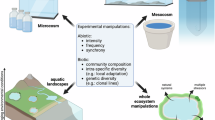
Abstract
We are beginning to understand the ecotoxicological effects of plastic pollution at the suborganismal, individual, population and community levels, but research has only just begun to explore the ecological and evolutionary impacts of plastic as a new habitat. The global introduction of plastic waste into aquatic environments introduces diverse and variable habitat modifications, altering ecosystems and potentially forming new ecological niches. This widespread habitat modification spans several aquatic ecosystems, including the pelagic ocean, deep-sea benthos, lakes and rivers. Recent studies suggest that habitat modification may interact with and alter ecological and evolutionary processes, affecting populations, communities and species, for example, through feeding ecology, mating behaviour and dispersal. However, further research is necessary to understand the potential long-term effects of plastic pollution on ecological and evolutionary processes across global aquatic ecosystems. Here, we review this emerging field of research and its trajectory.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borrelle, S. B. et al. Predicted growth in plastic waste exceeds efforts to mitigate plastic pollution. Science 369, 1515–1518 (2020).
Bean, T. H. Effects of garbage on fish. Forest and Stream 38, 1 (1892).
Bucci, K., Tulio, M. & Rochman, C. M. What is known and unknown about the effects of plastic pollution: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Ecol. Appl. 30, e02044 (2020).
Høiberg, M. A., Woods, J. S. & Verones, F. Global distribution of potential impact hotspots for marine plastic debris entanglement.Ecol. Indic. 135, 108509 (2022).
Koelmans, A. A. et al. Risk assessment of microplastic particles. Nat. Rev. Mater. 7, 138–152 (2022).
Mehinto, A. C. et al. Risk-based management framework for microplastics in aquatic ecosystems. Microplast. Nanoplast. 2, 17 (2022).
Hermabessiere, L. et al. Occurrence and effects of plastic additives on marine environments and organisms: a review. Chemosphere 182, 781–793 (2017).
Bridson, J. H., Gaugler, E. C., Smith, D. A., Northcott, G. L. & Gaw, S. et al. Leaching and extraction of additives from plastic pollution to inform environmental risk: a multidisciplinary review of analytical approaches. J. Hazard. Mater. 414, 125571 (2021).
Li, Y. et al. Leaching of chemicals from microplastics: a review of chemical types, leaching mechanisms and influencing factors. Sci. Total Environ. 906, 167666 (2024).
Teuten, E. L. et al. Transport and release of chemicals from plastics to the environment and to wildlife. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 364, 2027–2045 (2009).
Godoy, V., Blázquez, G., Calero, M., Quesada, L. & Martín-Lara, M. A. The potential of microplastics as carriers of metals. Environ. Pollut. 255, 113363 (2019).
Puckowski, A., Cwięk, W., Mioduszewska, K., Stepnowski, P. & Białk-Bielińska, A. Sorption of pharmaceuticals on the surface of microplastics. Chemosphere 263, 127976 (2021).
Atugoda, T. et al. Interactions between microplastics, pharmaceuticals and personal care products: implications for vector transport. Environ. Int. 149, 106367 (2021).
Diepens, N. J. & Koelmans, A. A. Accumulation of plastic debris and associated contaminants in aquatic food webs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 8510–8520 (2018).
Lambert, S., Scherer, C. & Wagner, M. Ecotoxicity testing of microplastics: considering the heterogeneity of physicochemical properties. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 13, 470–475 (2017).
Cózar, A. et al. Plastic debris in the open ocean. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 111, 10239–10244 (2014).
Lebreton, L. et al. Evidence that the Great Pacific Garbage Patch is rapidly accumulating plastic. Sci. Rep. 8, 4666 (2018).
Pinheiro, H. T. et al. Plastic pollution on the world’s coral reefs. Nature 619, 311–316 (2023).
Zhu, X., Rochman, C. M., Hardesty, B. D. & Wilcox, C. Plastics in the deep sea—a global estimate of the ocean floor reservoir. Deep-Sea Res. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 206, 104266 (2024).
Nava, V. et al. Plastic debris in lakes and reservoirs. Nature 619, 317–322 (2023).
Weiss, L. et al. The missing ocean plastic sink: gone with the rivers. Science 373, 107–111 (2021).
Barnes, D. K. A. Invasions by marine life on plastic debris. Nature 416, 808–809 (2002).
Haram, L. E. et al. Extent and reproduction of coastal species on plastic debris in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 7, 687–697 (2023).
Goldstein, M. C., Rosenberg, M. & Cheng, L. Increased oceanic microplastic debris enhances oviposition in an endemic pelagic insect. Biol. Lett. 8, 817–820 (2012).
Zettler, E. R., Mincer, T. J. & Amaral-Zettler, L. A. Life in the ‘plastisphere’: microbial communities on plastic marine debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 7137–7146 (2013).
Harrison, J. P. et al. Rapid bacterial colonization of low-density polyethylene microplastics in coastal sediment microcosms. BMC Microbiol. 14, 232 (2014).
McCormick, A., Hoellein, T., Mason, S. A., Schluep, J. & Kelly, J. J. Microplastic is an abundant and distinct microbial habitat in an urban river. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 11863–11871 (2014).
Lazcano, R. F., Kelly, J. J. & Hoellein, T. J. Biofilms on plastic litter in an urban river: community composition and activity vary by substrate type. Water Environ. Res. 96, e11008 (2024).
Wright, R. J., Erni-Cassola, G., Zadjelovic, V., Latva, M., & Christie-Oleza, J. A. Marine plastic debris: a new surface for microbial colonization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 54, 11657–11672 (2020).
Davidson, T. M. Boring crustaceans damage polystyrene floats under docks polluting marine waters with microplastic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 64, 1821–1828 (2012).
Jang, M., Shim, W. J., Han, G. M., Song, Y. K. & Hong, S. H. Formation of microplastics by polychaetes (Marphysa sanguinea) inhabiting expanded polystyrene marine debris. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 131, 365–369 (2018).
Zheng, Y., Zhu, J., Li, J., Li, G. & Shi, H. Burrowing invertebrates induce fragmentation of mariculture styrofoam floats and formation of microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 447, 130764 (2023).
Rech, S. et al. A desert in the ocean—depauperate fouling communities on marine litter in the hyper-oligotrophic South Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Sci. Total Environ. 759, 143545 (2021).
Barry, P. J., Silburn, B., Bakir, A., Russell, J. & Tidbury, H. J. Seafloor macrolitter as a settling platform for non-native species: a case study from UK waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 204, 116499 (2024).
Bottari, T. et al. Plastic litter colonization in a brackish water environment. Sci. Total Environ. 912, 169177 (2024).
Orpwood, J. E., Magurran, A. E., Armstrong, J. D. & Griffiths, S. W. Minnows and the selfish herd: effects of predation risk on shoaling behaviour are dependent on habitat complexity. Anim. Behav. 76, 143–152 (2008).
Figueiredo, B. R., Mormul, R. P. & Thomaz, S. M. Swimming and hiding regardless of the habitat: prey fish do not choose between a native and a non-native macrophyte species as a refuge. Hydrobiologia 746, 285–290 (2014).
Grabowski, J. H. Habitat complexity disrupts predator–prey interactions but not the trophic cascade on oyster reefs. Ecology 85, 995–1004 (2004).
Crowder, L. B. & Cooper, W. E. Habitat structural complexity and the interaction between bluegills and their prey. Ecology 63, 1802–1813 (1982).
Lamb, J. B. et al. Plastic waste associated with disease on coral reefs. Science 359, 460–462 (2018).
Jagiello, Z., Dylewski, Ł. & Szulkin, M. The plastic homes of hermit crabs in the Anthropocene. Sci. Total Environ. 913, 168959 (2024).
Elwood, R. W., Marks, N. & Dick, J. T. A. Consequences of shell-species preferences for female reproductive success in the hermit crab Pagurus bernhardus. Mar. Biol. 123, 431–434 (1995).
Goldstein, M. C., Carson, H. S. & Eriksen, M. Relationship of diversity and habitat area in North Pacific plastic-associated rafting communities. Mar. Biol. 161, 1441–1453 (2014).
Adams, T. P., Miller, R. G., Aleynik, D. & Burrows, M. T. Offshore marine renewable energy devices as stepping stones across biogeographical boundaries. J. Appl. Ecol. 51, 330–338 (2014).
Degraer, S. et al. Offshore wind farm artificial reefs affect ecosystem structure and functioning. Oceanography 33, 48–57 (2020).
McLean, D. L. et al. Influence of offshore oil and gas structures on seascape ecological connectivity. Glob. Change Biol. 28, 3515–3536 (2022).
Benadon, C. et al. Marine debris facilitates the long-distance dispersal of fish species. Mar. Biol. 171, 43 (2024).
Sheridan, E. A. et al. Plastic pollution fosters more microbial growth in lakes than natural organic matter. Nat. Commun. 13, 4175 (2022).
Romera-Castillo, C., Pinto, M., Langer, T. M., Álvarez-Salgado, X. A. & Herndl, G. J. Dissolved organic carbon leaching from plastics stimulates microbial activity in the ocean. Nat. Commun. 9, 1430 (2018).
Li, H.-X. et al. Effects of toxic leachate from commercial plastics on larval survival and settlement of the barnacle Amphibalanus amphitrite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50, 924–931 (2016).
Soberón, J. & Nakamura, M. Niches and distributional areas: concepts, methods, and assumptions. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 19644–19650 (2009).
Yoshida, S. et al. A bacterium that degrades and assimilates poly(ethylene terephthalate). Science 351, 1196–1199 (2016).
Jacquin, J. et al. Microbial ecotoxicology of marine plastic debris: a review on colonization and biodegradation by the ‘plastisphere’. Front. Microbiol. 10, 865 (2019).
Amobonye, A., Bhagwat, P., Singh, S. & Pillai, S. Plastic biodegradation: frontline microbes and their enzymes. Sci. Total Environ. 759, 143536 (2021).
Okada, H., Negoro, S., Kimura, H. & Nakamura, S. Evolutionary adaptation of plasmid-encoded enzymes for degrading nylon oligomers. Nature 306, 203–206 (1983).
Kinoshita, S. et al. Utilization of a cyclic dimer and linear oligomers of ε-aminocaproic acid by Achrornobacter guttatus KI 72. Agric. Biol. Chem. 39, 1219–1223 (1974).
Prijambada, I. D., Negoro, S., Yomo, T. & Urabe, I. Emergence of nylon oligomer degradation enzymes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO through experimental evolution. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61, 2020–2022 (1995).
Winchell, K. M., Reynolds, R. G., Prado-Irwin, S. R., Puente-Rolón, A. R. & Revell, L. J. Phenotypic shifts in urban areas in the tropical lizard Anolis cristatellus. Evolution 70, 1009–1022 (2016).
Velasquez, E. et al. Age and area predict patterns of species richness in pumice rafts contingent on oceanic climatic zone encountered. Ecol. Evol. 8, 5034–5046 (2018).
Diamond, J. Animal art: variation in bower decorating style among male bowerbirds Amblyornis inornatus. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 83, 3042–3046 (1986).
Marshall, A. J. Bower‐birds. Biol. Rev. 29, 1–45 (1954).
Diamond, J. Bower building and decoration by the bowerbird Amblyornis inornatus. Ethology 74, 177–204 (1987).
Diamond, J. Experimental study of bower decoration by the bowerbird Amblyornis inornatus, using colored poker chips. Am. Nat. 131, 631–653 (1988).
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by a Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada Discovery grant awarded to C.M.R.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.H. and C.M.R. collaborated on the design of this study. The study was led by J.H. J.H. wrote the first draft of the manuscript. C.M.R. reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Ecology & Evolution thanks Linsey Haram and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Haney, J., Rochman, C.M. Plastic pollution has the potential to alter ecological and evolutionary processes in aquatic ecosystems. Nat Ecol Evol 9, 762–768 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-025-02678-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-025-02678-8
This article is cited by
-
Animal personalities are important in a changing world
Nature Reviews Biodiversity (2026)
-
Museum foraminifera archive historical marine plastic pollution
npj Emerging Contaminants (2026)