80 (2010).
Hui, X. & Kan, E. C. Radio ranging with ultrahigh resolution using a harmonic radio-frequency identification system. Nat. Electron. 2, 125–131 (2019).
Zhu, X. et al. Agile manipulation of the time-frequency distribution of high-speed electromagnetic waves. Nat. Commun. 15, 8942 (2024).
Li, X. et al. Meta-surface-assisted high-power broadband rectangular TE1,0 mode window for vacuum electronic devices. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 73, 1–7 (2025).
Zhang, J. et al. Research progresses on cherenkov and transit-time high-power microwave sources at NUDT. Matter Radiat. Extremes 1, 163–178 (2016).
James, B., Edl, S., Coty, S. J. A., S. J. & Peng, Z. High Power Microwaves (Taylor & Francis Group, Abingdon, 2024).
Ayllon, N. Microwave high power amplifier technologies for spaceborne applications. In Proc. IEEE Annual Wireless and Microwave Technology Conference, (Cocoa Beach, FL, USA, 2015).
Prakash, D. J. et al. Self-winding helices as slow-wave structures for sub-millimeter traveling-wave tubes. ACS Nano 15, 1229–1239 (2021).
Wang, Y. et al. Electro-thermal co-simulation of high-frequency structure of staggered double-grating traveling wave tube based on finite difference time domain. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 61, 104833 (2024).
Sharma, R. et al. Power characteristics of a high-performance helix traveling wave tube. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 56, 104199 (2024).
Trubetskov, D. I. & Vdovina, G. M. Traveling wave tubes: a history of people and fates. Phys. Uspekhi 63, 1–13 (2020).
Wu, G. et al. Theory and hot test of high-power broadband helix traveling-wave tube based on a double-graded radius and pitch circuit. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 42, 1868–1870 (2021).
Qiu, C. et al. Dirac-source field-effect transistors as energy-efficient, high-performance electronic switches. Sci. Found. China 361, 387–392 (2018).
Guo, S. et al. Ultrascaled double-gate monolayer SnS2 MOSFETs for high-performance and low-power applications. Phys. Rev. Appl. 14, 044031 (2020).
D’Ambrosio, R. et al. Improved densification of SiCf/SiC composites by microwave-assisted chemical vapor infiltration process based on multifrequency solid-state sources excitation. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 45, 116950 (2025).
Rayrat, G. et al. A new sinter-forging process based on a 915 MHz solid-state microwave source for sintering of oxide ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 45, 117262 (2025).
Jing, X. D. et al. A 150-W spaceborne GaN solid-state power amplifier for Beidou navigation satellite system. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 58, 2383–2393 (2022).
Giofre, R. et al. Design realization and tests of a space-borne GaN solid-state power amplifier for second generation Galileo navigation system. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 54, 2383–2396 (2018).
Naderi, P. & Fallahi, F. A design strategy for bandwidth enhancement in three-stage Doherty power amplifier with extended dynamic range. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 66, 1024–1033 (2018).
Zhou, H. et al. A generic theory for design of efficient three-stage Doherty power amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 70, 1242–1253 (2022).
Xia, J. et al. Improved three-stage Doherty amplifier design with impedance compensation in load combiner for broadband applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 67, 778–786 (2019).
De Chatellus, H. G. et al. Reconfigurable photonic generation of broadband chirped waveforms using a single CW laser and low-frequency electronics. Nat. Commun. 9, 1–12 (2018).
Cohen, L. M. et al. Silicon photonic microresonator-based high-resolution line-by-line pulse shaping. Nat. Commun. 15, 7878 (2024).
Supradeepa, V. R. et al. Comb-based radiofrequency photonic filters with rapid tunability and high selectivity. Nat. Photon. 6, 186–194 (2012).
Xie, X. et al. Photonic microwave signals with zeptosecond-level absolute timing noise. Nat. Photon. 11, 44–47 (2017).
Jiang, H. et al. Simultaneous achieving negative photoconductivity response and volatile resistive switching in Cs2CoCl4 single crystals towards artificial optoelectronic synapse. Light Sci. Appl. 13, 316 (2024).
Capmany, J. & Novak, D. Microwave photonics combines two worlds. Nat. Photon. 1, 319–330 (2007).
Gu, Y. et al. High-power microsecond ultraviolet burst-mode pulse laser with a rectangular envelope and GHz-adjustable intra-burst pulses. High. Power Laser Sci. Eng. 13, e23 (2025).
Fang, J. et al. Electron transport properties of AlxGa1-xN/GaN transistors based on first-principles calculations and Boltzmann-equation Monte Carlo simulations. Phys. Rev. Appl. 11, 044045 (2019).
Zhang, Y. et al. Highly sensitive photoelectric detection and imaging enhanced by the pyro-phototronic effect based on a photoinduced dynamic Schottky effect in 4H-SiC. Adv. Mater. 34, 2204363 (2022).
Choi, S. H. et al. Heterogeneous integration of wide bandgap semiconductors and 2D materials: processes, applications, and perspectives. Adv. Mater. 37, 2411108 (2024).
Wang, S. J. et al. Highly efficient modulation doping: a path toward superior organic thermoelectric devices. Sci. Adv. 8, 9264 (2022).
Xun, T. et al. Recent progress of parameter-adjustable high-power photonic microwave generation based on wide-bandgap photoconductive semiconductors. Chin. Opt. Lett. 22, 118–127 (2024).
He, T. et al. Effect of donor–acceptor compensation on transient performance of vanadium-doped SiC photoconductive switches using 532-nm laser. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 71, 1–8 (2024).
Najarian, A. M. et al. Photophysical properties of materials for high-speed photodetection. Nat. Rev. Phys. 6, 219–230 (2024).
Franklyn, Q. The photodetection of ultrashort optical pulse trains for low noise microwave signal generation. Laser Photonics Rev. 17, 1 (2023).
Petter, L. & Heck, M. J. R. High-power microwave generation through distributed optical amplification into a photodiode array on an open indium phosphide platform. J. Lightwave Technol. 38, 5526–5535 (2020).
Keye, S. & Andreas, B. High-speed photodetectors for microwave photonics. Appl. Sci. 9, 623 (2019).
Zeng, L. et al. Dual-stacked SiC vertical photoconductive switch for modulation bandwidth extension of frequency-agile power microwave. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 45, 992–995 (2024).
Chu, X. et al. Wide-range frequency-agile microwave generation up to 10 GHz based on vanadium-compensated 4H-SiC photoconductive semiconductor switch. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 43, 1 (2022).
Acknowledgements
The work was supported in part by a Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62434010, awarded to T. X.), the National Key R&D Program (Grant No. 2024YFE0102400, awarded to H. J.), and the Hunan Provincial Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars (Grant No. 2025JJ20065, awarded to T. X.). We would like to thank Dr. Yanran Gu and Dr. Ting He for the sincere help and support on the fabrication and test.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.X., L.W., and Jun Z. conceived the idea of using linear control of photonic semiconductors to generate high-power microwaves. X.N., H.Y., and Jiande Z. contributed to the theoretical simulation models. B.Z., Jing H., and J.Y. developed the laser source platform. X.N., M.Y., and Junpu L. were responsible for the system link setup and testing. X.N., H.J., and Q.Z. drafted the main sections of the manuscript. Jinliang L. and Jiande Z. contributed to the data processing and analysis. B.J., Juntao H., and X.X. coordinated the experimental instruments, progress, and site management.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, X., Wang, L., Zhang, B. et al. A pulsed optoelectronic microwave source with high power and frequency tunability. Nat Commun (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-69582-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-69582-y