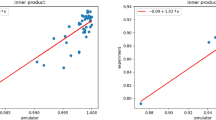
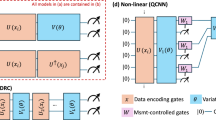
Abstract
Quantum machine learning (QML) has emerged as a promising domain to leverage the computational capabilities of quantum systems to solve complex classification tasks. In this work, we present the first comprehensive QML study by benchmarking the MedMNIST-a diverse collection of medical imaging datasets on a 127-qubit real IBM quantum hardware, to evaluate the feasibility and performance of quantum models (without any classical neural networks) in practical applications. This study explores recent advancements in quantum computing such as device-aware quantum circuits, error suppression, and mitigation for medical image classification. The proposed methodology is comprised of three stages: preprocessing, generation of noise-resilient and hardware-efficient quantum circuits, optimizing/training of quantum circuits on classical hardware, and inference on real IBM quantum hardware. Firstly, we process all input images in the preprocessing stage to reduce the spatial dimension due to quantum hardware limitations. We generate hardware-efficient quantum circuits using backend properties expressible to learn complex patterns for medical image classification. After classical optimization of QML models, we perform inference on real quantum hardware. We also incorporate advanced error suppression and mitigation techniques in our QML workflow, including dynamical decoupling (DD), gate twirling (Twir), and matrix-free measurement mitigation (M3) to mitigate the effects of noise and improve classification performance. The experimental results showcase the potential of quantum computing for medical imaging and establish a benchmark for future advancements in QML applied to healthcare.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The MedMNIST datasets used in this benchmarking study can be accessed using https://medmnist.com/.
Code availability
All the related codes are available at https://github.com/gurinder-hub/QML_MedMNIST.
References
Yang, J. et al. Medmnist v2–A large-scale lightweight benchmark for 2d and 3d biomedical image classification. Sci. Data. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-022-01721-8 (2023).
Kumar, R., Kumbharkar, P., Vanam, S. & Sharma, S. Medical images classification using deep learning: A survey. Multimed. Tools Appl. 83, 19683–19728 (2024).
Yue, Y. & Li, Z. Medmamba: Vision mamba for medical image classification (2024). arXiv:2403.03849.
Ma, J. et al. Segment anything in medical images. Nat. Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-44824-z (2024).
Zhang, Y., Shen, Z. & Jiao, R. Segment anything model for medical image segmentation: Current applications and future directions (2024). arXiv:2401.03495.
Webber, G. & Reader, A. J. Diffusion models for medical image reconstruction. BJR Artif. Intell. 1, ubae013 (2024).
Khader, F. et al. Medical diffusion: Denoising diffusion probabilistic models for 3d medical image generation (2023). arXiv:2211.03364.
Liu, Y., Arunachalam, S. & Temme, K. A rigorous and robust quantum speed-up in supervised machine learning. Nat. Phys. 17, 1013–1017. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-021-01287-z (2021).
Abbas, A. et al. The power of quantum neural networks. Nat. Comput. Sci. 1, 403–409. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43588-021-00084-1 (2021).
Jin, H. & Jr, K. M. M. Integrating machine learning and quantum circuits for proton affinity predictions (2024). arXiv:2411.17856.
Yamasaki, H., Isogai, N. & Murao, M. Advantage of quantum machine learning from general computational advantages (2023). arXiv:2312.03057.
Xiao, T., Zhai, X., Wu, X., Fan, J. & Zeng, G. Practical advantage of quantum machine learning in ghost imaging. Commun. Phys. 6, 171 (2023).
Acharya, R. et al. Quantum error correction below the surface code threshold (2024). arXiv:2408.13687.
Grant, E. et al. Hierarchical quantum classifiers. NPJ Quant. Inform. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-018-0116-9 (2018).
Farhi, E. & Neven, H. Classification with quantum neural networks on near term processors (2018). arXiv:1802.06002.
Havlíček, V. et al. Supervised learning with quantum-enhanced feature spaces. Nature 567, 209–212. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-0980-2 (2019).
Kerenidis, I., Landman, J. & Prakash, A. Quantum algorithms for deep convolutional neural networks (2019). arXiv:1911.01117.
Cong, I., Choi, S. & Lukin, M. D. Quantum convolutional neural networks. Nat. Phys. 15, 1273–1278. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-019-0648-8 (2019).
Allcock, J., Hsieh, C.-Y., Kerenidis, I. & Zhang, S. Quantum algorithms for feedforward neural networks (2019). arXiv:1812.03089.
Hernández, H. I. G., Ruiz, R. T. & Sun, G.-H. Image classification via quantum machine learning (2020). arXiv:2011.02831.
Kiani, B. T., Villanyi, A. & Lloyd, S. Quantum medical imaging algorithms (2020). arXiv:2004.02036.
Nakaji, K. & Yamamoto, N. Quantum semi-supervised generative adversarial network for enhanced data classification. Sci. Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98933-6 (2021).
Schuld, M., Sweke, R. & Meyer, J. J. Effect of data encoding on the expressive power of variational quantum-machine-learning models. Phys. Rev. A 103, 032430 (2021).
Schuld, M., Petruccione, F., Schuld, M. & Petruccione, F. Quantum models as kernel methods. Mach. Learn. Quant. Computers. 217–245 (2021).
Kollias, G., Kalantzis, V., Salonidis, T. & Ubaru, S. Quantum graph transformers. In ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 1–5 (IEEE, 2023).
Cherrat, E. A. et al. Quantum vision transformers. Quantum 8, 1265 (2024).
Fan, F., Shi, Y., Guggemos, T. & Zhu, X. X. Hybrid quantum-classical convolutional neural network model for image classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2023).
Wang, A., Hu, J., Zhang, S. & Li, L. Shallow hybrid quantum-classical convolutional neural network model for image classification. Quant. Inform. Process. 23, 17 (2024).
Benedetti, M., Lloyd, E., Sack, S. & Fiorentini, M. Parameterized quantum circuits as machine learning models. Quant. Sci. Technol. 4, 043001. https://doi.org/10.1088/2058-9565/ab4eb5 (2019).
Mitarai, K., Negoro, M., Kitagawa, M. & Fujii, K. Quantum circuit learning. Phys. Rev. A 98, 032309 (2018).
Adhikary, S., Dangwal, S. & Bhowmik, D. Supervised learning with a quantum classifier using multi-level systems. Quant. Inform. Process. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-020-2587-9 (2020).
Schuld, M., Bocharov, A., Svore, K. M. & Wiebe, N. Circuit-centric quantum classifiers. Phys. Rev. A. https://doi.org/10.1103/physreva.101.032308 (2020).
Acar, E. & Yilmaz, I. Covid-19 detection on ibm quantum computer with classical-quantum transfer learning. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Computer Sci. 29, 46–61 (2021).
Moradi, S. et al. Clinical data classification with noisy intermediate scale quantum computers. Sci. Rep. 12, 1851 (2022).
Houssein, E. H., Abohashima, Z., Elhoseny, M. & Mohamed, W. M. Hybrid quantum-classical convolutional neural network model for covid-19 prediction using chest x-ray images. J. Comput. Design En. 9, 343–363 (2022).
Toledo-Cortés, S., Useche, D. H., Müller, H. & González, F. A. Grading diabetic retinopathy and prostate cancer diagnostic images with deep quantum ordinal regression. Comput. Biol. Med. 145, 105472 (2022).
Azevedo, V., Silva, C. & Dutra, I. Quantum transfer learning for breast cancer detection. Quant. Mach. Intell. 4, 5 (2022).
Parisi, L., Neagu, D., Ma, R. & Campean, F. Quantum relu activation for convolutional neural networks to improve diagnosis of parkinson’s disease and covid-19. Expert Syst. Appl. 187, 115892 (2022).
Landman, J. et al. Quantum methods for neural networks and application to medical image classification. Quantum 6, 881 (2022).
Scikit-learn Developers. ROC AUC Score – Scikit-learn Documentation (2025). Accessed: January 3, 2025.
IBM Quantum. Combine error mitigation options with the estimator primitive. https://learning.quantum.ibm.com/tutorial/combine-error-mitigation-options-with-the-estimator-primitive (2025). Accessed: June 26, 2025.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S. & Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 770–778 (2016).
Feurer, M. et al. Auto-sklearn: Efficient and Robust Automated Machine Learning 113–134 (Springer International Publishing, 2019).
Jin, H., Song, Q. & Hu, X. Auto-keras: An efficient neural architecture search system. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery & data mining, 1946–1956 (2019).
Google automl vision. https://cloud.google.com/vision/automl/docs.
Anagolum, S. et al. élivágar: Efficient quantum circuit search for classification (2024). arXiv:2401.09393.
Wang, H. et al. Quantumnas: Noise-adaptive search for robust quantum circuits. In The 28th IEEE International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA-28) (2022).
Nation, P. D., Kang, H., Sundaresan, N. & Gambetta, J. M. Scalable mitigation of measurement errors on quantum computers. PRX Quant. https://doi.org/10.1103/prxquantum.2.040326 (2021).
Acknowledgements
We extend our sincere gratitude to Danil Kaliakin (Research Associate, Cleveland Clinic) and Abdullah Ash Saki (Researcher at IBM Quantum) for their valuable insights and support throughout this project. We are also grateful to the authors of Élivágar and Torchquantum for their great work and open-sourcing the code.
Funding
The research is funded by the NIH (GM130641).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G. Singh and H. Jin proposed and designed the study of benchmarking MedMNIST datasets using quantum machine learning on real IBM Cleveland hardware. G. Singh and H. Jin performed the experiments under the supervision of K.M. Merz. G. Singh wrote the manuscript, with inputs and contributions from all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, G., Jin, H. & Merz Jr., K.M. Benchmarking MedMNIST dataset on real quantum hardware. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35605-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35605-3