Abstract
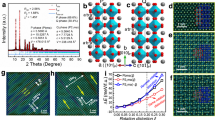
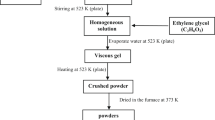
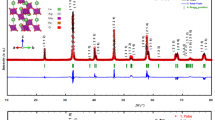
In this work, Ag/AgNbO3−δ composite was prepared by solid-state method. Rietveld refined X-ray diffraction pattern revealed that the sample crystallized in orthorhombic (Pbcm) perovskite structure with small impurities of metallic Ag and confirmed by transmission electron microscopy technique. Fourier transform infrared analysis of this composite indicated the formation of NbO6 octahedral structure. Raman spectroscopy of this composite revealed the suppression of the ferroelectric distortion compared with pure of AgNbO3. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy results revealed the existence of the Ag1+, Ag0, Nb5+, and O2− states as well as oxygen vacancies in this composite. UV-Vis. analysis revealed that this composite has direct and indirect band gap energies of 3.75 and 1.70 eV, respectively. Differential scanning calorimetry and dielectric measurements of Ag/AgNbO3−δ composite revealed that the phase transitions shifted toward lower temperature compared to pure AgNbO3 perovskite. The polarization-field hysteresis loops of this composite exhibited weak ferroelectric behavior at low electric fields. These results indicated that the lead-free Ag/AgNbO3−δ composite is a promising material for dielectric applications, particularly in dielectric devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data are available within this paper.
References
Park, S. et al. A-/B-site engineering of AgNbO3-based ceramics for high-efficiency relaxor antiferroelectric energy storage. J. Adv. Ceram. 14, 9221174 (2025).
Moriwake, H., Fisher, C. A., Kuwabara, A. & Fu, D. First-Principles study of point defect formation in AgNbO3. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 52, 09KF08 (2013).
Tian, Y. et al. High energy density in silver niobate ceramics. J. Mater. Chem. A. 4, 17279–17287 (2016).
Farid, U., Gibbs, A. S. & Kennedy, B. J. Impact of Li doping on the structure and phase stability in AgNbO3. Inorg. Chem. 59, 12595–12607 (2020).
Zhang, X., Han, W., Shen, B. & Guo, S-Q. A review of advances in XNbO3 perovskite-type piezo-photocatalysts: structure, modification strategies and applications. J. Alloys Compd. 1014, 178714 (2025).
An, K. et al. Enhanced energy storage performance of AgNbO3:xCeO2 by synergistic strategies of tolerance factor and density regulations. Coatings 13, 534 (2023).
Du, J., Zhao, Y., Li, Y., Sun, N. & Hao, X. Positive and negative electrocaloric effect in lead-free silver niobate antiferroelectric ceramic depending on affluent phase transition. Crystals 13, 86 (2023).
Kania, A. et al. Silver deficiency and excess effects on quality, dielectric properties and phase transitions of AgNbO3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34, 1761–1770 (2014).
Sciau, P., Kania, A., Dkhil, B., Suard, E. & Ratuszna, A. Structural investigation of AgNbO3 phases using x-ray and neutron diffraction. J. Phys. : Condens. Matter. 16, 2795–2810 (2004).
Tian, Y. et al. Silver niobate perovskites: structure, properties and multifunctional applications. J. Mater. Chem. A. 10, 14747–14787 (2022).
Li, S. et al. Significantly enhanced energy storage performance of rare-earth-modified silver niobate lead-free antiferroelectric ceramics via local chemical pressure tailoring. J. Mater. Chem. C. 7, 1551–1560 (2019).
Chen, G. et al. Disassembling and reassembling perovskites for oxygen electrocatalysis. EES Catal. 3, 1030–1043 (2025).
Zhou, J. et al. Enhanced the energy storage performance in AgNbO3-based antiferroelectric ceramics via manipulation of oxygen vacancy. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 43, 6059–6068 (2023).
Chao, W., Gao, J., Yang, T. & Li, Y. Excellent energy storage performance in La and Ta co-doped AgNbO3 antiferroelectric ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 41, 7670–7677 (2021).
Khan, A. et al. Lithium storage behaviour of AgNbO3 perovskite: Understanding electrochemical activation and charge storage mechanisms. Energy Storage Mater. 70, 103431 (2024).
Shu, H. et al. Structural characterization and photocatalytic activity of NiO/AgNbO3. J. Alloys Compd. 496, 633–637 (2010).
Abdel-Khalek, E. K., Mohamed, E. A. & Ismail, Y. A. M. Study the role of oxygen vacancies and Mn oxidation States in nonstoichiometric CaMnO3–δ perovskite nanoparticles. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 113, 461–472 (2025).
Nain, R. & Dwivedi, R. K. Studies on structural, optical and electrical behavior of La and cr modified NaNbO3 (x ≤ 0.15). J. Solid State Chem. 329, 124378 (2024).
Boukriba, M., Sediri, F. & Gharbi, N. Hydrothermal synthesis and electrical properties of NaNbO3. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 574–580 (2013).
Yashima, M. et al. Structure of ferroelectric silver niobate AgNbO3. Chem. Mater. 23 1643–1645. (2011).
Mi, L. et al. A new silver metaniobate semiconductor of Ag0.5La0.5Nb2O6 with defect-perovskite structure. Spectrochim Acta Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 192, 59–66 (2018).
Yang, M. et al. Highly efficient Ag2O/AgNbO3 p-n heterojunction photocatalysts with enhanced visible-light responsive activity. J. Alloy Compd. 811, 151831 (2019).
Lu, Z. et al. Mechanism of enhanced energy storage density in AgNbO3-based lead-free antiferroelectrics. Nano Energy. 79, 105423 (2021).
Wang, D., Kako, T. & Ye, J. New series of solid-solution semiconductors (AgNbO3)1-x(SrTiO3)x with modulated band structure and enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. J. Phys. Chem. C. 113, 3789 (2009).
Yu, Z. et al. Synthesis of high efficient and stable plasmonic photocatalyst Ag/AgNbO3 with specific exposed crystal-facets and intimate heterogeneous interface via combustion route. Appl. Surf. Sci. 488, 485–493 (2019).
Zhang, T. et al. Photocatalytic water splitting for hydrogen generation on cubic, orthorhombic, and tetragonal KNbO3 microcubes. Nanoscale 5, 8375 (2013).
Yang, D. et al. AgNbO3-based antiferroelectric ceramics with superior energy storage performance via Gd/Ta substitution at A/B sites. Ceram. Int. 49, 18143–18152 (2023).
Jesusa, K. F. S. et al. Structural evolution of La-modified AgNbO3 lead-free ceramics: perspective from octahedral tilting and tolerance factor. Ceram. Int. 48, 20506–20515 (2022).
Kruczek, M., Talik, E. & Kania, A. Electronic structure of AgNbO3 and NaNbO3 studied by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Solid State Commun. 137, 469–473 (2006).
Li, Y. et al. Electrochemical exsolution of ag nanoparticles from agNbO3 sensing electrode for enhancing the performance of mixed potential type NH3 sensors. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 344, 130296 (2021).
Lu, Y. et al. Photoinduced in situ growth of ag nanoparticles on agNbO3. J. Phys. Chem. C. 120, 28712–28716 (2016).
Xu, N., Takei, T., Miura, A. & Kumada, N. Preparation and phase transformation of ag or Bi ion-exchanged layered niobate perovskite and their photocatalytic properties. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 123, 690–694 (2015). [8].
Sikdar, S., Pathak, S. & Ghorai, T. K. Aqueous phase photodegradation of rhodamine B and p-nitrophenol desctruction using titania based nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. Lett. 6(10), 867–873 (2015).
Liu, X. X. et al. A silver niobate photocatalyst AgNb7O18 with perovskite-like structure. J. Alloy Compd. 724, 381–388 (2017).
Zhang, D. et al. Photocatalytic degradation of ofloxacin by perovskite-type NaNbO3 nanorods modified g-C3N4 heterojunction under simulated solar light: theoretical calculation, ofloxacin degradation pathways and toxicity evolution. Chem. Eng. J. 400, 125918 (2020).
Nain, R. & Dwivedi, R. K. Photocatalytic activity in graded off-valent cations substituted NaNbO3. Heliyon 10, e29121 (2024).
Zhou, F., Zhu, J., Lai, Z., Liu, Y. & Zhao, X. Surface plasmon resonances behavior in visible light of non-metal perovskite oxides AgNbO3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 231121 (2014).
Abdel-Khalek, E. K., Ibrahim, I., Salama, T. M., Elseman, A. M. & Mohamed, M. M. Structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic properties of Bi1 – xLaxFeO3 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 465, 309–315 (2018).
Xia, W., Wu, H., Xue, P. & Zhu, X. Microstructural, magnetic, and optical properties of Pr-doped perovskite manganite La0.67Ca0.33MnO3 nanoparticles synthesized via Sol-Gel process. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 13, 135 (2018).
Kania, A. An additional phase transition in silver niobate AgNbO3. Ferroelectrics 205, 19–28 (1998).
Gao, J. et al. Local structure heterogeneity in Sm-doped AgNbO3 for improved energy-storage performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 12, 6097–6104 (2020).
Lu, Z. et al. Mechanism of enhanced energy storage in AgNbO3-based lead-free antiferroelectrics. Nano Energy. 79, 105423 (2021).
Xie, Z. & Liu, H. A novel method of preparing antiferroelectric silver niobate AgNbO3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 46, 6955–6957 (2020).
Li, J. et al. Silver deficiency effect on dielectric properties and energy storage performance of AgNbO3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 47, 26178–22618 (2021).
Gao, J., Li, Q., Zhang, S. & Li, J-F. Lead-free antiferroelectric AgNbO3: phase transitions and structure engineering for dielectric energy storage applications. J. Appl. Phys. 128, 070903–070908 (2020).
Yoneda, Y., Yoshii, K. & Kohara, S. Structural investigations of AgNbO3 phases using high-energy X-ray diffraction. Trans. Mat. Res. Soc. Japan. 37[1], 73–76 (2012).
Ai, J., Chen, X., Luo, L., Zheng, R. & Yu, L. Novel transparent Eu and hf co-doped AgNbO3 antiferroelectric ceramic with high-quality energy-storage performance. Ceram. Int. 47, 26178–26184 (2021).
Kirana, K., Gangadhar, V. & Prasad, G. Synthesis and characterization of multi functional NaNbO3-KNbO3 mixed ceramics. Mater. Today Proc. 11, 971–979 (2019).
Abdel–Khalek, E. K., El–Naser, A. A., Nabhan, E. & Gaafar, M. S. Abd El–Aal, the enhancement of the optical, magnetic, and ferroelectric properties of BaTiO3–δ by doping with SrFeO3–δ. Appl. Phys. A. 131, 338 (2025).
Xu, C. et al. La/Mn Co doped AgNbO3 lead-free antiferroelectric ceramics with large energy density and power density. CS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 12, 16151–16159 (2018).
Kania, A. & Miga, S. Preparation and dielectric properties of Ag1 – xLixNbO3 (ALN) solid solutions ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 86, 128–133 (2001).
Fu, D., Endo, M., Taniguchi, H., Taniyama, T. & Itoh, M. AgNbO3: A lead-free material with large polarization and electromechanical response. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 252907 (2007).
Yan, Z. et al. Silver niobate based lead-free ceramics with high energy storage density. J. Mater. Chem. A. 7, 10702–10711 (2019).
Nautiyal, O. P., Bhatt, S. C., Pant, R. P. & Semwal, B. S. Dielectric properties of silver sodium niobate mixed ceramic system. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 48, 357–362 (2010).
Cheng, H. et al. Sol-gel auto-combustion synthesis of KxNa1–xNbO3 nanopowders and ceramics: dielectric and piezoelectric properties. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. 28, 1801–1807 (2018).
Luo, L. et al. Influence of conductivity on Raman scattering intensity in Li-modified AgNbO3 crystals. Ferroelectrics. 470, 212–220 (2014).
Zhao, D., Chen, Z., Li, B., Feng, S. & Luo, N. Growth, Structure, and electrical properties of AgNbO3 antiferroelectric single crystal. Crystals 14(3), 235 (2024).
Muduli, R. et al. Dielectric, ferroelectric and impedance spectroscopic studies in TiO2-doped AgNbO3 ceramic. J. Alloys Compd. 664, 715–725 (2016).
Acknowledgements
This article is derived from a research grant funded by the Research, Development, and Innovation Authority (RDIA) - Kingdom of Saudi Arabia - with grant number (20005-IUM-2023-R-2-1-EI-).
Funding
Research, Development, and Innovation Authority (RDIA) - Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Abdullah Almohammedi: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft. E. K. Abdel-Khalek: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft. Yasser A. M. Ismail: Investigation, Methodology, Writing-original draft.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
All authors of this paper consent for publishing manuscript, tables, and figures in this journal.
Consent to participate
I, E. K. Abdel-Khalek, on behalf of all authors, hereby declare that we participated in this manuscript.
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Almohammedi, A., Abdel-Khalek, E.K. & Ismail, Y.A.M. Study the influence of the precipitation of metallic Ag on the phase transitions in AgNbO3−δ perovskite. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37405-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37405-1