Abstract
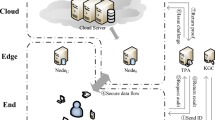
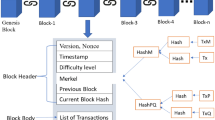
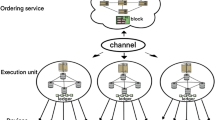
In the rapidly evolving landscape of wireless communication, the traditional model of data exchange predominantly relies on a centralized infrastructure, where all communications, even between nearby devices, are routed through a base station (BS) and potentially the core network. Device-to-device (D2D) communication emerges as a transformative paradigm that challenges this conventional model. The concept of D2D communication has gained considerable traction, especially with the advent of 4G LTE and its crucial role in 5G and beyond. D2D aims to unlock numerous benefits, including improved spectral efficiency, increased throughput, reduced latency, enhanced energy efficiency, and better network offloading. In this paper, we focus on secure D2D communication using D2D-ECDH key exchange protocol with blockchain smart contracts along with blockchain Verkle tree data structure. This approach helps to improve secure communication between IoT devices and avoids Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks, replay attacks, and central points of failure. The Verkle tree approach provides a smaller proof size to verify the root commitment value compared to the traditional Merkle tree data structure. The simulation has been executed in both Python and Solidity coding. Python has executed in VS Code generator, and Solidity code has executed in Remix IDE, Ethereum network V0.65.0. The Remix IDE was developed in Ganache V2.7.1 for blockchain smart contracts. Compared to the traditional Merkle tree approach, the Verkle tree provides less proof size up to 33 times.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the results and findings of this work/study can be provided by corresponding author upon responsible request.
References
Jayakumar, S. & Nandakumar, S. A review on resource allocation techniques in D2D communication for 5G and B5G technology. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-020-00962-x (2020).
Chandrakar, P., Amin, R. & Bagga, R. Blockchain based security protocol for device to device secure communication in internet of things networks. Secur. Priv. https://doi.org/10.1002/spy2.267 (2023).
Sakho, S., Jianbiao, Z., Essaf, F. & Blockchain Perspectives and issues. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-190449 (2019).
IBM. What are smart contracts on blockchain? https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/smart-contracts (2025).
Stute, M., Kohnhauser, F., Freisleben, B. & RESCUE A resilient and secure device-to-device communication framework for emergencies. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secure Comput. 19 (3). https://doi.org/10.1109/TDSC.2020.3036224 (2022).
Mahdi, W. H. & Taspinar, N. Bee system-based self configurable optimized resource allocation technique in device-to-device (D2D) communication networks. IEEE Access 12 (2024).
Lou, C., Cao, M. & Wu, R. A lightweight key generation scheme for secure device-to-device (D2D) communication. Wirel Commun. Mob. Comput. Article 6642605 https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6642605 (2021).
Lu, S. P., Lei, C. L. & Ho, C. Y. Distributed Ledger technology based architecture for decentralized device-to-device communication network. IEEE Access 10 https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3199880 (2022).
Gaba, G. S., Kumar, G. & Kim, T. H. Secure device-to-device communications for 5G enabled internet of things applications. Comput. Commun. 169, 114–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2021.01.010 (2021).
Shang, Z., Ma, M. & Li, X. A secure group-oriented device-to-device authentication protocol for 5G wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 19 (11). https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2020.3007702 (2020).
Bouchaala, M., Ghazel, C. & Saidane, L. A. Enhancing security and efficiency in cloud computing authentication and key agreement scheme based on smart card. J. Supercomput. 78, 497–522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-03857-7 (2022).
Ryu, J., Oh, J. & Kwon, D. Secure ECC-based three-factor mutual authentication protocol for Telecare medical information system. IEEE Access 10 https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3145959 (2022).
Das, A. K., Yannam, A. R. & Rodrigues, J. J. P. C. Provably secure ECC-based device access control and key agreement protocol for IoT environment. IEEE Access 7 https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2912998 (2019).
Vivekanandan, M. BIDAPSCA5G: blockchain based IoT device to device authentication protocol for smart City applications using 5G technology. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 14, 403–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-020-00963-w (2021).
Vishwakarma, L. & Das, D. SCAB-IoTA: secure communication and authentication for IoT applications using blockchain. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 154, 94–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2021.04.003 (2021).
Kuszmaul, J. & Verkle trees. https://math.mit.edu/research/highschool/primes/materials/2018/Kuszmaul.pdf (2019).
Iavich, M. & Kapalova, N. Asymmetric post-quantum digital signature scheme with k-ary verkle trees. Symmetry 17, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17030437 (2025).
Iavich, M., Kuchukhidze, T. & Bocu, R. A post-quantum digital signature using verkle trees and lattices. Symmetry 15, 2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15122165 (2023).
Iavich, M., Kuchukhidze, T. & Okhrimenko, T. Verkle tree-based post-quantum digital signature scheme using stateless updatable vector commitment. In: Proc. CPITS-2023-II, Kyiv, Ukraine (2023).
Vimitha, R., Lakshmi, V., Kumar, G. K. & VADIA Verkle tree-based approach for dealing data integrity attacks in opportunistic mobile social networks. J. Wirel. Mob. Netw. Ubiquitous Comput. Dependable Appl. 15 (1), 154–171. https://doi.org/10.58346/JOWUA.2024.I1.011 (2024).
Guo, Z., Gao, Z. & Liu, Q. Verkle-accumulator-based stateless transaction validation (VA-STV) scheme for the blockchain-based IoT network. IEEE Internet Things J. 11 (1). https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2023.3287210 (2024).
Kate, A., Zaverucha, G. M. & Goldberg, I. Constant-size commitments to polynomials and their applications. In: ASIACRYPT 2010, LNCS 6477 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-17373-8_11 (2010).
Shahidinejad, A., Abawajy, J. & Huda, S. Highly-Secure yet efficient Blockchain-Based CRL-Free key management protocol for IoT-Enabled smart grid environments. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 19, 6738–6750. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2024.3423724 (2024).
Shahidinejad, A. & Abawajy, J. H. Anonymous Blockchain-Assisted authentication protocols for secure Cross-Domain IoD communications. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 11 (3), 2661–2674. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSE.2023.3347594 (2024).
Shahidinejad, A. & Abawajy, J. Efficient provably secure authentication protocol for multidomain IIoT using a combined Off-Chain and On-Chain approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 11 (9), 15241–15251. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2023.3347677 (2024).
Ali Shahidinejad and Jemal Abawajy. An all-inclusive taxonomy and critical review of blockchain-assisted authentication and session key generation protocols for IoT. ACM Comput. Surv. 56, 38 https://doi.org/10.1145/3645087 (2024).
Singh, A. K., Nayyar, A. & Garg, A. A secure elliptic curve based anonymous authentication and key establishment mechanism for IoT and cloud. Multimed Tools Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-14140-z (2023).
Merkle, R. A certified digital signature. In: CRYPTO ’89, LNCS 435 https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-34805-0_21 (1990).
Ugbedeojo, M. et al. RSA and elliptic curve encryption system: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Inf. Secur. Priv. 18 (1). https://doi.org/10.4018/IJISP.340728 (2024).
Funding
Open access funding provided by Vellore Institute of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Simbu A: Writing the original draft, figures, software, methodology, investigation, validation, formal analysis, and conceptualization. Nandakumar S* and Saravanan K: Writing—review and editing the manuscripts, validation, visualization, supervision, investigation, conceptualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Simbu, A., Nandakumar, S. & Saravanan, K. Blockchain-driven smart contract with key exchange protocol for secure device-to-device communication using verkle tree K-ary structures. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-38035-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-38035-3