Abstract
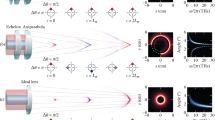
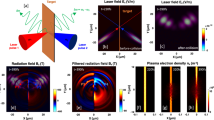
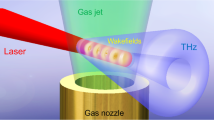
We investigate terahertz (THz) radiation generation at the vacuum-plasma interface driven by the oblique incidence of s-polarized Gaussian laser pulse(s) on a semi-infinite underdense plasma. Extending beyond the conventional single-frequency bipolar pulse (B-pulse), this work focuses on leveraging two-color mixed-frequency pulse– (M-pulse) excitation to enhance THz performance in terms of strength and broadening that can be tuned through controlled amplitude and phase of the constituent pulses of the M-pulse. A new expression for the ponderomotive force (PF)—which acts as the main driver of THz radiation at the vacuum-plasma boundary—is derived to capture the hitherto unexplored effects of phase asymmetry intrinsic to the M-pulse, in contrast to a single B-pulse where its phase is irrelevant. This PF formulation captures the underlying cycle-to-cycle symmetry-breaking for the M-pulse field, responsible for efficient THz emission. We demonstrate analytically that such M-pulses of the same total energy as a B-pulse may generate significantly enhanced PF, leading to THz yields several orders of magnitude higher. With a judicious choice of low-frequency to high-frequency ratio, the M-pulse configuration is shown to emerge as a highly efficient, phase-controllable driver of THz radiation and offers a promising route for optimizing THz source design via tailored two-color laser-plasma interactions. Particle-in-cell simulations performed with a finite-size plasma corroborate the main findings of the analytical model.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of this article are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. However, due to other novel findings, authors won’t be able to make the raw data public. Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to M.K.
References
Tonouchi, M. Cutting-edge terahertz technology. Nat. Photon. 1, 97–105 (2007).
Ferguson, B. & Zhang, X.-C. Materials for terahertz science and technology. Nat. Mater. 1, 26–33 (2002).
Kang, B. J. et al. Time-resolved thz stark spectroscopy of molecules in solution. Nat. Commun. 15, 4212 (2024).
Zhang, F. et al. Application of thz vibrational spectroscopy to molecular characterization and the theoretical fundamentals: An illustration using saccharide molecules. Chem.-An Asian J. 12, 324–331 (2017).
Pickwell, E., Cole, B., Fitzgerald, A., Wallace, V. & Pepper, M. Simulation of terahertz pulse propagation in biological systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 2190–2192 (2004).
Pickwell, E., Cole, B. E., Fitzgerald, A. J., Pepper, M. & Wallace, V. P. In vivo study of human skin using pulsed terahertz radiation. Phys. Med. Biol. 49, 1595 (2004).
Bergé, L. et al. Terahertz spectroscopy from air plasmas created by two-color femtosecond laser pulses: The altesse project. Europhys. Lett. 126, 24001. https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/126/24001 (2019).
Liu, K. et al. High-speed 0.22 thz communication system with 84 gbps for real-time uncompressed 8k video transmission of live events. Nat. Commun. 15, 8037 (2024).
Sarieddeen, H., Saeed, N., Al-Naffouri, T. Y. & Alouini, M.-S. Next generation terahertz communications: A rendezvous of sensing, imaging, and localization. IEEE Commun. Mag. 58, 69–75 (2020).
Li, B., Zhang, D. & Shen, Y. Study on terahertz spectrum analysis and recognition modeling of common agricultural diseases. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 243, 118820 (2020).
Hadjiloucas, S., Karatzas, L. S. & Bowen, J. W. Measurements of leaf water content using terahertz radiation. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 47, 142–149 (1999).
Tzydynzhapov, G. et al. New real-time sub-terahertz security body scanner. J. Infrared Millimeter Terahertz Waves 41, 632–641 (2020).
Palka, N. et al. Thz spectroscopy and imaging in security applications. In 2012 19th International Conference on Microwaves, Radar & Wireless Communications, vol. 1, pp. 265–270 (IEEE, 2012).
Johnston, M. B., Whittaker, D. M., Corchia, A., Davies, A. & Linfield, E. H. Simulation of terahertz generation at semiconductor surfaces. Phys. Rev. B 65, 165301 (2002).
Dekorsy, T., Auer, H., Bakker, H. J., Roskos, H. G. & Kurz, H. Thz electromagnetic emission by coherent infrared-active phonons. Phys. Rev. B 53, 4005 (1996).
Heyman, J. et al. Terahertz emission from gaas and inas in a magnetic field. Phys. Rev. B 64, 085202 (2001).
Dey, I. et al. Highly efficient broadband terahertz generation from ultrashort laser filamentation in liquids. Nat. Commun. 8, 1184. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01382-x (2017).
Yun, H., Bae, L. J., Mirzaie, M. & Kim, H. T. Laser-plasma-based radiation sources with intense laser pulses. Rev. Modern Plasma Phys. 9, 13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41614-025-00181-y (2025).
Carrig, T. J., Rodriguez, G., Sharp Clement, T., Taylor, A. J. & Stewart, K. R. Generation of terahertz radiation using electro-optic crystal mosaics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 66, 10–12 (1995).
Zhong, H., Karpowicz, N. & Zhang, X.-C. Terahertz emission profile from laser-induced air plasma. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, (2006).
Xie, X., Xu, J., Dai, J. & Zhang, X.-C. Enhancement of terahertz wave generation from laser induced plasma. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, (2007).
Thiele, I. et al. Theory of terahertz emission from femtosecond-laser-induced microplasmas. Phys. Rev. E 94, 063202 (2016).
Cheng, C.-C., Wright, E. M. & Moloney, J. V. Generation of electromagnetic pulses from plasma channels induced by femtosecond light strings. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 213001 (2001).
Sheng, Z.-M., Mima, K., Zhang, J. & Sanuki, H. Emission of electromagnetic pulses from laser wakefields through linear mode conversion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 095003 (2005).
Sheng, Z.-M., Mima, K. & Zhang, J. Powerful terahertz emission from laser wake fields excited in inhomogeneous plasmas. Phys. Plasmas 12, (2005).
Déchard, J., Debayle, A., Davoine, X., Gremillet, L. & Bergé, L. Terahertz pulse generation in underdense relativistic plasmas: From photoionization-induced radiation to coherent transition radiation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 144801. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.144801 (2018).
Gorbunov, L. & Frolov, A. Transition radiation generated by a short laser pulse at a plasma-vacuum interface. Plasma Phys. Rep. 32, 850–865 (2006).
Frolov, A. Terahertz wave emission at an oblique incidence of the laser pulse on rarefied plasma. Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 62, 095002 (2020).
Lei, H.-Y. et al. Highly efficient generation of gv/m-level terahertz pulses from intense femtosecond laser-foil interactions. Iscience 25, (2022).
Hua, J. et al. Enhanced terahertz radiation generated by intense laser interaction with a two-layer thin solid target. Phys. Rev. Accelerat. Beams 27, 081301 (2024).
Shao, S.-T. et al. Efficiently laser driven terahertz surface plasmon polaritons on long metal wire. Phys. Rev. X 15, 031025. https://doi.org/10.1103/mkyj-77k8 (2025).
Malik, A. K., Malik, H. K. & Stroth, U. Terahertz radiation generation by beating of two spatial-gaussian lasers in the presence of a static magnetic field. Phys. Rev. E-Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 85, 016401 (2012).
Bhasin, L., Tripathi, V. & Kumar, P. Laser beat wave resonant terahertz generation in a magnetized plasma channel. Phys. Plasmas 23, (2016).
Nguyen, A. et al. Spectral dynamics of thz pulses generated by two-color laser filaments in air: The role of kerr nonlinearities and pump wavelength. Opt. Express 25, 4720–4740 (2017).
Malevich, V. L., Adomavicius, R. & Krotkus, A. Thz emission from semiconductor surfaces. Comptes Rendus. Physique 9, 130–141 (2008).
Si, K. et al. Terahertz surface emission from layered semiconductor wse2. Appl. Surf. Sci. 448, 416–423 (2018).
Arkhipov, R. M., Arkhipov, M. V. & Rosanov, N. N. Unipolar light: Existence, generation, propagation, and impact on microobjects. Quantum Electron. 50, 801 (2020).
Rosanov, N. N. Unipolar pulse of an electromagnetic field with uniform motion of a charge in a vacuum. Usp. Fiz. Nauk 193, 1127–1133 (2023).
Gorelov, S. D., Novokovskaya, A. L., Bodrov, S. B., Sarafanova, M. V. & Bakunov, M. I. Unipolar fields produced by ultrafast optical gating of terahertz pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 126, 011104. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0243002 (2025).
Calegari, F., Sansone, G., Stagira, S., Vozzi, C. & Nisoli, M. Advances in attosecond science. J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 49, 062001. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-4075/49/6/062001 (2016).
Hassan, M. T. et al. Optical attosecond pulses and tracking the nonlinear response of bound electrons. Nature 530, 66–70. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16528 (2016).
Zeng, Z. et al. Generation of isolated attosecond pulses in the far field by two-color laser fields. Phys. Rev. A 76, 021804. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.76.021804 (2007).
Jones, R. R., You, D. & Bucksbaum, P. H. Ionization of rydberg atoms by subpicosecond half-cycle electromagnetic pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1236–1239. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.70.1236 (1993).
You, D., Jones, R. R. & Bucksbaum, P. H. Generation of single-cycle pulses in the far-infrared by optical rectification. Opt. Lett. 20, 431–433. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.20.000431 (1995).
Rousseau, P. et al. Efficient laser pulse steepening in plasma for applications to high-order harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 163901. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.163901 (2006).
Matsuoka, T. et al. Pulse compression and asymmetric pulse shaping in plasma for laser-wakefield acceleration. Opt. Express 16, 18152–18159. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.16.018152 (2008).
Gopal, K., Gupta, D. N., Kim, Y. K., Hur, M. S. & Suk, H. Large-scale magnetic field generation by asymmetric laser-pulse interactions with a plasma in low-intensity regime. J. Appl. Phys. 119, 123101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4943180 (2016).
Singh, M., Gopal, K. & Gupta, D. N. Temporally asymmetric laser pulse for magnetic-field generation in plasmas. Phys. Lett. A 380, 1437–1441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2016.02.015 (2016).
Birdsall, C. K. & Langdon, A. B. Plasma Physics via Computer Simulation Series on Plasma Physics. (Adam Hilger, New York, 1991).
Kundu, M. Beyond the conventional collisional absorption of laser light in under-dense plasma: A particle-in-cell simulation study. Pramana J. Phys. 92, 50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-018-1716-9 (2019).
Chen, F. F. Introduction to Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion (Springer, 1984).
Lichters, R., Meyer-ter-Vehn, J. & Pukhov, A. Short-pulse laser harmonics from oscillating plasma surfaces driven at relativistic intensity. Phys. Plasmas 3, 3425–3437. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.871619 (1996).
Pfund, R. E. W., Lichters, R. & Meyer-ter Vehn, J. Lpic++ a parallel one-dimensional relativistic electromagnetic particle-in-cell code for simulating laser-plasma-interaction. AIP Conf. Proc. 426, 141–146. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.55199 (1998).
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge Dr. Sudip Sengupta for careful reading of the manuscript and ANTYA HPC facility at IPR for executing numerical programs as well as visualization.
Funding
Authors received no specific funding for this work. It is covered by the Institute for Plasma Research, under the Department of Atomic Energy, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.K.P. and M.K. developed the methodology and worked for formal analysis; M.K. conceptualized the work; A.K.P. and R.K.S. validated results; A.K.P., M.K., and R.K.S. prepared figures and the original draft of the manuscript; Review and editing of the final manuscript done by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Anjana, K.P., Srivastav, R.K. & Kundu, M. Enhanced terahertz radiation generation by phase-controlled two-color laser pulses interacting with an under-dense plasma. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35800-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35800-2