Abstract
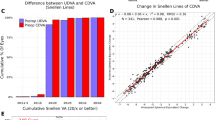
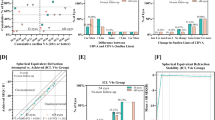
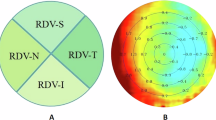
This study aimed to investigate the relationship between myopia and retinal vascular oxygen saturation, after accounting for optical factors and individual variations. This was a prospective, observational, single-center study. Adults with anisometropia were included. All the participants underwent femtosecond-assisted laser in situ keratomileusis (FS-LASIK), and before and after the surgery, all the patients underwent the examination of visual acuity, intraocular pressure (IOP), spherical equivalent (SE), average keratometry (K), central corneal thickness, and retinal oximeter. A total of 196 adult patients with myopic anisometropia were enrolled. The SE of the less myopic eyes before surgery was − 3.89 ± 3.24 D, which was significantly higher than that of the more myopic eyes − 6.75 ± 3.10 D (p < 0.001). The retinal arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) of the less myopic eyes was 94.08 ± 1.61%, which was significantly higher than that of the more myopic eyes 93.36 ± 1.74% (p = 0.003). After FS-LASIK, the SaO2 of the less myopic eyes (93.29 ± 1.72%) remained significantly higher than that of the more myopic eyes (92.76 ± 1.83%) (p = 0.038). In the multivariate regression analysis, the postoperative SaO2 was still significantly negatively correlated with axial length (AL) (B = -0.252, P = 0.009). After excluding optical factors and individual variations, SaO2 remains negatively correlated with AL. Myopia exerts an optical magnification effect on SaO2.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AL:
-
Axial length
- AVD:
-
Retinal arteriovenous oxygen saturation difference
- CCT:
-
Central corneal thickness
- CDVA:
-
Corrected distance visual acuity
- FS-LASIK:
-
Femtosecond-assisted laser in situ keratomileusis
- ICL:
-
Implantable collamer lens
- IOP:
-
Intraocular pressure
- K:
-
Average keratometry
- SaO2 :
-
Retinal arterial oxygen saturation
- SE:
-
Spherical equivalent
- SvO2 :
-
Retinal venous oxygen saturation
- UCVA:
-
Uncorrected distance visual acuity
References
Liu, X. et al. Retinal oxygen saturation in 1461 healthy children aged 7–19 and its associated factors. Acta Ophthalmol. 97(3), 287–295 (2019).
Lim, L. S., Lim, X. H. & Tan, L. Retinal vascular oxygen saturation and its variation with refractive error and axial length. Transl Vis. Sci. Technol. 8(4), 22 (2019).
Liu, X. et al. Retinal oxygen saturation in Chinese adolescents. Acta Ophthalmol. 95(1), e54–e61 (2017).
Ge, S., Yang, L., Zhou, Y., Li, C. & Zhang, J. Retinal vascular oxygen saturation in adults with anisometropia. Transl Vis. Sci. Technol. 12(4), 14 (2023).
Ge, S., Zhou, Y., Li, C. & Zhang, M. Retinal vascular oxygen saturation in a sample of Chinese myopic adults. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 64(14), 13 (2023).
Ma, X., Ge, S., Yang, X. & Zhou, Y. Changes in retinal oxygen saturation 1 month after femtosecond LASIK treatment in Chinese adults with myopia. Ophthalmol. Ther. (2025).
Chen, P. et al. Assessing oxygen saturation in retinal vessels in high myopia patients pre- and post-implantable collamer lens implantation surgery. Acta Ophthalmol. 95(6), 576–582 (2017).
Bennett, A. G., Rudnicka, A. R. & Edgar, D. F. Improvements on Littmann’s method of determining the size of retinal features by fundus photography. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. = Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fur klinische und experimentelle Ophthalmologie. 232(6), 361–367 (1994).
Wang, P. et al. Transient alteration of retinal microvasculature after refractive surgery. Ophthalmic Res. 64(1), 128–138 (2021).
Fan, H. et al. Reduced macular vascular density in myopic eyes. Chin. Med. J. 130(4), 445–451 (2017).
Grudzińska, E. M., Zaborski, D. & Modrzejewska, M. Correlation between retrobulbar blood flow parameters and retinal nerve fiber, ganglion cell and inner plexus layer thickness in myopia. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 32(1), 643–650 (2022).
Luu, C. D., Lau, A. M. & Lee, S. Y. Multifocal electroretinogram in adults and children with myopia. Arch. Ophthalmol. 124(3), 328–3 34 (2006).
Man, R. E. K. et al. Axial length, retinal function, and oxygen consumption: A potential mechanism for a lower risk of diabetic retinopathy in longer eyes. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 54(12), 7691–7698 (2013).
Zheng, Q. et al. Retinal vessel oxygen saturation and vessel diameter in high myopia. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 35(5), 562–569 (2015).
Liu, X. et al. Choroidal thickness and choriocapillaris vascular density in myopic anisometropia. Eye Vis. (Lond). 8(1), 48 (2021).
Xiao, G. et al. Relationship between axial length and retinal oxygen dynamics in adults with myopia. Transl Vis. Sci. Technol. 14(1), 18 (2025).
Lim, L. S. et al. Influence of refractive error and axial length on retinal vessel geometric characteristics. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 52(2), 669–678 (2011).
Palkovits, S. et al. Retinal oxygen metabolism during normoxia and hyperoxia in healthy subjects. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 55(8), 4707–4713 (2014).
Waizel, M., Türksever, C. & Todorova, M. G. Normative values of retinal vessel oximetry in healthy children against adults. Acta Ophthalmol. 96(7), e828–e34 (2018).
Iester, M., Mete, M., Figus, M. & Frezzotti, P. Incorporating corneal pachymetry into the management of glaucoma. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 35(9), 1623–1628 (2009).
Funding
No funding or sponsorship was received for this study or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shanshan Ge, Xiaoqi Ma, Xiuli Zhou and Yuehua Zhou made substantial contributions to the conception, design of the work, the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data. Shanshan Ge drafted the work. Yuehua Zhou revised it critically for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Medical Ethics Committee of the Ineye Hospital of Chengdu University of TCM approved this study, and the number was 2021yh-022. The study was in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, S., Ma, X., Zhou, X. et al. Changes in retinal oxygen saturation before and after femtosecond LASIK in adult myopic individuals with anisometropia. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37955-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37955-4