Abstract
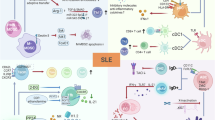
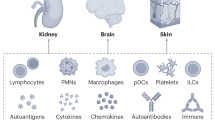
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by protean clinical manifestations that are associated with immune system dysregulation. Of these manifestations, pain and pain-related symptoms such as fatigue, mood disturbance and cognitive impairment are the most common features reported by patients and represent important determinants of quality of life. Nevertheless, the relationship of these symptoms to underlying immune mechanisms is unclear. To advance scientific study and patient-centric care, this Review will consider the origin of pain in SLE and the clinical ramifications. Although many of the inflammatory aspects of SLE, including arthritis, serositis and skin disease, can be associated with nociceptive pain, patients frequently report pain that seems out of proportion to the degree of inflammation. In many of these patients, pain might reflect central and peripheral nervous system sensitization that mediates nociplasticity, a change in brain processing; with nociplasticity, changes in neuronal function and brain connections can amplify the experience of pain and pain-related symptoms. The close interplay between the immune and the nervous systems means that widespread pain and the associated symptoms can be considered as essential features of SLE; these features might share pathogenic mechanisms with other autoimmune diseases and nociplastic pain syndromes such as fibromyalgia.
Key points
-
Symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are protean but differ in their relationship to inflammation and autoreactivity as determined by current biomarkers.
-
Pain and pain-associated symptoms such as fatigue, mood changes and cognitive impairment are important determinants of quality of life in patients with SLE.
-
Many aspects of the patient response to disease, including interoception, sickness behaviour and nociplasticity, complicate the assessment of pain in patients with SLE.
-
Pain and pain-associated symptoms might reflect immune-mediated peripheral and central nervous system sensitization that results in nociplasticity.
-
The term lupus-associated nociplasticity might help to explain many of the symptoms identified as most concerning by patients living with SLE.
-
Managing pain in SLE requires a multimodal approach that uses pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions directed at both pain and inflammation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaul, A. et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2, 16039 (2016).
Barr, S. G., Zonana-Nacach, A., Magder, L. S. & Petri, M. Patterns of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 42, 2682–2688 (1999).
Piga, M. et al. Clinical patterns of disease: from early systemic lupus erythematosus to late-onset disease. Best practice & research. Clin. Rheumatol. 37, 101938 (2023).
Ruperto, N. et al. International consensus for a definition of disease flare in lupus. Lupus 20, 453–462 (2011).
Pisetsky, D. S., Clowse, M. E. B., Criscione-Schreiber, L. G. & Rogers, J. L. A novel system to categorize the symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Care Res. 71, 735–741 (2019).
Pisetsky, D. S. et al. Nociplasticity: a proposed concept to understand the symptomatology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 77, 966–970 (2025).
Schett, G., Mackensen, A. & Mougiakakos, D. CAR T-cell therapy in autoimmune diseases. Lancet 402, 2034–2044 (2023).
Pisetsky, D. S. & Lipsky, P. E. New insights into the role of antinuclear antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 16, 565–579 (2020).
Pisetsky, D. S. Anti-DNA antibodies-quintessential biomarkers of SLE. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 12, 102–110 (2016).
Mustelin, T., Lood, C. & Giltiay, N. V. Sources of pathogenic nucleic acids in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 10, 1028 (2019).
Soni, C. & Reizis, B. Self-DNA at the epicenter of SLE: immunogenic forms, regulation, and effects. Front. Immunol. 10, 1601 (2019).
Rönnblom, L. & Leonard, D. Interferon pathway in SLE: one key to unlocking the mystery of the disease. Lupus Sci. Med. 6, e000270 (2019).
Vallin, H., Perers, A., Alm, G. V. & Rönnblom, L. Anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies and immunostimulatory plasmid DNA in combination mimic the endogenous IFN-alpha inducer in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 163, 6306–6313 (1999).
Barrat, F. J., Elkon, K. B. & Fitzgerald, K. A. Importance of nucleic acid recognition in inflammation and autoimmunity. Annu. Rev. Med. 67, 323–336 (2016).
Venner, A. A. et al. Comparison of three anti-dsDNA assays: performance and correlation with systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity. Clin. Biochem. 46, 317–320 (2013).
Weinstein, A., Alexander, R. V. & Zack, D. J. A review of complement activation in SLE. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 23, 16 (2021).
Rogers, J. L. et al. Evaluation of Type 2 SLE symptoms in patients with a range of lupus nephritis activity. Clin. Rheumatol. 43, 1319–1326 (2024).
Alarcón, G. S. et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups. XI. Sources of discrepancy in perception of disease activity: a comparison of physician and patient visual analog scale scores. Arthritis Rheum. 47, 408–413 (2002).
Golder, V. et al. Discordance of patient and physician health status concerns in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 27, 501–506 (2018).
Basbaum, A. I., Bautista, D. M., Scherrer, G. & Julius, D. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pain. Cell 139, 267–284 (2009).
Todd, A. J. Neuronal circuitry for pain processing in the dorsal horn. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 11, 823–836 (2010).
Fillingim, R. B. Individual differences in pain: understanding the mosaic that makes pain personal. Pain 158, S11–S18 (2017).
Gilam, G., Gross, J. J., Wager, T. D., Keefe, F. J. & Mackey, S. C. What is the relationship between pain and emotion? Bridging constructs and communities. Neuron 107, 17–21 (2020).
Pinto, A. M. et al. Neurophysiological and psychosocial mechanisms of fibromyalgia: a comprehensive review and call for an integrative model. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 151, 105235 (2023).
Porreca, F., Ossipov, M. H. & Gebhart, G. F. Chronic pain and medullary descending facilitation. Trends Neurosci. 25, 319–325 (2002).
Chen, C. et al. Neural circuit basis of placebo pain relief. Nature 632, 1092–1100 (2024).
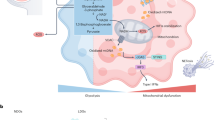
Ji, R. R., Xu, Z. Z. & Gao, Y. J. Emerging targets in neuroinflammation-driven chronic pain. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 13, 533–548 (2014).
Donnelly, C. R., Chen, O. & Ji, R. R. How do sensory neurons sense danger signals? Trends Neurosci. 43, 822–838 (2020).
Woolf, C. J. & Costigan, M. Transcriptional and posttranslational plasticity and the generation of inflammatory pain. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 7723–7730 (1999).
Gold, M. S. & Gebhart, G. F. Nociceptor sensitization in pain pathogenesis. Nat. Med. 16, 1248–1257 (2010).
Ji, R. R., Nackley, A., Huh, Y., Terrando, N. & Maixner, W. Neuroinflammation and central sensitization in chronic and widespread pain. Anesthesiology 129, 343–366 (2018).
Fanouriakis, A. et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus: 2023 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 83, 15–29 (2024).
Grossman, J. M. Lupus arthritis. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 23, 495–506 (2009).
Di Matteo, A., De Angelis, R., Cipolletta, E., Filippucci, E. & Grassi, W. Systemic lupus erythematosus arthropathy: the sonographic perspective. Lupus 27, 794–801 (2018).
Shumilova, A. & Vital, E. M. Musculoskeletal manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 37, 101859 (2023).
Corzo Garcia, P. et al. Musculoskeletal involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus: a contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging study in 107 subjects. Rheumatology 63, 423–429 (2024).
Steiner, G. & Toes, R. E. M. Autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis - rheumatoid factor, anticitrullinated protein antibodies and beyond. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 36, 217–224 (2024).
Trouw, L. A., Rispens, T. & Toes, R. E. M. Beyond citrullination: other post-translational protein modifications in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 13, 331–339 (2017).
Singh, J. et al. Moonlighting chromatin: when DNA escapes nuclear control. Cell Death Differ. 30, 861–875 (2023).
Antonini, L., Le Mauff, B., Marcelli, C., Aouba, A. & de Boysson, H. Rhupus: a systematic literature review. Autoimmun. Rev. 19, 102612 (2020).
Frade-Sosa, B. et al. A comparative study on clinical and serological characteristics between patients with rhupus and those with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Lupus 29, 1216–1226 (2020).
Jurczak, A. et al. Insights into FcγR involvement in pain-like behavior induced by an RA-derived anti-modified protein autoantibody. Brain Behav. Immun. 113, 212–227 (2023).
Wigerblad, G. et al. Autoantibodies to citrullinated proteins induce joint pain independent of inflammation via a chemokine-dependent mechanism. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 75, 730–738 (2016).
Krishnamurthy, A. et al. Combination of two monoclonal anti-citrullinated protein antibodies induced tenosynovitis, pain, and bone loss in mice in a peptidyl arginine deiminase-4-dependent manner. Arthritis Rheumatol. 75, 164–170 (2023).
Raposo, B. et al. Divergent and dominant anti-inflammatory effects of patient-derived anticitrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) in arthritis development. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 82, 724–726 (2023).
He, Y. et al. A subset of antibodies targeting citrullinated proteins confers protection from rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Commun. 14, 691 (2023).
Lacagnina, M. J. et al. B cells drive neuropathic pain-related behaviors in mice through IgG-Fc gamma receptor signaling. Sci. Transl. Med. 16, eadj1277 (2024).
Bai, Z. et al. Synovial fibroblast gene expression is associated with sensory nerve growth and pain in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Transl. Med. 16, eadk3506 (2024).
Simon, N. et al. Characterisation of the antinociceptive effect of baricitinib in the collagen antibody-induced arthritis mouse model. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 84, 421–434 (2025).
Hubbard, E. L. et al. Analysis of gene expression from systemic lupus erythematosus synovium reveals myeloid cell-driven pathogenesis of lupus arthritis. Sci. Rep. 10, 17361 (2020).
Nzeusseu Toukap, A. et al. Identification of distinct gene expression profiles in the synovium of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 56, 1579–1588 (2007).
Kasturi, S. & Goodman, S. Current perspectives on arthroplasty in systemic lupus erythematosus: rates, outcomes, and adverse events. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 18, 59 (2016).
Long, Y. et al. Risk of osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: an 11-year Chinese single-center cohort study. Lupus 30, 1459–1468 (2021).
Dhital, R. et al. Trends in avascular necrosis and related arthroplasties in hospitalized patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 66, 152444 (2024).
Motta, F., Timilsina, S., Gershwin, M. E. & Selmi, C. Steroid-induced osteonecrosis. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 5, 100168 (2022).
Kaplan, C. M. et al. Deciphering nociplastic pain: clinical features, risk factors and potential mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 20, 347–363 (2024).
Fitzcharles, M. A. et al. Nociplastic pain: towards an understanding of prevalent pain conditions. Lancet 397, 2098–2110 (2021).
Woolf, C. J. Central sensitization: implications for the diagnosis and treatment of pain. Pain 152, S2–S15 (2011).
Kosek, E. et al. Chronic nociplastic pain affecting the musculoskeletal system: clinical criteria and grading system. Pain 162, 2629–2634 (2021).
Rafferty, C. & Ward, J. Fibromyalgia is linked to increased subjective sensory sensitivity across multiple senses. Perception 53, 276–286 (2024).
Staud, R., Godfrey, M. M. & Robinson, M. E. Fibromyalgia patients are not only hypersensitive to painful stimuli but also to acoustic stimuli. J. Pain 22, 914–925 (2021).
López-Solà, M. et al. Towards a neurophysiological signature for fibromyalgia. Pain 158, 34–47 (2017).
Middleton, G. D., McFarlin, J. E. & Lipsky, P. E. The prevalence and clinical impact of fibromyalgia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 37, 1181–1188 (1994).
Mistry, S., Daoud, A., Magrey, M. N. & Pamuk, O. N. The frequency of fibromyalgia in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and associated factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 44, 9–21 (2025).
Staud, R. Are patients with systemic lupus erythematosus at increased risk for fibromyalgia? Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 8, 430–435 (2006).
Wolfe, F., Michaud, K., Li, T. & Katz, R. S. Chronic conditions and health problems in rheumatic diseases: comparisons with rheumatoid arthritis, noninflammatory rheumatic disorders, systemic lupus erythematosus, and fibromyalgia. J. Rheumatol. 37, 305–315 (2010).
Maixner, W., Fillingim, R. B., Williams, D. A., Smith, S. B. & Slade, G. D. Overlapping chronic pain conditions: implications for diagnosis and classification. J. Pain 17, T93–T107 (2016).
Murphy, A. E., Minhas, D., Clauw, D. J. & Lee, Y. C. Identifying and managing nociplastic pain in individuals with rheumatic diseases: a narrative review. Arthritis Care Res. 75, 2215–2222 (2023).
Meng, C. F. et al. Characterizing nonarticular pain at early rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis: evolution over the first year of treatment and impact on remission in a prospective real-world early rheumatoid arthritis cohort. Arthritis Rheumatol. 77, 405–413 (2025).
Schrepf, A. et al. Top down or bottom up? An observational investigation of improvement in fibromyalgia symptoms following hip and knee replacement. Rheumatology 59, 594–602 (2020).
Gnall, K. E. et al. Changes in interoception in mind-body therapies for chronic pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Behav. Med. 31, 833–847 (2024).
Todd, J. et al. Heightened interoception in adults with fibromyalgia. Biol. Psychol. 186, 108761 (2024).
Valenzuela-Moguillansky, C., Reyes-Reyes, A. & Gaete, M. I. Exteroceptive and interoceptive body-self awareness in fibromyalgia patients. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 11, 117 (2017).
Fillingim, R. B. et al. Psychological factors associated with development of TMD: the OPPERA prospective cohort study. J. Pain 14, T75–T90 (2013).
Falasinnu, T. et al. The problem of pain in rheumatology: clinical profiles associated with concomitant diagnoses with chronic overlapping pain conditions. ACR Open. Rheumatol. 4, 890–896 (2022).
The American College of Rheumatology nomenclature and case definitions for neuropsychiatric lupus syndromes. Arthritis Rheum. 42, 599–608 (1999).
Oomatia, A., Fang, H., Petri, M. & Birnbaum, J. Peripheral neuropathies in systemic lupus erythematosus: clinical features, disease associations, and immunologic characteristics evaluated over a twenty-five-year study period. Arthritis Rheumatol. 66, 1000–1009 (2014).
Galosi, E. et al. Clinical, histologic, and immunologic signatures of small fiber neuropathy in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 29, 315–328 (2024).
Florica, B. et al. Peripheral neuropathy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 41, 203–211 (2011).
Lauria, G. et al. Intraepidermal nerve fiber density at the distal leg: a worldwide normative reference study. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 15, 202–207 (2010).
Lukashenko, M. V. et al. Corneal confocal microscopy in the diagnosis of small fiber neuropathy: faster, easier, and more efficient than skin biopsy? Pathophysiology 29, 1–8 (2021).
Grayston, R. et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of small fiber pathology in fibromyalgia: implications for a new paradigm in fibromyalgia etiopathogenesis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 48, 933–940 (2019).
Dumolard, A. et al. Central sensitization and small-fiber neuropathy are associated in patients with fibromyalgia. Clin. J. Pain 39, 8–14 (2023).
Jänsch, S. et al. Distinguishing fibromyalgia syndrome from small fiber neuropathy: a clinical guide. Pain. Rep. 9, e1136 (2024).
Hoeijmakers, J. G. J., Merkies, I. S. J. & Faber, C. G. Small fiber neuropathies: expanding their etiologies. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 35, 545–552 (2022).
Dantzer, R., O’Connor, J. C., Freund, G. G., Johnson, R. W. & Kelley, K. W. From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 46–56 (2008).
Kelley, K. W. et al. Cytokine-induced sickness behavior. Brain, Behav., Immun. 17, S112–S118 (2003).
Sleijfer, S., Bannink, M., Van Gool, A. R., Kruit, W. H. & Stoter, G. Side effects of interferon-ɑ therapy. Pharm. World Sci. 27, 423–431 (2005).
Gimeno-Torres, L. et al. Prevalence and risk factors for serositis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a case-control study. Lupus 30, 2095–2101 (2021).
Louthrenoo, W. et al. Clinical features, imaging findings, and outcomes of acute abdominal pain in systemic lupus erythematosus: comparing mesenteric vasculitis, non-mesenteric vasculitis, and surgical conditions. Clin. Rheumatol. 43, 3699–3712 (2024).
Feld, J., Tayer-Shifman, O. E., Su, J., Anderson, M. & Touma, Z. Primary headache in SLE -systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 69, 152566 (2024).
Hanly, J. G. et al. Headache in systemic lupus erythematosus: results from a prospective, international inception cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 65, 2887–2897 (2013).
Yan, D. et al. Cutaneous lupus concerns from the patient perspective: a qualitative study. Lupus Sci. Med. 8, e000444 (2021).
Stull, C., Sprow, G. & Werth, V. P. Cutaneous involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus: a review for the rheumatologist. J. Rheumatol. 50, 27–35 (2023).
Kim, H. J. Pruritus in autoimmune connective tissue diseases. Ann. Transl. Med. 9, 441 (2021).
Samotij, D. et al. Clinical characteristics of itch in cutaneous lupus erythematosus: a prospective, multicenter, multinational, cross-sectional study. Lupus 30, 1385–1393 (2021).
Wolfe, F. Fibromyalgianess. Arthritis Rheum. 61, 715–716 (2009).
Wolfe, F. et al. Fibromyalgia, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and evaluation of SLE activity. J. Rheumatol. 36, 82–88 (2009).
Rogers, J. L. et al. Using clinical characteristics and patient-reported outcome measures to categorize systemic lupus erythematosus subtypes. Arthritis Care Res. 73, 386–393 (2021).
Robl, R. et al. Molecular endotypes of type 1 and type 2 SLE. Lupus Sci. Med. 10, e000861 (2023).
Condon, L. F. et al. Parabrachial calca neurons drive nociplasticity. Cell Rep. 43, 114057 (2024).
Duffield, S. J., Miller, N., Zhao, S. & Goodson, N. J. Concomitant fibromyalgia complicating chronic inflammatory arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology 57, 1453–1460 (2018).
Nichilatti, L. P., Fernandes, J. M. & Marques, C. P. Physiopathology of pain in systemic erythematosus lupus. Lupus 29, 721–726 (2020).
Pisetsky, D. S., Eudy, A. M., Clowse, M. E. B. & Rogers, J. L. The categorization of pain in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 47, 215–228 (2021).
Rogers, J. L. et al. Patient and physician perspectives of systemic lupus erythematosus flare: a qualitative study. J. Rheumatol. 51, 488–494 (2024).
Album, D. & Westin, S. Do diseases have a prestige hierarchy? A survey among physicians and medical students. Soc. Sci. Med. 66, 182–188 (2008).
Johannessen, L. E. F., Album, D. & Rasmussen, E. B. Do nurses rate diseases according to prestige? A survey study. J. Adv. Nurs. 76, 1691–1697 (2020).
Matsuda, M., Huh, Y. & Ji, R. R. Roles of inflammation, neurogenic inflammation, and neuroinflammation in pain. J. Anesth. 33, 131–139 (2019).
Kavelaars, A. & Heijnen, C. J. Immune regulation of pain: friend and foe. Sci. Transl. Med. 13, eabj7152 (2021).
Troubat, R. et al. Neuroinflammation and depression: a review. Eur. J. Neurosci. 53, 151–171 (2021).
Brock, J. et al. Immune mechanisms of depression in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 19, 790–804 (2023).
Druce, K. L. & Basu, N. Predictors of fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 58, v29–v34 (2019).
Oláh, C. et al. Cognitive dysfunction in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res. Ther. 22, 78 (2020).
Lacagnina, M. J., Heijnen, C. J., Watkins, L. R. & Grace, P. M. Autoimmune regulation of chronic pain. Pain. Rep. 6, e905 (2021).
Mountford, R. et al. Antibody-mediated autoimmunity in symptom-based disorders: position statement and proceedings from an international workshop. Pain. Rep. 9, e1167 (2024).
Fiore, N. T. et al. Reducing IgG accumulation via neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) blockade relieves neuropathic pain. Brain, Behav., Immun. 125, 371–387 (2025).
Berwick, R. J. et al. Postacute COVID-19 syndrome and fibromyalgia syndrome are associated with anti-satellite glial cell IgG serum autoantibodies but only fibromyalgia syndrome serum-IgG is pronociceptive. Pain. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003629 (2025).
Goebel, A. et al. Passive transfer of fibromyalgia symptoms from patients to mice. J. Clin. Invest. 131, e144201 (2021).
Fanton, S. et al. Anti-satellite glia cell IgG antibodies in fibromyalgia patients are related to symptom severity and to metabolite concentrations in thalamus and rostral anterior cingulate cortex. Brain, Behav., Immun. 114, 371–382 (2023).
Krock, E. et al. Fibromyalgia patients with elevated levels of anti-satellite glia cell immunoglobulin G antibodies present with more severe symptoms. Pain 164, 1828–1840 (2023).
Seefried, S. et al. Autoantibodies in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Pain 166, 1922–1933 (2025).
Robinson, W. H. et al. Cutting-edge approaches to B-cell depletion in autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 15, 1454747 (2024).
Nestor, J. et al. Lupus antibodies induce behavioral changes mediated by microglia and blocked by ACE inhibitors. J. Exp. Med. 215, 2554–2566 (2018).
Zarfeshani, A., Carroll, K. R., Volpe, B. T. & Diamond, B. Cognitive impairment in SLE: mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 23, 25 (2021).
Brimberg, L. et al. Antibodies as mediators of brain pathology. Trends Immunol. 36, 709–724 (2015).
Carroll, K. R. et al. Lupus autoantibodies initiate neuroinflammation sustained by continuous HMGB1:RAGE signaling and reversed by increased LAIR-1 expression. Nat. Immunol. 25, 671–681 (2024).
Martucci, K. T., Weber, K. A. 2nd & Mackey, S. C. Altered cervical spinal cord resting-state activity in fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheumatol. 71, 441–450 (2019).
Mawla, I. et al. Large-scale momentary brain co-activation patterns are associated with hyperalgesia and mediate focal neurochemistry and cross-network functional connectivity in fibromyalgia. Pain 164, 2737–2748 (2023).
Ichesco, E. et al. Altered fMRI resting-state connectivity in individuals with fibromyalgia on acute pain stimulation. Eur. J. Pain 20, 1079–1089 (2016).
Mackay, M., Tang, C. C. & Vo, A. Advanced neuroimaging in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 33, 353–361 (2020).
Basu, N. et al. Functional and structural magnetic resonance imaging correlates of fatigue in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 58, 1822–1830 (2019).
Iancheva, D., Trenova, A., Mantarova, S. & Terziyski, K. Functional magnetic resonance imaging correlations between fatigue and cognitive performance in patients with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. Front. Psychiatry 10, 754 (2019).
Toikumo, S. et al. A multi-ancestry genetic study of pain intensity in 598,339 veterans. Nat. Med. 30, 1075–1084 (2024).
Diatchenko, L., Fillingim, R. B., Smith, S. B. & Maixner, W. The phenotypic and genetic signatures of common musculoskeletal pain conditions. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 9, 340–350 (2013).
Yuan, J. H. et al. Genetic, electrophysiological, and pathological studies on patients with SCN9A-related pain disorders. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 28, 597–607 (2023).
Chen, L. et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing in the context of neuropathic pain: progress, challenges, and prospects. Transl. Res. 251, 96–103 (2023).
Tansley, S. et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals time- and sex-specific responses of mouse spinal cord microglia to peripheral nerve injury and links ApoE to chronic pain. Nat. Commun. 13, 843 (2022).
Hubbard, E., Bachali, P., Grammer, A. C. & Lipsky, P. E. Validation of eight endotypes of lupus based on whole-blood RNA profiles. Lupus Sci. Med. 12, e001526 (2025).
Catalina, M. D., Owen, K. A., Labonte, A. C., Grammer, A. C. & Lipsky, P. E. The pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus: harnessing big data to understand the molecular basis of lupus. J. Autoimmun. 110, 102359 (2020).
Navratilova, E., Fillingim, R. B. & Porreca, F. Sexual dimorphism in functional pain syndromes. Sci. Transl. Med. 13, eabj7180 (2021).
Jiwrajka, N. & Anguera, M. C. The X in seX-biased immunity and autoimmune rheumatic disease. J. Exp. Med. 219, e20211487 (2022).
Andrade, R. M. et al. Accelerated damage accrual among men with systemic lupus erythematosus: XLIV. Results from a multiethnic US cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 56, 622–630 (2007).
Jolly, M. et al. Sex differences in quality of life in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Care Res. 71, 1647–1652 (2019).
Jiang, T. E., Mackey, S., Darnall, B. D., Simard, J. F. & Falasinnu, T. The problem of pain in systemic lupus erythematosus: a comprehensive analysis of pain distribution using the CHOIR body map and PROMIS measures. Lupus 34, 47–56 (2025).
Minhas, D., Murphy, A. & Clauw, D. J. Fibromyalgia and centralized pain in the rheumatoid arthritis patient. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 35, 170–174 (2023).
Di Carlo, M. et al. Fibromyalgia: one year in review 2024. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 42, 1141–1149 (2024).
Eller-Smith, O. C., Nicol, A. L. & Christianson, J. A. Potential mechanisms underlying centralized pain and emerging therapeutic interventions. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 12, 35 (2018).
Aringer M., & Pisetsky D. S. The dynamics of antinuclear antibody production in systemic lupus erythematosus: new insights for new therapies. Arthritis Rheumatol. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.43220 (2025).
Clowse, M. E. B. et al. Development and psychometric evaluation of a physician global assessment for type 2 systemic lupus erythematosus symptoms. Lupus Sci. Med. 10, e001016 (2023).
Martínez-Lavín, M. Dorsal root ganglia: fibromyalgia pain factory? Clin. Rheumatol. 40, 783–787 (2021).
Ji, R. R., Chamessian, A. & Zhang, Y. Q. Pain regulation by non-neuronal cells and inflammation. Science 354, 572–577 (2016).
Park, C. K. et al. Extracellular microRNAs activate nociceptor neurons to elicit pain via TLR7 and TRPA1. Neuron 82, 47–54 (2014).
Lehmann, S. M. et al. An unconventional role for miRNA: let-7 activates Toll-like receptor 7 and causes neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 15, 827–835 (2012).
Latremoliere, A. & Woolf, C. J. Central sensitization: a generator of pain hypersensitivity by central neural plasticity. J. Pain 10, 895–926 (2009).
Martucci, K. T. & Mackey, S. C. Neuroimaging of pain: human evidence and clinical relevance of central nervous system processes and modulation. Anesthesiology 128, 1241–1254 (2018).
Wolfe, F. et al. 2016 revisions to the 2010/2011 fibromyalgia diagnostic criteria. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 46, 319–329 (2016).
Wolfe, F., Walitt, B. T., Rasker, J. J., Katz, R. S. & Häuser, W. The use of polysymptomatic distress categories in the evaluation of fibromyalgia (FM) and FM severity. J. Rheumatol. 42, 1494–1501 (2015).
Sun, K. et al. Using PROMIS-29 to determine symptom burdens in the context of the type 1 and 2 systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) model: a cross sectional study. J. Patient Rep. Outcomes 7, 136 (2023).
Craig, B. M. et al. US valuation of health outcomes measured using the PROMIS-29. Value Health 17, 846–853 (2014).
Yost, K. J., Eton, D. T., Garcia, S. F. & Cella, D. Minimally important differences were estimated for six patient-reported outcomes measurement information system-cancer scales in advanced-stage cancer patients. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 64, 507–516 (2011).
Arcani, R., Jouve, E., Chiche, L. & Jourde-Chiche, N. Categorization of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus using disease activity, patient-reported outcomes, and transcriptomic signatures. Clin. Rheumatol. 42, 1555–1563 (2023).
Eudy, A. M. et al. The use of patient-reported outcome measures to classify type 1 and 2 systemic lupus erythematosus activity. Lupus 31, 697–705 (2022).
Petri, M., Hellmann, D. & Hochberg, M. Validity and reliability of lupus activity measures in the routine clinic setting. J. Rheumatol. 19, 53–59 (1992).
Buyon, J. P. et al. The effect of combined estrogen and progesterone hormone replacement therapy on disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 142, 953–962 (2005).
Clauw, D. J. Why don’t we use a body map in every chronic pain patient yet? Pain 165, 1660–1661 (2024).
Scherrer, K. H. et al. Development and validation of the collaborative health outcomes information registry body map. Pain. Rep. 6, e880 (2021).
Brummett, C. M. et al. Preliminary validation of the Michigan Body Map. Pain 157, 1205–1212 (2016).
Raja, S. N. et al. The revised International Association for the Study of Pain definition of pain: concepts, challenges, and compromises. Pain 161, 1976–1982 (2020).
Lumley, M. A. et al. Emotional awareness and other emotional processes: implications for the assessment and treatment of chronic pain. Pain. Manag. 11, 325–332 (2021).
Boersma, K. & Flink, I. K. Key aspects concerning the role of emotion in the chronic pain experience. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 62, 102000 (2025).
Falasinnu, T. et al. The problem of pain in the United States: a population-based characterization of biopsychosocial correlates of high impact chronic pain using the national health interview survey. J. Pain. 24, 1094–1103 (2023).
Vergne-Salle, P. et al. The burden of pain in rheumatoid arthritis: impact of disease activity and psychological factors. Eur. J. Pain. 24, 1979–1989 (2020).
Garg, S. et al. Multiplicative impact of adverse social determinants of health on outcomes in lupus nephritis: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Arthritis care Res. 76, 1232–1245 (2024).
Williams, E. M. et al. Cost-effectiveness of a peer mentoring intervention to improve disease self-management practices and self-efficacy among African American women with systemic lupus erythematosus: analysis of the peer approaches to lupus self-management (PALS) pilot study. Lupus 28, 937–944 (2019).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Yul Huh for assistance in generating the figures included in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors contributed equally to all aspects of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Rheumatology thanks Daniel Clauw, Elisabet Welin and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Glossary
- Allodynia
-
A condition in which ordinarily non-painful stimuli (such as touch) elicit pain.
- Central nervous system sensitization
-
A key feature of nociplastic pain. This form of sensitization involves changes in the processing of pain information at multiple levels in the nervous system and leads to pain amplification.
- Dysesthesia
-
An unusual sensation that is elicited by touch and can be experienced as unpleasant or strange. Dysesthesia can be described as burning, tingling or pins and needles among other sensations.
- Fibromyalgia
-
A form of nociplastic pain characterized by widespread pain in association with symptoms such as fatigue, mood disturbances and cognitive impairment. Fibromyalgia can occur alone or in association with nociceptive and/or neuropathic pain from another disease process. Fibromyalgia involves pain amplification that arises from central nervous system sensitization.
- Hyperalgesia
-
A manifestation of pain amplification in which a stimulus elicits more pain than expected from the intensity of the stimulus.
- Lupus-associated nociplasticity
-
A condition in which central sensitization leads to amplification of pain and other symptoms, most prominently fatigue, mood disturbance and cognitive impairment. The term builds upon the terminology of nociplastic pain but is not confined only to pain.
- Neuropathic pain
-
A form of pain that results from nerve injury or dysfunction.
- Neuropsychiatric SLE
-
An array of neurological and psychological manifestations that can affect all levels of the nervous system in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (ranging from mood disturbance to transverse myelitis). Determining the cause of these manifestations is key and often involves testing to determine whether the condition can be explained by another process (such as adverse effects of medication).
- Nociceptive pain
-
A form of pain that results from stimulation of nociceptors by noxious stimuli. Nociceptive pain has a protective function.
- Nociplastic pain
-
A form of pain that occurs in the absence of inflammation or other evidence of tissue injury. Nociplastic pain arises from changes in pain processing at various levels, is chronic and lacks an apparent protective function.
- Nosology
-
A branch of medical science involved with the classification of disease. This classification can be based on cause, pathogenesis or symptoms.
- Peripheral nervous system sensitization
-
This form of sensitization alters the sensitivity of the peripheral nervous system to noxious stimuli. This process involves changes in the activation threshold of nociceptive neurons and therefore increased signalling.
- Peripheral neuropathy
-
Damage or injury to peripheral nerves (that is, nerves outside of the CNS) that can arise from a wide variety of causes including inflammatory, metabolic and degenerative processes. Symptoms depend on the nerves affected and can involve disturbances of sensory and motor function and autonomic dysfunction.
- Serositis
-
Inflammation of serosal surfaces such as the pleura or pericardium. Serositis can be experienced as painful and can occur in association with symptoms such as fever. Serositis can be visualized using imaging (such as radiography or ultrasonography), although it can be inferred from characteristic symptoms.
- Sickness behaviour
-
An array of symptoms such as weakness, fatigue and malaise that can arise in response to infection, systemic inflammation or the administration of cytokine therapies. Sickness behaviour might promote host defence by influencing energy fluxes and expenditure necessary to mount an immune response.
- Small-fibre neuropathy
-
A form of peripheral neuropathy that affects the small-fibre nerves, both myelinated and unmyelinated, involved with the sensation of skin and other organs.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pisetsky, D.S., Eudy, A.M., Rogers, J.L. et al. Pain in systemic lupus erythematosus: emerging insights and paradigms. Nat Rev Rheumatol 21, 626–639 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-025-01290-1
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-025-01290-1