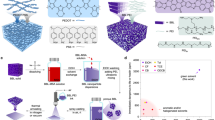
Abstract
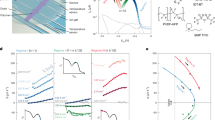
Electrolyte-gated transistors (EGTs) are typically limited to p-type operation, with stable n-type devices remaining scarce. In this study, we demonstrate high-performance n-type EGTs using a poly(benzimidazobenzophenanthroline) (BBL) polymer semiconductor gated by ionogel electrolytes. Electrochemical doping in BBL induces ion pathways in amorphous regions during initial doping, facilitating efficient electron transport. This yields exceptional device performance, including a geometry-normalized transconductance of 4.6 S cm−1, an ON/OFF ratio of ≈105, a product of electron mobility and volumetric capacitance (μC* ≈ 16.4 F cm–1 V–1 s–1), and minimal hysteresis (<0.1 V). These features surpass most reported n-type EGTs, demonstrating the importance of ion-driven electrochemical doping in BBL. Furthermore, we not only fabricate all-polymer complementary inverters, NAND, and NOR gates but also demonstrate flexible circuits by integrating n-type BBL and p-type polythiophene EGTs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Cho, J. H. et al. Printable ion-gel gate dielectrics for low-voltage polymer thin-film transistors on plastic. Nat. Mater. 7, 900–906 (2008).
Kim, S. H. et al. Electrolyte-gated transistors for organic and printed electronics. Adv. Mater. 25, 1822–1846 (2013).
Rivnay, J. et al. Organic electrochemical transistors. Nat. Rev. Mater. 3, 17086 (2018).
Gkoupidenis, P. et al. Neuromorphic device architectures with global connectivity through electrolyte gating. Nat. Commun. 8, 15448 (2017).
Sarkar, T. et al. An organic artificial spiking neuron for in situ neuromorphic sensing and biointerfacing. Nat. Electron. 5, 774–783 (2022).
Ho, D. H. et al. Non-von Neumann multi-input spike signal processing enabled by an artificial synaptic multiplexer. Sci. Adv. 8, eabn1838 (2022).
Harikesh, P. C. et al. Ion-tunable antiambipolarity in mixed ion-electron conducting polymers enables biorealistic organic electrochemical neurons. Nat. Mater. 22, 242–248 (2023).
Lim, D. U. et al. Monolithic tandem vertical electrochemical transistors for printed multi-valued logic. Adv. Mater. 35, 2208757 (2023).
Laswick, Z. et al. Tunable anti-ambipolar vertical bilayer organic electrochemical transistor enable neuromorphic retinal pathway. Nat. Commun. 15, 6309 (2024).
Yamashita, Y. et al. Efficient molecular doping of polymeric semiconductors driven by anion exchange. Nature 572, 634–638 (2019).
Cho, K. G. et al. Sub-band filling and hole transport in polythiophene-based electrolyte-gated transistors: effect of side-chain length and density. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2303700 (2023).
Jacobs, I. E. et al. Structural and dynamic disorder, not ionic trapping, controls charge transport in highly doped conducting polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 3005–3019 (2022).
Guo, J. J. et al. Understanding asymmetric switching times in accumulation mode organic electrochemical transistors. Nat. Mater. 23, 656–663 (2024).
Neusser, D. et al. High conductivities of disordered P3HT films by an electrochemical doping strategy. Chem. Mater. 32, 6003–6013 (2020).
Rivnay, J. et al. High-performance transistors for bioelectronics through tuning of channel thickness. Sci. Adv. 1, e1400251 (2015).
Cho, K. Y. et al. Tuning gate potential profiles and current-voltage characteristics of polymer electrolyte-gated transistors by capacitance engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 16, 19309–19317 (2024).
Cho, K. G. et al. Tuning threshold voltage of electrolyte-gated transistors by binary ion doping. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 50004–50012 (2022).
Zeglio, E. & Inganäs, O. Active materials for organic electrochemical transistors. Adv. Mater. 30, 1800941 (2018).
Giovannitti, A. et al. N-type organic electrochemical transistors with stability in water. Nat. Commun. 7, 13066 (2016).
Deng, S. H. et al. High-performance and ecofriendly organic thermoelectrics enabled by n-type polythiophene derivatives with doping-induced molecular order. Adv. Mater. 36, 2309679 (2024).
Kuang, Y. Z. et al. Matching P- and N-type organic electrochemical transistor performance enables a record high-gain complementary inverter. Adv. Mater. 37, 2417691 (2024).
Sun, H. D. et al. Complementary logic circuits based on high-performance n-type organic electrochemical transistors. Adv. Mater. 30, 1704916 (2018).
Wu, H. Y. et al. Influence of molecular weight on the organic electrochemical transistor performance of ladder-type conjugated polymers. Adv. Mater. 34, 2106235 (2022).
Yang, C. Y. et al. A high-conductivity n-type polymeric ink for printed electronics. Nat. Commun. 12, 2354 (2021).
Surgailis, J. et al. Mixed conduction in an N-type organic semiconductor in the absence of hydrophilic side-chains. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2010165 (2021).
Guo, J. J. et al. Hydration of a side-chain-free N-type semiconducting ladder polymer driven by electrochemical doping. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 1866–1876 (2023).
Wang, M. X. et al. Glassy gels toughened by solvent. Nature 631, 313–318 (2024).
Fan, X. T. et al. Ionogels: recent advances in design, material properties and emerging biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 52, 2497–2527 (2023).
Luo, Z. H. et al. Roles of ionic liquids in adjusting nature of ionogels: a mini review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2203988 (2022).
Kim, Y. M. et al. Functional ion gels: versatile electrolyte platforms for electrochemical applications. Chem. Mater. 33, 2683–2705 (2021).
Wang, M. X. et al. Tough ionogels: synthesis, toughening mechanisms, and mechanical properties?A perspective. JACS Au 2, 2645–2657 (2022).
Wang, M. et al. Tough and stretchable ionogels by in situ phase separation. Nat. Mater. 21, 359–365 (2022).
Lv, D. et al. Microphase-separated elastic and ultrastretchable ionogel for reliable ionic skin with multimodal sensation. Adv. Mater. 36, 2309821 (2024).
Tang, W. et al. A microphase-separation ionogel electrolyte for highly stretchable all-solid-state supercapacitors. Chem. Eng. J. 501, 157726 (2024).
Hyun, W. J. et al. Layered heterostructure ionogel electrolytes for high-performance solid-state lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 33, 2007864 (2021).
Kim, M. S. et al. 3D printable double-network ionogels with a multi-angle zigzag pattern for enhanced linearity and sensitivity of stretchable ionic sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 504, 158573 (2025).
Wu, X. et al. High performing solid-state organic electrochemical transistors enabled by glycolated polythiophene and ion-gel electrolyte with a wide operation temperature range from− 50 to 110 C. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2209354 (2023).
Chouhdry, H. H. et al. A flexible artificial chemosensory neuronal synapse based on chemoreceptive ionogel-gated electrochemical transistor. Nat. Commun. 14, 821 (2023).
He, R. et al. Organic electrochemical transistor based on hydrophobic polymer tuned by ionic gels. Angew. Chem. 135, e202304549 (2023).
Cho, K. G. et al. Thermostable ion gels for high-temperature operation of electrolyte-gated transistors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 15464–15471 (2020).
Tang, C. G. et al. A universal biocompatible and multifunctional solid electrolyte in p-type and n-type organic electrochemical transistors for complementary circuits and bioelectronic interfaces. Adv. Mater. 36, 2405556 (2024).
Yang, C. Y. et al. Low-power/high-gain flexible complementary circuits based on printed organic electrochemical transistors. Adv. Electron. Mat. 8, 2100907 (2022).
Baek, J. et al. Enhanced stability of N-type organic electrochemical transistors via small-molecule passivation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 35, 2414916 (2025).
Zhong, Y. et al. High-performance fiber-shaped vertical organic electrochemical transistors patterned by surface photolithography. Chem. Mater. 35, 9739–9746 (2023).
Hou, K. et al. High performance, flexible, and thermally stable all-solid-state organic electrochemical transistor based on thermoplastic polyurethane ion gel. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 5, 2215–2226 (2023).
Zhang, Y. et al. High-performance organic electrochemical transistors and neuromorphic devices comprising naphthalenediimide-dialkoxybithiazole copolymers bearing glycol ether pendant groups. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2201593 (2022).
Chen, Q. et al. Impact of Al/Ti electrodes on the performance and operational stability of n-channel solution-processed solid-state electrolyte-gated transistors: applications in reservoir computing. Adv. Electron. Mat. 11, 2500038. (2025).
Huang, W. et al. Vertical organic electrochemical transistors for complementary circuits. Nature 613, 496–502 (2023).
Kim, J. et al. Monolithically integrated high-density vertical organic electrochemical transistor arrays and complementary circuits. Nat. Electron. 7, 234–243 (2024).
Herlogsson, L. et al. Polyelectrolyte-gated organic complementary circuits operating at low power and voltage. Adv. Mater. 23, 4684–4689 (2011).
He, T. & Frisbie, C. D. Sub-band filling, mott-like transitions, and ion size effects in C60 single crystal electric double layer transistors. ACS nano 16, 4823–4830 (2022).
Cho, K. G. et al. Band filling, electrochemical reaction, and re-entrant insulating behavior in electrolyte-gated BBL polymer semiconductor films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 17, 15718–15727 (2025).
Bisquert, J. Hysteresis in organic electrochemical transistors: distinction of capacitive and inductive effects. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 14, 10951–10958 (2023).
Cavassin, P. et al. Electrochemical doping in ordered and disordered domains of organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors. Adv. Mater. 35, 2300308 (2023).
Wang, S. et al. An organic electrochemical transistor for multi-modal sensing, memory and processing. Nat. Electron. 6, 281–291 (2023).
Jackson, S. R. et al. Crystallinity determines ion injection kinetics and local ion density in organic mixed conductors. Chem. Mater. 35, 5392–5400 (2023).
Kim, S. H. et al. Performance and stability of aerosol-jet-printed electrolyte-gated transistors based on poly(3-hexylthiophene). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 6580–6585 (2013).
Xu, K. et al. On the origin of Seebeck coefficient inversion in highly doped conducting polymers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2112276 (2022).
Wang, S. et al. Thermoelectric properties of solution-processed n-doped ladder-type conducting polymers. Adv. Mater. 28, 10764 (2016).
Guardado, J. O. & Salleo, A. Structural effects of gating poly(3-hexylthiophene) through an Ionic Liquid. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27, 1701791 (2017).
Lu, L. et al. Stretchable all-gel organic electrochemical transistors. Nat. Commun. 16, 3831 (2025).
Guo, K. et al. Rapid single-molecule detection of COVID-19 and MERS antigens via nanobody-functionalized organic electrochemical transistors. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 5, 666–677 (2021).
Khodagholy, D. et al. In vivo recordings of brain activity using organic transistors. Nat. Commun. 4, 1575 (2013).
Bai, J. et al. Coin-sized, fully integrated, and minimally invasive continuous glucose monitoring system based on organic electrochemical transistors. Sci. Adv. 10, eadl1856 (2024).
Cho, K. G. et al. Optimizing electrochemically active surfaces of carbonaceous electrodes for ionogel based supercapacitors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 2002053 (2020).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Korea Basic Science Institute (National research Facilities and Equipment Center) grant funded by the Ministry of Education (2021R1A6C101A404), Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) and the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE) of the Republic of Korea (No. P0017363), the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (Ministry of Science and ICT, MSIT) (RS-2025-24523099), and Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT) Core Project (KS2621-20). This work was partially supported by the MRSEC program of the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) under Grant Number DMR-2011401.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.J.K. and D.H.P. contributed equally to this work. K.H.L., C.D.F., and K.G.C. conceived the idea and designed the experiments. S.J.K., D.H.P. and Y.N.L. performed device fabrication and characterization. M.S.K. and K.H. supported device characterization. S.J.K., K.G.C. and K.H.L. wrote the manuscript with input from C.D.F. and K.H. All authors contributed to discussions on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.J., Park, D.H., Lee, Y.N. et al. Sub-1V, flexible, all-polymer complementary logic circuits based on electrolyte-gated transistors. npj Flex Electron (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41528-026-00530-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41528-026-00530-y