Abstract
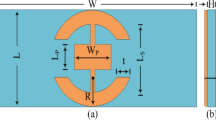
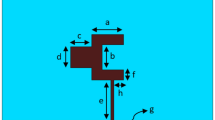
The increasing demand for high-speed communication has driven the development of antennas with improved performance characteristics for millimeter-wave (mm-Wave) 5G applications. A mm-wave 8-port Multi-Input-Multi-Output (MIMO) antenna aiming for 360° pattern diversity and high gain for 28 GHz applications has been presented in this paper. The antenna is made up of fully covered ground plane on Rogers RT-droid 5880 substrate (dielectric constant of 2.2 and electric tangent 0.0009) having eight port MIMO array system. The unit element offers a gain of 7.37 dBi which is improved to 12 dBi by converting into an unconventional three element array. The array offers an operational bandwidth of 27.6–28.4 GHz, covering almost 800 MHz, which provides sufficient spectrum for high-frequency applications such as 5G communication, radar systems, and millimeter-wave technologies. Despite the observed trade-off among reduced bandwidth and enhanced gain, the proposed design offers a viable solution for applications such as point-to-point communication, backhaul links, and other 5G mm-wave infrastructure. The array is further extended to eight port MIMO configurations that enhance data throughput and spectral efficiency while improving spatial diversity and 360° beam steering which consequently improves the overall efficiency of the modern-day wireless systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data is provided within the manuscript.
References
Zheng, X. et al. A low-coupling broadband MIMO array antenna design for Ku-band based on metamaterials. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 24, 666–673 (2024).
Li, D. et al. Ground-to-UAV sub-terahertz channel measurement and modeling. Opt. Express. 32, 32482–32494 (2024).
Hwang, I. J. et al. Millimeter-wave far-field range antenna measurement system for a W-band monopulse antenna. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 24, 494–503 (2024).
Meng, Z., Shen, F. & Gazor, S. WLB-CANUN: widely linear beamforming in coprime array with non-uniform noise. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 74, 5833–5842 (2025).
Andrews, J. G. et al. What will 5G be? IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 32, 1065–1082 (2014).
Hong, S., Nam, S., Choi, S., Joo, J. & Han, J. Advanced beam Estimation for antennas via patterned coupling-line detection board in Ka-band. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 24, 524–529 (2024).
Rappaport, T. S. et al. Millimeter-wave mobile communications for 5G cellular: it will work! IEEE Access. 1, 335–349 (2013).
Abd Hamid, S. H. & Goh, C. H. Rapid prototyping of microstrip patch antenna design: A review and bibliometric analysis for future research directions. Mater. Sci. Additive Manufactring. 4, 025260052 (2025).
Qualcomm Spectrum for 4G and 5G. (2017). https://www.qualcomm.com/news/media-center (accessed on 10 October 2025).
European 5G Observatory. National 5G spectrum assignment. (2020). https://5gobservatory.eu/ (accessed on 10 October 2025).
Hussain, N., Jeong, M. J., Park, J. & Kim, N. A broadband circularly-polarized Fabry-Pérot resonant antenna using a single-layered PRS for 5G MIMO applications. IEEE Access. 7, 42897–42907 (2019).
Alqwaifly, N. A., Awan, W. A., Alsaab, N., Alsunaydih, F. N. & Alhassoon, K. Array-inspired wideband and high-gain antenna with enhanced pattern diversity for 5G mm-wave networks. Sci. Rep. 15, 845 (2025).
Hussain, M. et al. Single-iterated fractal-inspired UWB antenna with reconfigurable Notch bands for compact electronics. Heliyon 9, e21419 (2023).
Moradi Ardekani, M. H., Dastranj, A. & Bornapour, S. M. A wideband high-gain all-metal antenna under quad resonances realized by folding a simple patch. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 24, 611–619 (2024).
Attia, H., Abdelghani, M. L. & Denidni, T. A. Wideband and high-gain millimeter-wave antenna based on FSS Fabry–Perot cavity. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 65, 5589–5594 (2017).
Uddin, M. N. & Alwan, E. A. A shared-aperture Pentaband antenna with high-impedance surface for CubeSat application. Sci. Rep. 14, 16146 (2024).
Yin, R., Peng, J., Cai, Y., Wu, C. & Champagne, B. Al-Dhahir, N. Radar-assisted predictive beamforming for UAV-aided networks: a deep-learning solution. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 74, 1–15 (2025).
Feng, D. et al. Multi-domain index modulation for MIMO-OTFS and a coarse-to-fine network for detection. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. (2025).
Malik, B. T., Khan, S. & Koziel, S. Beam steerable MIMO antenna based on conformal passive reflective metasurface for 5G millimeter wave applications. Sci. Rep. 14, 24086 (2024).
Xu, Y. et al. Joint pseudo-range and doppler positioning method with LEO satellites’ signals of opportunity. Satell. Navig. 6, 10 (2025).
Yin, R. et al. Joint beamforming and frame structure design for ISAC networks under imperfect synchronization. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 11, 2259–2274 (2025).
Sharma, M. et al. Flexible four-port MIMO antenna for 5G NR-FR2 tri-band MmWave application with SAR analysis. Sci. Rep. 14, 29100 (2024).
Wang, Q. et al. Robust design and tolerance analysis of shaped reflector antennas based on interval analysis. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 24, 2392–2396 (2025).
Zou, X. et al. Miniaturized low-profile ultrawideband antipodal Vivaldi antenna array loaded with edge techniques. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 73, 1–1 (2025).
Gültekin, S. S. & Yerlikaya, M. Enhanced-gain dual-port compact printed meandered log-periodic monopole array antenna design with octagonal-ring-shaped FSS for broadband 28 ghz applications. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 49, 16729–16741 (2024).
Tiwari, R. N., Sharma, D., Singh, P. & Kumar, P. A flexible dual-band 4×4 MIMO antenna for 5G mm-wave 28/38 GHz wearable applications. Sci. Rep. 14, 14324 (2024).
Dutta, S. et al. A 28 GHz FSS-backed SIW slotted array antenna with ultra-reduced sidelobes for ground surveillance & RADAR applications. Proc. IEEE Wireless Antennas Microw. Symp (WAMS) 1–5 (2024).
Meates, S. et al. F. A compact high-gain 28 GHz antenna array for beyond 5G wireless networks. Proc. Eur. Conf. Antennas Propag. (EuCAP) 1–3 (2024).
Shereen, M. K., Khattak, M. I., Basit, A. & Ahmad, G. Intelligent frequency, radiation-pattern and polarization-reconfigurable antenna for 5G applications. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 19, 3339–3353 (2024).
Abbasi, N. A. et al. High-isolation array antenna design for 5G mm-wave MIMO applications. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves. 46, 12 (2025).
Tiwari, P. et al. A high isolated, high gain millimeter wave quad-port MIMO antenna array for wideband 5G new radio application. Sci. Rep. 15, 34484 (2025).
Ghosh, S., Baghel, G. S. & Swati, M. V. Dual-port circular patch antenna array: enhancing gain and minimizing cross-polarization for mm-wave 5G networks. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 38, e5990 (2025).
Alsaab, N. et al. High-performance series-fed array multiple-input multiple-output antenna for millimeter-wave 5G networks. Sensors 25, 1036 (2025).
Lu, P. & Yang, X. S. Pattern-reconfigurable rectenna with omnidirectional/directional radiation modes for MPT with multiple transmitting antennas. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 29, 826–829 (2019).
Zhao, S., Wang, Z. & Dong, Y. Pattern-reconfigurable antenna using low-profile electric and magnetic radiators. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 22, 616–620 (2023).
Wang, Z., Liu, S. & Dong, Y. A compact, broadband, monopole-like endfire antenna with reconfigurable patterns for 5G applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 70, 7199–7204 (2022).
Wang, Z., Liu, S. & Dong, Y. Low-profile multifunctional pattern-reconfigurable antenna using periodic capacitor-loaded surface for 5G and beyond. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 70, 3277–3286 (2022).
Yan, Z., Lai, C. & Han, K. A compact millimeter-wave pattern-reconfigurable antenna with 360-degree beam coverage. Proc. Int. Conf. Microw. Millim. Wave Technol. (ICMMT). 1, 1–3 (2024).
Kim, S. & Nam, S. Implementation of an integrated LoRa and dual-band GNSS antenna in a compact package. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 24, 632–640 (2024).
Zhang, G. & Zhou, S. A methodology for designing high-efficiency power amplifiers using simple microstrip harmonic tuning circuits. Electronics 14, 4767 (2025).
Nikolova, T. M. & Lecture October 13: Linear array theory – Part I. McMaster University. (2025). https://www.ece.mcmaster.ca/faculty/nikolova/antenna_dload/current_lectures/L13_Arrays1.pdf.
Nguyen, T. T., Kim, D. H., Choi, J. H. & Jung, C. W. Circularly polarized series array and MIMO application for sub-millimeter wave/terahertz band. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 24, 294–304 (2024).
Bilal, M., Naqvi, S. I., Hussain, N., Amin, Y. & Kim, N. High-isolation MIMO antenna for 5G millimeter-wave communication systems. Electronics 11, 962 (2022).
Khan, I. et al. Hybrid technique-based circularly polarized MIMO antenna with low mutual coupling for millimeter-wave communications. Opt. Express. 33(8), 17782–17801 (2025).
Li, R., Qu, L. & Kim, H. A compact MIMO antenna design using the wideband ground-radiation technique for 5G terminals. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 24, 89–97 (2024).
Elmannai, H., Alkanhel, R. I., Savci, H. Ş., Kiani, S. H. & Bakar, H. S. A. Dual-band sub-6 ghz MIMO antenna system for enhanced connectivity in smartphones. Measurement 252, 117381 (2025).
Shariff, B. G. P. et al. High gain narrow beam MIMO array antenna operating at n260 band for millimeter wave applications. IEEE Access. 13, 69395–69412 (2025).
Verma, R. & Sharma, R. Four-element biodegradable substrate-integrated MIMO DRA with radiation diversity. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 24, 109–119 (2024).
Funding
This work was supported by Institute of Information & communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No.RS-2024-00466966, A systematic study on health risk of EMF exposure in advanced wireless service environments).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A., W.A.A., D.S. and N.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A., W.A.A., D.C. and N.H.; writing—review and editing, A.A., W.A.A., D.S. and N.K.; methodology, formal analysis, investigation, A.A., W.A.A., D.C. and N.H.; visualization and project administration, D.S. and N.K. All authors have read and agreed to the submitted version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Abaas, A., Awan, W.A., Choi, D. et al. A high-gain Y-shaped patch array with an 8-port MIMO configuration for pattern diversity in mm-wave applications. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35545-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35545-y