Abstract
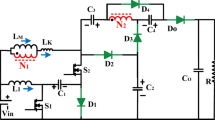
This paper presents a non-isolated high step-up DC–DC converter based on a modified three-winding coupled inductor, which is proposed for renewable energy applications. The proposed converter, which embeds a modified voltage multiplier cell utilizing a secondary winding of a coupled inductor, achieves an ultra-high voltage gain without requiring extreme duty cycles. and not only minimizes the overall component count but also significantly reduces voltage stress across semiconductors and capacitors, thereby lowering system cost. Moreover, the employed cell based on the coupled inductor offers simplicity and flexibility, making it suitable for integration into other converter topologies as well. The architecture further ensures a continuous, low-ripple input current and maintains a common-ground connection between source and load, making it highly compatible with photovoltaic and fuel-cell integration. Comprehensive analysis of the operating principles, steady-state performance, and device stresses is provided, together with theoretical efficiency estimation and comparative evaluation against recent state-of-the-art designs. Experimental validation is conducted using a 250 W prototype converting 24 V to 400 V, achieving a peak efficiency of 95.3%, which substantiates the analytical predictions and highlights the practical effectiveness of the proposed topology for next-generation renewable energy systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Anand, S. & Fernandes, B. Optimal voltage level for DC microgrids, in IECON 2010-36th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, 3034–3039 (IEEE, 2010).
Kala, C. S., Mahesh, G., Rao, B. T. & Swapna, G. A Review on Various Supply Sources for DC Micro Grids, in 2023 International Conference on Intelligent and Innovative Technologies in Computing, Electrical and Electronics (IITCEE), 533–538 (IEEE, 2023).
Zhang, M., Li, H., Hao, Y., Li, K. & Ding, X. A modified switched-coupled-inductor quasi-Z-source inverter. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 9 (3), 3634–3646 (2020).
Kumar, B. H. et al. A Review of Non-Isolated DC-DC Converter Topologies, in 2024 International Conference on Recent Innovation in Smart and Sustainable Technology (ICRISST), 1–6 (IEEE, 2024).
Sun, C., Zhang, X. & Cai, X. A step-up nonisolated modular multilevel DC–DC converter with self-voltage balancing and soft switching. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 35 (12), 13017–13030 (2020).
Vosoughi, N., Hosseini, S. H. & Sabahi, M. A new single-phase transformerless grid-connected inverter with boosting ability and common ground feature. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 67 (11), 9313–9325 (2019).
Ai, J., Lin, M. & Yin, M. A family of high step-up cascade DC–DC converters with clamped circuits. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 35 (5), 4819–4834 (2019).
Nguyen, M. K., Duong, T. D. & Lim, Y. C. Switched-capacitor-based dual-switch high-boost DC–DC converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 33 (5), 4181–4189 (2017).
Axelrod, B., Berkovich, Y. & Ioinovici, A. Switched-capacitor/switched-inductor structures for getting transformerless hybrid DC–DC PWM converters. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 55 (2), 687–696 (2008).
Andrade, A. & Guisso, R. Quasi-Z-source network DC–DC converter with different techniques to achieve a high voltage gain. Electron. Lett. 54(11), 710–712 (2018).
Rostami, S., Abbasi, V. & Kerekes, T. Switched capacitor based Z-source DC–DC converter. IET Power Electron. 12 (13), 3582–3589 (2019).
Haji-Esmaeili, M. M., Babaei, E. & Sabahi, M. High step-up quasi-Z source DC–DC converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 33 (12), 10563–10571 (2018).
Khalilzadeh, M. & Abbaszadeh, K. Non-isolated high step-up DC–DC converter based on coupled inductor with reduced voltage stress. IET Power Electron. 8(11), 2184–2194 (2015).
Wang, S. Research of inductive power transfer system for electric vehicle, (2016).
Narayana, C. L., Suryawanshi, H., Nachankar, P., Reddy, P. V. V. & Govind, D. A quintupler boost high conversion gain soft-switched converter for DC microgrid. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs. 69 (3), 1287–1291 (2021).
Ardi, H., Ajami, A. & Sabahi, M. A novel high step-up DC–DC converter with continuous input current integrating coupled inductor for renewable energy applications. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 65 (2), 1306–1315 (2017).
Liang, T. J., Luo, P. & Chen, K. H. A high step-up DC–DC converter with three-winding coupled inductor for sustainable energy systems. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 69 (10), 10249–10258 (2021).
Poorali, B., Torkan, A. & Adib, E. High step-up Z-source DC–DC converter with coupled inductors and switched capacitor cell. IET Power Electron. 8(8), 1394–1402 (2015).
Rezaie, M. & Abbasi, V. Ultrahigh step-up DC–DC converter composed of two stages boost converter, coupled inductor, and multiplier cell. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 69 (6), 5867–5878 (2021).
Liu, T., Lin, M. & Ai, J. High step-up interleaved DC–DC converter with asymmetric voltage multiplier cell and coupled inductor. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 8 (4), 4209–4222 (2019).
Poorali, B., Jazi, H. M. & Adib, E. Improved high step-up Z-source DC–DC converter with single core and ZVT operation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 33 (11), 9647–9655 (2017).
Abdi, H., Maalandish, M., Nadermohammadi, A., Hosseini, S. H. & Rostami, N. Non-Isolated SIDO DC–DC converter with a high controllability for PV applications. IET Renew. Power Gener. 19(1), e70034 (2025).
Baddipadiga, B. P. R., Prabhala, V. A. K. & Ferdowsi, M. A family of high-voltage-gain DC–DC converters based on a generalized structure. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 33 (10), 8399–8411 (2017).
Zheng, Y., Brown, B., Xie, W., Li, S. & Smedley, K. High step-up DC–DC converter with zero voltage switching and low input current ripple. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 35 (9), 9416–9429 (2020).
Nouri, T., Kurdkandi, N. V. & Husev, O. An improved ZVS high step-up converter based on coupled inductor and built-in transformer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 36 (12), 13802–13816 (2021).
Du, R., Samavatian, V., Samavatian, M., Gono, T. & Jasiński, M. Development of a high-gain step-up DC/DC power converter with magnetic coupling for low-voltage renewable energy. IEEE Access, 11, pp. 90038-90051,(2023).
Ji, Y., Liu, H., Feng, Y., Wu, F. & Wheeler, P. High step-up Y-source coupled-inductor impedance network boost DC–DC converters with common ground and continuous input current. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 8 (3), 3174–3183 (2019).
Imanlou, A., Najmi, E. S., Behkam, R., Nazari-Heris, M. & Gharehpetian, G. B. A new high voltage gain active switched-inductor based high step-up DC–DC converter with coupled-inductor. IEEE Access. 11, 56749–56765 (2023).
Zhou, M., Liu, C., Zhang, M., Mao, X. & Zhang, Y. High Step-Up Soft-Switching DC–DC converter integrated with Y-Source network. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 11 (3), 3348–3358 (2023).
He, Y., Sun, X., Liu, S. & Wang, N. High step-up DC–DC converter using coupled inductor voltage multiplier cell and differential connection method. IET Power Electron. 16 (4), 542–557 (2023).
M. Izadi, A. Mosallanejad, and A. L. Eshkevari, "An improved coupled inductor‐based quadratic step‐up DC–DC converter with a high step‐up factor and reduced voltage overshoot on the power switch," IET Power Electronics, 17 (9), pp. 986-1004, (2024).
Ding, J., Zhao, S., Gao, S. & Yin, H. A single-switch high step-up DC–DC converter based on three-winding coupled inductor and pump capacitor unit. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 37 (3), 3053–3061 (2021).
Babaei, E., Saadatizadeh, Z. & Cecati, C. High step-up high step-down bidirectional DC/DC converter. IET Power Electron. 10(12), 1556–1571 (2017).
Nadermohammadi, A. et al. Cost-Effective quadratic Ultra-High gain DC-DC converter with high power density for DC microgrid applications. IEEE Open. J. Power Electronics, 6 1703-1723, (2025).
Rostami, R., Hosseini, S. H. & Sharifian, M. B. B. High gain non-isolated step-up DC-DC converter proper for renewable energy applications. Sci Rep 15, 43608, (2025).
Abdi, H., Shokrani, M., Rostami, N. & Babaei, E. Cost-Effective Ultra-High Step-Up SEPIC-Based DC-DC converter integrated with Coupled-Inductor for Solar-Powered DC microgrids. IET Power Electron. 18(1), e70094 (2025).
Nadermohammadi, A. et al. Cost-effective soft-switching ultra-high step-up DC–DC converter with high power density for DC microgrid application. Scientific Reports, 14, 1, p. 20407, (2024).
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors reviewed the manuscript. MH.T, M. S., MB. B., and E. B. performed the dataanalysis and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Tehranidoost Tabrizi, M.H., Sabahi, M., Bannae Sharifian, M. et al. Modified design TWCI-based high step-up DC-DC converter with reduced elements and low input current ripple for renewable applications. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37346-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37346-9