Abstract
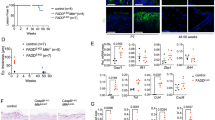
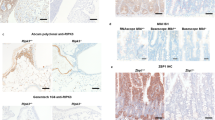
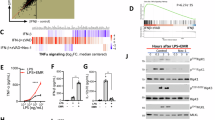
Conditional deletion of Caspase-8 in epidermal keratinocytes (Casp8E-KO) causes necroptosis-driven lethal dermatitis1-7. Here, we discover that Casp8 loss leads to accumulation of cytosolic DNA responsible for the activation of a cyclic-GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)/stimulator of interferon (IFN) gene (STING)-mediated transcriptional program. Genetic and biochemical evidence indicate that STING upregulates both Z-DNA binding protein-1 (ZBP1), and mixed lineage kinase domain-like (MLKL). Combined Casp8-deficiency- and STING-activation-driven accumulation of Z-nuclei acids, activates ZBP1 and triggers formation of a ZBP1–RIPK1–RIPK3 complex independently of FADD-RIPK1-RIPK3 complex enabling necroptosis execution. Genetically, we reveal a functional overlap between STING and ZBP1 as drivers of lethal dermatitis independently of TNFR1, uncovering a novel aetiology of necroptotic inflammation. Since gain-of-function mutations in human STING cause STING-Associated Vasculopathy with onset in Infancy (SAVI), we assessed the role of STING-induced necroptosis in SAVI’s aetiology. Chronic activation of STING in patients orchestrates a necroptotic transcriptional program which is confirmed in the N153S-SAVI preclinical mouse model where immune cell–driven pathology and lethality are remarkably rescued by RIPK3 co-deletion. These findings establish STING-driven ZBP1-mediated necroptosis as a central pathogenic mechanism in both Casp8-deficient inflammation and SAVI and suggest that targeting the ZBP1-RIPK3-MLKL axis holds therapeutic potential for interferonopathies characterised by excessive necroptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
from$1.95
to$39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Figures 1-9 and Supplementary Tables 1-9.
Supplementary Data
Source Data for Supplementary Figures 2-5 and 7.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kelepouras, K., Saggau, J., Bonasera, D. et al. STING induces ZBP1-mediated necroptosis independently of TNFR1 and FADD. Nature (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09536-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09536-4
This article is cited by
-
STING-driven necroptosis linked to autoinflammatory disease
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2025)