Abstract
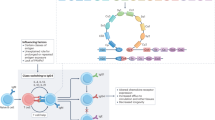
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a fibro-inflammatory disorder usually characterized by multi-organ involvement. Its pathogenesis is complex and involves genetic and environmental factors, while immune responses usually mediate organ damage and promote fibrosis, which is a key feature of the disease. IgG4 responses, however, are not exclusive to IgG4-RD and can be encountered in other diseases with phenotypes that partially overlap that of IgG4-RD. Although IgG4-RD has clinical and histological hallmarks, the lack of validated diagnostic criteria often makes the diagnosis challenging, requiring a multi-dimensional approach that integrates clinical, radiological and serological data. The present Review covers recent advances in the understanding of disease drivers and its clinical phenotypes, mainly focusing on the differential diagnosis with potential IgG4-RD mimickers, namely histiocytoses, lymphoproliferative disorders, systemic vasculitides and other immune-mediated conditions. The Review also provides a schematic approach to IgG4-RD treatment, including a brief overview of glucocorticoid-sparing agents and emerging therapies, from B cell-depleting monoclonal antibodies to cytokine-targeting drugs, the majority of which are currently under investigation in randomized clinical trials.
Key points
-
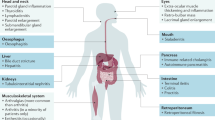
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a fibro-inflammatory disease characterized by slow-growing and often pseudotumoural lesions that can be solitary or occur in multiple organs.
-
The diagnosis of IgG4-RD requires the exclusion of a wide array of neoplastic, infectious and autoimmune disorders as well as of rare proliferative conditions such as histiocytoses and Castleman disease.
-
The different subphenotypes of IgG4-RD (Mikulicz, head-and-neck limited, pancreato-hepato-biliary, retroperitoneal and/or aortic disease) differ in terms of patients’ demographic features, clinical manifestations and serum IgG4 levels.
-
Treatment of IgG4-RD is based on the use of glucocorticoids, but B cell-depleting therapies (for example, rituximab or inebilizumab) are being incorporated into the standard therapeutic regimens.
-
IgG4-RD is a chronic–relapsing disorder and therefore requires careful and long-term follow-up.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamano, H. et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 344, 732–738 (2001).
Hamano, H. et al. Hydronephrosis associated with retroperitoneal fibrosis and sclerosing pancreatitis. Lancet 359, 1403–1404 (2002).
Kamisawa, T. et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J. Gastroenterol. 38, 982–984 (2003).
Stone, J. H., Zen, Y. & Deshpande, V. IgG4-related disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 366, 539–551 (2012).
Maritati, F. et al. Clinical and prognostic significance of serum IgG4 in chronic periaortitis. An analysis of 113 patients. Front. Immunol. 10, 693 (2019).
Nishikori, A. et al. Diagnostic challenges of the idiopathic plasmacytic lymphadenopathy (IPL) subtype of idiopathic multicentric Castleman disease (iMCD): factors to differentiate from IgG4-related disease. J. Clin. Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp-2023-209280 (2024).
Chazal, T. et al. Clinical phenotypes and long-term outcome of kidney involvement in Erdheim-Chester histiocytosis. Kidney Int. 103, 177–186 (2023).
Mazzariol, M. et al. Kidney involvement in Rosai-Dorfman disease. Kidney Int. 103, 231–232 (2023).
Jha, I. et al. Sex as a predictor of clinical phenotype and determinant of immune response in IgG4-related disease: a retrospective study of patients fulfilling the American College of Rheumatology-European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria. Lancet Rheumatol. 6, e460–e468 (2024).
Perugino, C. A. & Stone, J. H. IgG4-related disease: an update on pathophysiology and implications for clinical care. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 16, 702–714 (2020).
Vaglio, A., Pipitone, N. & Salvarani, C. Chronic periaortitis: a large-vessel vasculitis? Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 23, 1–6 (2011).
Katz, G. et al. IgG4-related disease as a variable-vessel vasculitis: a case series of 13 patients with medium-sized coronary artery involvement. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 60, 152184 (2023).
Palmisano, A. et al. Chronic periaortitis with thoracic aorta and epiaortic artery involvement: a systemic large vessel vasculitis? Rheumatology 54, 2004–2009 (2015).
Corradi, D., Nicastro, M. & Vaglio, A. Immunoglobulin G4-related disease: some missing pieces in a still unsolved complex puzzle. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 25, 90–92 (2016).
Accorsi Buttini, E., Maritati, F. & Vaglio, A. [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and response to therapy in idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. Eur. Urol. 73, 145–146 (2018).
Kamisawa, T., Zen, Y., Nakazawa, T. & Okazaki, K. Advances in IgG4-related pancreatobiliary diseases. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 3, 575–585 (2018).
Yamamoto, M. et al. A new conceptualization for Mikulicz’s disease as an IgG4-related plasmacytic disease. Mod. Rheumatol. 16, 335–340 (2006).
Dahlgren, M., Khosroshahi, A., Nielsen, G. P., Deshpande, V. & Stone, J. H. Riedel’s thyroiditis and multifocal fibrosclerosis are part of the IgG4-related systemic disease spectrum. Arthritis Care Res. 62, 1312–1318 (2010).
Zhang, X. et al. Novel advances in the study of IgG4-related disease in the eye and ocular adnexa. Ophthalmic Res. 65, 605–614 (2022).
Marinelli, J. P. et al. Manifestations of skull base IgG4-related disease: a multi-institutional study. Laryngoscope 130, 2574–2580 (2020).
Vaglio, A. & Maritati, F. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 27, 1880–1889 (2016).
Chaba, A. et al. Clinical and prognostic factors in patients with IgG4-related kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 18, 1031–1040 (2023).
Peyronel, F. & Vaglio, A. IgG4-related kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 18, 994–996 (2023).
Wallace, Z. S. et al. Clinical phenotypes of IgG4-related disease: an analysis of two international cross-sectional cohorts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 78, 406–412 (2019).
Wallace, Z. S. et al. IgG4-related disease: clinical and laboratory features in one hundred twenty-five patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 67, 2466–2475 (2015).
Katz, G. et al. Proliferative features of IgG4-related disease. Lancet Rheumatol. 6, e481–e492 (2024).
Lanzillotta, M. et al. Fibrotic phenotype of IgG4-related disease. Lancet Rheumatol. 6, e469–e480 (2024).
Chang, M. C. et al. T-cell regulatory gene CTLA-4 polymorphism/haplotype association with autoimmune pancreatitis. Clin. Chem. 53, 1700–1705 (2007).
Park, D. H. et al. Substitution of aspartic acid at position 57 of the DQβ1 affects relapse of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 134, 440–446 (2008).
Ota, UmemuraT., Hamano, M., Katsuyama, H., Kiyosawa, Y. & Kawa, K. S. Genetic association of Fc receptor-like 3 polymorphisms with autoimmune pancreatitis in Japanese patients. Gut 55, 1367–1368 (2006).
Umemura, T. et al. Association of autoimmune pancreatitis with cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 gene polymorphisms in Japanese patients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 103, 588–594 (2008).
Chang, M. C. et al. Human cationic trypsinogen but not serine peptidase inhibitor, Kazal type 1 variants increase the risk of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 29, 2038–2042 (2014).
Liu, Q. et al. IKZF1 and UBR4 gene variants drive autoimmunity and Th2 polarization in IgG4-related disease. J. Clin. Invest. 134, e178692 (2024).
Terao, C. et al. IgG4-related disease in the Japanese population: a genome-wide association study. Lancet Rheumatol. 1, e14–e22 (2019).
Martorana, D. et al. A large-scale genetic analysis reveals an autoimmune origin of idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 142, 1662–1665 (2018).
de Buy Wenniger, L. J., Culver, E. L. & Beuers, U. Exposure to occupational antigens might predispose to IgG4-related disease. Hepatology 60, 1453–1454 (2014).
Wallwork, R. et al. The association of smoking with immunoglobulin G4-related disease: a case-control study. Rheumatology 60, 5310–5317 (2021).
Goldoni, M. et al. Asbestos and smoking as risk factors for idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: a case-control study. Ann. Intern. Med. 161, 181–188 (2014).
Uibu, T. et al. Asbestos exposure as a risk factor for retroperitoneal fibrosis. Lancet 363, 1422–1426 (2004).
Maillette de Buy Wenniger, L. J. et al. Immunoglobulin G4+ clones identified by next-generation sequencing dominate the B cell receptor repertoire in immunoglobulin G4 associated cholangitis. Hepatology 57, 2390–2398 (2013).
Mattoo, H. et al. De novo oligoclonal expansions of circulating plasmablasts in active and relapsing IgG4-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 134, 679–687 (2014).
Hubers, L. M. et al. Annexin A11 is targeted by IgG4 and IgG1 autoantibodies in IgG4-related disease. Gut 67, 728–735 (2018).
Perugino, C. A. et al. Identification of galectin-3 as an autoantigen in patients with IgG4-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 143, 736–745.e6 (2019).
Shiokawa, M. et al. Laminin 511 is a target antigen in autoimmune pancreatitis. Sci Transl Med 10, eaaq0997 (2018).
Liu, H. et al. Disease severity linked to increase in autoantibody diversity in IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 72, 687–693 (2020).
Trampert, D. C., Hubers, L. M., van de Graaf, S. F. J. & Beuers, U. On the role of IgG4 in inflammatory conditions: lessons for IgG4-related disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1864, 1401–1409 (2018).
van der Neut Kolfschoten, M. et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of human IgG4 antibodies by dynamic Fab arm exchange. Science 317, 1554–1557 (2007).
Della-Torre, E., Lanzillotta, M. & Doglioni, C. Immunology of IgG4-related disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 181, 191–206 (2015).
Shiokawa, M. et al. Pathogenicity of IgG in patients with IgG4-related disease. Gut 65, 1322–1332 (2016).
Campochiaro, C. et al. Long-term efficacy of maintenance therapy with rituximab for IgG4-related disease. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 74, 92–98 (2020).
Della-Torre, E. et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab biosimilar (CT-P10) in IgG4-related disease: an observational prospective open-label cohort study. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 84, 63–67 (2021).
Lanzillotta, M. et al. Effects of glucocorticoids on B-cell subpopulations in patients with IgG4-related disease. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 37, 159–166 (2019).
Allard-Chamard, H. et al. Extrafollicular IgD−CD27−CXCR5−CD11c− DN3 B cells infiltrate inflamed tissues in autoimmune fibrosis and in severe COVID-19. Cell Rep. 42, 112630 (2023).
Della-Torre, E. et al. B lymphocytes directly contribute to tissue fibrosis in patients with IgG4-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 145, 968–981.e14 (2020).
Della-Torre, E. et al. A CD8α− subset of CD4+SLAMF7+ cytotoxic T cells is expanded in patients with IgG4-related disease and decreases following glucocorticoid treatment. Arthritis Rheumatol. 70, 1133–1143 (2018).
Heeringa, J. J. et al. Expansion of blood IgG4+ B, TH2, and regulatory T cells in patients with IgG4-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 141, 1831–1843.e10 (2018).
Maehara, T. et al. Lesional CD4+ IFN-γ+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 76, 377–385 (2017).
Munemura, R. et al. Distinct disease-specific Tfh cell populations in 2 different fibrotic diseases: IgG4-related disease and Kimura disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 150, 440–455.e17 (2022).
Perugino, C. A. et al. CD4+ and CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes may induce mesenchymal cell apoptosis in IgG4-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 147, 368–382 (2021).
Mattoo, H. et al. Clonal expansion of CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with IgG4-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 138, 825–838 (2016).
Rovati, L. et al. Mer tyrosine kinase as a possible link between resolution of inflammation and tissue fibrosis in IgG4-related disease. Rheumatology 60, 4929–4941 (2021).
Katz, G. & Stone, J. H. Clinical perspectives on IgG4-related disease and its classification. Annu. Rev. Med. 73, 545–562 (2022).
Gianfreda, D. et al. Erdheim-Chester disease as a mimic of IgG4-related disease: a case report and a review of a single-center cohort. Medicine 95, e3625 (2016).
Vaglio, A. et al. IgG4 immune response in Churg-Strauss syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 71, 390–393 (2012).
Wallace, Z. S. et al. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Classification Criteria for IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 72, 7–19 (2020).
Liu, Z. et al. The external validation of the 2019 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for IgG4-related disease in a large cohort from China. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 61, 152202 (2023).
Writing Group of the Histiocyte Society. Histiocytosis syndromes in children. Lancet 1, 208–209 (1987).
Okada, F. et al. A suspected case of IgG4-related bilateral arthritis of the knee. J. Orthop. Sci. 21, 100–104 (2016).
Wheeler, S., Andeen, N. & Reddy, R. Isolated IgG4 related disease of the trachea. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 49, 102031 (2024).
Danlos, F. X. et al. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides and IgG4-related disease: a new overlap syndrome. Autoimmun. Rev. 16, 1036–1043 (2017).
Yamamoto, M. et al. A case with good response to belimumab for lupus nephritis complicated by IgG4-related disease. Lupus 28, 786–789 (2019).
Batani, V. et al. Association of IgG4-related disease and systemic rheumatic disorders. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 111, 63–68 (2023).
Abad, S. et al. IgG4-related disease in patients with idiopathic orbital inflammation syndrome: data from the French SIOI prospective cohort. Acta Ophthalmol. 97, e648–e656 (2019).
Rossi, G. M. et al. Idiopathic mediastinal fibrosis: a systemic immune-mediated disorder. a case series and a review of the literature. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 52, 446–459 (2017).
Trivioli, G., Bond, M., Emmi, G. & Vaglio, A. IgG4-related disease: not just a matter of IgG4. Rheumatology 60, iii35–iii38 (2021).
Umehara, H. et al. The 2020 revised comprehensive diagnostic (RCD) criteria for IgG4-RD. Mod. Rheumatol. 31, 529–533 (2021).
Umehara, H. et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod. Rheumatol. 22, 21–30 (2012).
Kogami, M. et al. Performance of classification and diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease and comparison of patients with and without IgG4-related disease. Sci. Rep. 13, 2509 (2023).
Seth, A., Ansari, M. S., Trikha, V. & Mittal, R. Retroperitoneal fibrosis: a rare complication of Pott’s disease. J. Urol. 166, 622–623 (2001).
Greco, P. et al. Tuberculosis as a trigger of retroperitoneal fibrosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 41, e72–e75 (2005).
Keller-Sarmiento, L. et al. Increased prevalence of malignancies in patients with IgG4-related disease: implications for clinical care. Rheumatology 64, 1326–1332 (2025).
Garcia-Solis, B. et al. IgG4-related disease and B-cell malignancy due to an IKZF1 gain-of-function variant. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 154, 819–826 (2024).
Wallace, Z. S., Wallace, C. J., Lu, N., Choi, H. K. & Stone, J. H. Association of IgG4-related disease with history of malignancy. Arthritis Rheumatol. 68, 2283–2289 (2016).
Inoue, D. et al. IgG4-related disease: dataset of 235 consecutive patients. Medicine 94, e680 (2015).
Matsui, S. et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related lung disease: clinicoradiological and pathological features. Respirology 18, 480–487 (2013).
Hua, T. et al. Coronary periarteritis and pericarditis are rare but distinct manifestations of heart involvement in IgG4-related disease: a retrospective cohort study. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 19, 266 (2024).
Estrada-Veras, J. I. et al. The clinical spectrum of Erdheim-Chester disease: an observational cohort study. Blood Adv. 1, 357–366 (2017).
Cohen-Aubart, F. et al. Phenotypes and survival in Erdheim-Chester disease: results from a 165-patient cohort. Am. J. Hematol. 93, E114–E117 (2018).
Arnaud, L. et al. CNS involvement and treatment with interferon-alpha are independent prognostic factors in Erdheim-Chester disease: a multicenter survival analysis of 53 patients. Blood 117, 2778–2782 (2011).
Arnaud, L. et al. Pulmonary involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease: a single-center study of thirty-four patients and a review of the literature. Arthritis Rheum. 62, 3504–3512 (2010).
Nikpanah, M. et al. Abdominal involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease (ECD): MRI and CT imaging findings and their association with BRAF(V600E) mutation. Eur. Radiol. 28, 3751–3759 (2018).
Mirmomen, S. M. et al. Thoracic involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease: computed tomography imaging findings and their association with the BRAF(V600E) mutation. Eur. Radiol. 28, 4635–4642 (2018).
Robinson, D. Jr. et al. Clinical epidemiology and treatment patterns of patients with multicentric Castleman disease: results from two US treatment centres. Br. J. Haematol. 165, 39–48 (2014).
Yu, L. et al. Clinical and pathological characteristics of HIV- and HHV-8-negative Castleman disease. Blood 129, 1658–1668 (2017).
Liu, A. Y. et al. Idiopathic multicentric Castleman’s disease: a systematic literature review. Lancet Haematol. 3, e163–e175 (2016).
Dispenzieri, A. et al. The clinical spectrum of Castleman’s disease. Am. J. Hematol. 87, 997–1002 (2012).
Dispenzieri, A. POEMS syndrome: 2019 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am. J. Hematol. 94, 812–827 (2019).
Schupp, J. C. et al. Phenotypes of organ involvement in sarcoidosis. Eur. Respir. J. 51, 1700991 (2018).
Baughman, R. P. et al. Clinical characteristics of patients in a case control study of sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 164, 1885–1889 (2001).
Rastelli, F. et al. Renal involvement in sarcoidosis: histological patterns and prognosis, an Italian survey. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 38, e2021017 (2021).
Danda, D. et al. Clinical course of 602 patients with Takayasu’s arteritis: comparison between childhood-onset versus adult onset disease. Rheumatology 60, 2246–2255 (2021).
Schmidt, J. et al. Diagnostic features, treatment, and outcomes of Takayasu arteritis in a US cohort of 126 patients. Mayo Clin. Proc. 88, 822–830 (2013).
Comarmond, C. et al. Long-term outcomes and prognostic factors of complications in Takayasu arteritis: a multicenter study of 318 patients. Circulation 136, 1114–1122 (2017).
Adams, T. N., Zhang, D., Batra, K. & Fitzgerald, J. E. Pulmonary manifestations of large, medium, and variable vessel vasculitis. Respir. Med. 145, 182–191 (2018).
Iudici, M. et al. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis: study of 795 patients from the French Vasculitis Study Group registry. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 51, 339–346 (2021).
Solans-Laque, R. et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of Spanish patients with ANCA-associated vasculitides: impact of the vasculitis type, ANCA specificity, and treatment on mortality and morbidity. Medicine 96, e6083 (2017).
Shimojima, Y. et al. Hypertrophic pachymeningitis in ANCA-associated vasculitis: a cross-sectional and multi-institutional study in Japan (J-CANVAS). Arthritis Res. Ther. 24, 204 (2022).
Junek, M. L. et al. Ocular manifestations of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Rheumatology 62, 2517–2524 (2023).
Gercik, O. et al. Splenic infarction is not rare in granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Clin. Rheumatol. 39, 1929–1934 (2020).
Zhou, J. et al. Clinical and radiologic differences in lung involvement between IgG4-related disease and plasma cell-type idiopathic multicentric Castleman disease. Lung 203, 20 (2025).
Pegoraro, F. et al. Erdheim-Chester disease: a rapidly evolving disease model. Leukemia 34, 2840–2857 (2020).
Pegoraro, F. et al. Childhood-onset Erdheim-Chester disease in the molecular era: clinical phenotypes and long-term outcomes of 21 patients. Blood 142, 1167–1171 (2023).
Cohen Aubart, F. et al. Central nervous system involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease: an observational cohort study. Neurology 95, e2746–e2754 (2020).
Gianfreda, D. et al. Cardiac involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease: an MRI study. Blood 128, 2468–2471 (2016).
Salvarani, C. et al. Vasculitis of the gastrointestinal tract in chronic periaortitis. Medicine 90, 28–39 (2011).
Emile, J. F., Vaglio, A., Cohen-Aubart, F. & Haroche, J. IgG4-related disease and Rosai-Dorfman-Destombes disease — authors’ reply. Lancet 398, 1214–1215 (2021).
Vaglio, A., Salvarani, C. & Buzio, C. Retroperitoneal fibrosis. Lancet 367, 241–251 (2006).
Haroche, J., Cohen-Aubart, F. & Amoura, Z. Erdheim-Chester disease. Blood 135, 1311–1318 (2020).
Haroche, J. et al. Reproducible and sustained efficacy of targeted therapy with vemurafenib in patients with BRAF(V600E)-mutated Erdheim-Chester disease. J. Clin. Oncol. 33, 411–418 (2015).
Goyal, G. et al. Erdheim-Chester disease: consensus recommendations for evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment in the molecular era. Blood 135, 1929–1945 (2020).
Ebbo, M. et al. Pathologies associated with serum IgG4 elevation. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 602809 (2012).
Razanamahery, J. et al. Erdheim-Chester disease with concomitant Rosai-Dorfman like lesions: a distinct entity mainly driven by MAP2K1. Haematologica 105, e5–e8 (2020).
Abla, O. et al. Consensus recommendations for the diagnosis and clinical management of Rosai-Dorfman-Destombes disease. Blood 131, 2877–2890 (2018).
Shimizu, A., Noguchi-Shinohara, M., Komatsu, J. & Ono, K. Multifocal intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease mimicking immunoglobulin G4-related pachymeningitis. Neurology 103, e209741 (2024).
Wang, L. et al. Rosai-Dorfman disease mimicking IgG4-related diseases: a single-center experience in China. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 15, 285 (2020).
Chen, L. Y. C., Huang, A. J., Stone, J. H. & Ferry, J. A. Case 30-2024: a 45-year-old woman with kidney lesions and lytic bone disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 391, 1140–1151 (2024).
Tomelleri, A. et al. Disease stratification in GCA and PMR: state of the art and future perspectives. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 19, 446–459 (2023).
van der Geest, K. S. M. et al. Large vessel giant cell arteritis. Lancet Rheumatol. 6, e397–e408 (2024).
Kataoka, K. et al. IgG4-related periarteritis in the superficial temporal artery, clinically mimicking giant cell arthritis. Eur. J. Dermatol. 34, 198–200 (2024).
Mason, J. C. Takayasu arteritis — advances in diagnosis and management. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 6, 406–415 (2010).
Vaglio, A., Buzio, C. & Zwerina, J. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss): state of the art. Allergy 68, 261–273 (2013).
Trivioli, G. et al. Genetics of ANCA-associated vasculitis: role in pathogenesis, classification and management. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 18, 559–574 (2022).
Vaglio, A. et al. ANCA-positive periaortic vasculitis: does it fall within the spectrum of vasculitis? J. Intern. Med. 251, 268–271 (2002).
Bennett, D. et al. Chitotriosidase: a biomarker of activity and severity in patients with sarcoidosis. Respir. Res. 21, 6 (2020).
Deshpande, V. et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod. Pathol. 25, 1181–1192 (2012).
Emile, J. F. et al. Revised classification of histiocytoses and neoplasms of the macrophage-dendritic cell lineages. Blood 127, 2672–2681 (2016).
Emile, J. F. et al. Histiocytosis. Lancet 398, 157–170 (2021).
Ebbo, M. et al. Usefulness of 2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography for staging and evaluation of treatment response in IgG4-related disease: a retrospective multicenter study. Arthritis Care Res. 66, 86–96 (2014).
Shimizu, M. et al. Effectiveness of imaging modalities for screening IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialadenitis (Mikulicz’s disease) and for differentiating it from Sjogren’s syndrome (SS), with an emphasis on sonography. Arthritis Res. Ther. 17, 223 (2015).
Vaglio, A. et al. 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in the diagnosis and followup of idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. Arthritis Rheum. 53, 122–125 (2005).
Carruthers, M. N., Khosroshahi, A., Augustin, T., Deshpande, V. & Stone, J. H. The diagnostic utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-related disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 74, 14–18 (2015).
Zhao, E. J., Carruthers, M. N., Li, C. H., Mattman, A. & Chen, L. Y. C. Conditions associated with polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia in the IgG4-related disease era: a retrospective study from a hematology tertiary care center. Haematologica 105, e121–e123 (2020).
Katz, G. et al. Multiorgan involvement and circulating IgG1 predict hypocomplementaemia in IgG4-related disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 83, 1773–1780 (2024).
Khosroshahi, A. et al. International consensus guidance statement on the management and treatment of IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 67, 1688–1699 (2015).
Masaki, Y. et al. A multicenter phase II prospective clinical trial of glucocorticoid for patients with untreated IgG4-related disease. Mod. Rheumatol. 27, 849–854 (2017).
Masamune, A. et al. Randomised controlled trial of long-term maintenance corticosteroid therapy in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 66, 487–494 (2017).
Vaglio, A. et al. Prednisone versus tamoxifen in patients with idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: an open-label randomised controlled trial. Lancet 378, 338–346 (2011).
Hart, P. A. et al. Treatment of relapsing autoimmune pancreatitis with immunomodulators and rituximab: the Mayo Clinic experience. Gut 62, 1607–1615 (2013).
Alberici, F. et al. Methotrexate plus prednisone in patients with relapsing idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 72, 1584–1586 (2013).
Scheel, P. J. Jr, Feeley, N. & Sozio, S. M. Combined prednisone and mycophenolate mofetil treatment for retroperitoneal fibrosis: a case series. Ann. Intern. Med. 154, 31–36 (2011).
Lanzillotta, M. et al. Emerging therapy options for IgG4-related disease. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 17, 471–483 (2021).
Topazian, M. et al. Rituximab therapy for refractory biliary strictures in immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 6, 364–366 (2008).
Lanzillotta, M. et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab for IgG4-related pancreato-biliary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pancreatology 21, 1395–1401 (2021).
Ebbo, M. et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of rituximab in IgG4-related disease: data from a French nationwide study of thirty-three patients. PLoS ONE 12, e0183844 (2017).
Carruthers, M. N. et al. Rituximab for IgG4-related disease: a prospective, open-label trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 74, 1171–1177 (2015).
Maritati, F. et al. Rituximab therapy for chronic periaortitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 71, 1262–1264 (2012).
Urban, M. L. et al. Rituximab for chronic periaortitis without evidence of IgG4-related disease: a long-term follow-up study of 20 patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 79, 433–434 (2020).
Stone, J. H. et al. Inebilizumab for treatment of IgG4-related disease. N. Engl. J. Med. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2409712 (2024).
Perugino, C. A. et al. Evaluation of the safety, efficacy, and mechanism of action of obexelimab for the treatment of patients with IgG4-related disease: an open-label, single-arm, single centre, phase 2 pilot trial. Lancet Rheumatol. 5, e442–e450 (2023).
Cai, S. et al. BLyS/APRIL dual inhibition for IgG4-RD: a prospective single-arm clinical trial of telitacicept. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 82, 881–883 (2023).
Kiyama, K. et al. Serum BAFF and APRIL levels in patients with IgG4-related disease and their clinical significance. Arthritis Res. Ther. 14, R86 (2012).
Matza, M. A. et al. Abatacept in IgG4-related disease: a prospective, open-label, single-arm, single-centre, proof-of-concept study. Lancet Rheumatol. 4, e105–e112 (2022).
Moussiegt, A. et al. IgG4-related disease and hypereosinophilic syndrome: overlapping phenotypes. Autoimmun. Rev. 20, 102889 (2021).
Simpson, R. S., Lau, S. K. C. & Lee, J. K. Dupilumab as a novel steroid-sparing treatment for IgG4-related disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 79, 549–550 (2020).
Ebbo, M. et al. Correspondence on: ‘Dupilumab as a novel steroid-sparing treatment for IgG4-related disease’ by Simpson et al. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 81, e26 (2022).
Cao, X. et al. Effectiveness of tofacitinib monotherapy for patients with IgG4-RD or idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 42, 1736–1743 (2024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors contributed equally to all aspects of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Rheumatology thanks Fleur Cohen-Aubart, Yoshito Nishimura and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Peyronel, F., Della-Torre, E., Maritati, F. et al. IgG4-related disease and other fibro-inflammatory conditions. Nat Rev Rheumatol 21, 275–290 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-025-01240-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-025-01240-x