Abstract
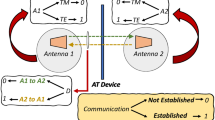
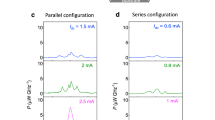
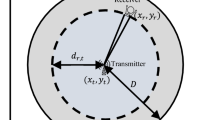
This study focuses on identifying an optimised synchronisation word based on multiple practical criteria for wireless internet-of-things systems, where reliable and energy-efficient synchronisation is essential to extend battery life by reducing unnecessary receiver activations (wake-ups) and false detections. To address the limitations of purely theoretical designs, a weighted multi-criteria evaluation framework is presented specifically tailored for resource-constrained receivers (e.g., IQRF). A mathematical receiver model utilising a correlation detector operating in additive white Gaussian noise is formulated, and the effects of synchronisation-word selection on detectability and the rate of false detections are analytically determined for both fixed alignment and sliding-window search methods. The methodology is augmented by laboratory measurements conducted on a pair of parallel Texas Instruments receivers. The resulting data are compared with theoretical expectations, and both agreements and discrepancies are analysed in terms of their underlying causes and system-level implications. The results yield practical design recommendations for low-power wireless internet-of-things devices, including recommendations on bit balance, suppression of aperiodic autocorrelation sidelobes, robustness to cyclic shifts, and diminished cross-correlation with recurring traffic patterns, demonstrating that the proposed framework identifies synchronisation words that reduce false alarms by orders of magnitude compared to standard baselines.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset for and scripts used in this study is available at https://doi.org/10.21227/rn06-dw82
References
Bernier, C., Dehmas, F. & Deparis, N. Low-complexity lora frame synchronization for ultra-low-power software-defined radios. IEEE Trans. Commun. 68, 3140–3152. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCOMM.2020.2974464 (2020).
Ghanaatian, R., Afisiadis, O., Cotting, M. & Burg, A. Lora digital receiver analysis and implementation. In ICASSP 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 1498–1502, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2019.8683504 (2019).
Kang, J.-M., Lim, D.-W. & Kang, K.-M. On the lora modulation for IoT: Optimal preamble detection and its performance analysis. IEEE Internet Things J. 9, 4973–4986. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2021.3108139 (2022).
Recayte, E. & Munari, A. On the performance of correlation-based packet detection techniques. Phys. Commun. 59, 102098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phycom.2023.102098 (2023).
Huang, Y., Yuan, L. & Gong, W. Research on IEEE 802.11 OFDM packet detection algorithms for household wireless sensor communication. Appl. Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12147232 (2022).
Savaux, V., Delacourt, C. & Savelli, P. On time-frequency synchronization in lora system: From analysis to near-optimal algorithm. IEEE Internet Things J. 9, 10200–10211. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2021.3120789 (2022).
Demeslay, C., Rostaing, P. & Gautier, R. Simple and efficient lora receiver scheme for multipath channel. IEEE Internet Things J. 9, 15771–15785. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2022.3151257 (2022).
Pham, C. & Ehsan, M. Dense deployment of lora networks: Expectations and limits of channel activity detection and capture effect for radio channel access. Sensors 21, 1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21030825 (2021).
Cheon, J., Hwang, H., Kim, D. & Jung, Y. IEEE 802.15.4 ZigBee-based time-of-arrival estimation for wireless sensor networks. Sensors 16, 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16020203 (2016).
Tiemann, J., Friedrich, J. & Wietfeld, C. Experimental evaluation of IEEE 802.15.4z UWB ranging performance under interference. Sensors 22, 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041643 (2022).
Afisiadis, O., Li, S., Tapparel, J., Burg, A. & Balatsoukas-Stimming, A. On the advantage of coherent lora detection in the presence of interference. IEEE Internet Things J. 8, 11581–11593. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2021.3058792 (2021).
Chiani, M. & Elzanaty, A. On the lora modulation for IoT: Waveform properties and spectral analysis. IEEE Internet Things J. 6, 8463–8470. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2019.2919151 (2019).
Song, J., Babu, P. & Palomar, D. P. Sequence design to minimize the weighted integrated and peak sidelobe levels. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64, 2051–2064. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2015.2510982 (2016).
Kerahroodi, M. A., Aubry, A., De Maio, A., Naghsh, M. M. & Modarres-Hashemi, M. A coordinate-descent framework to design low PSL/ISL sequences. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 65, 5942–5956. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2017.2723354 (2017).
Lin, R., Soltanalian, M., Tang, B. & Li, J. Efficient design of binary sequences with low autocorrelation sidelobes. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 67, 6397–6410. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2019.2954525 (2019).
Dimitrov, M., Baitcheva, T. & Nikolov, N. Efficient generation of low autocorrelation binary sequences. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 27, 341–345. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2020.2972127 (2020).
Brest, J. & Bošković, B. Low autocorrelation binary sequences: Best-known peak sidelobe level values. IEEE Access 9, 67713–67723. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3077541 (2021).
Bişkin, O. T. & Akay, O. Frequency domain sequence design algorithm minimising weighted integrated sidelobe level. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 13, 464–472. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5321 (2019).
Bişkin, O. T. & Akay, O. Designing radar transmit sequences satisfying simultaneous temporal integrated sidelobe level and spectral stopband constraints. Digital Signal Process. 107, 102867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2020.102867 (2020).
Bu, Y. et al. Constant modulus sequence set design with low weighted integrated sidelobe level in spectrally crowded environments. Sci. China Inf. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-020-3249-1 (2022).
Li, Y. & Vorobyov, S. A. Fast algorithms for designing unimodular waveform(s) with good correlation properties. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 66, 1197–1212. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2017.2787104 (2018).
Zhen, L. et al. Random access preamble design and detection for mobile satellite communication systems. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 36, 280–291. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2018.2804138 (2018).
Zhang, W., Sun, R. & Minn, H. Algorithm and performance analysis for frame detection based on matched filtering. IEEE Access 8, 40559–40572. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2975266 (2020).
Diskin, T., Beer, Y., Okun, U. & Wiesel, A. CFARnet: Deep learning for target detection with constant false alarm rate. Signal Process. 223, 109543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2024.109543 (2024).
Liu, G., Wang, J. & Ban, T. Frame detection based on cyclic autocorrelation and constant false alarm rate in burst communication systems. China Commun. 12, 55–63. https://doi.org/10.1109/CC.2015.7112044 (2015).
Zhou, H., Wang, J., Zhang, P. & Ban, T. A constant false alarm rate frame detector for satellite-based automatic identification system. Int. J. Satell. Commun. Network. 36, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/sat.1189 (2018).
Baddeley, M. et al. The impact of the physical layer on the performance of concurrent transmissions. In Proceedings—International Conference on Network Protocols, ICNP, vol. 2020-October, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNP49622.2020.9259407 (IEEE Computer Society, 2020).
Luo, X., Kalkanli, C., Zhou, H., Zhan, P. & Cohen, M. Secure ranging with IEEE 802.15.4z HRP UWB. In 2024 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), 2794–2811, https://doi.org/10.1109/SP54263.2024.00238 (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2024).
Grzegorz, D. & Vala, D. Knx-zigbee gateway. In M., J. (ed.) IFAC-PapersOnLine, vol. 58, 85–90, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2024.07.376 (Elsevier B.V., 2024).
Nilsson, D. Identifying bluetooth low energy devices via physical-layer hardware impairments (2022). Master Thesis, Uppsala University.
Barker, R. H. Group synchronizing of binary digital systems. In Jackson, W. (ed.) Communication Theory, 273–287 (Butterworth, London, 1953).
Golay, M. Complementary series. IRE Trans. Inf. Theory 7, 82–87. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIT.1961.1057620 (1961).
Duggal, G., Vishwakarma, S., Mishra, K. V. & Ram, S. S. Doppler-resilient 802.11ad-based ultrashort range automotive joint radar-communications system. IEEE Trans. Aerospace Electron. Syst. 56, 4035–4048. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAES.2020.2990393 (2020).
Golomb, S. W. Shift Register Sequences (Aegean Park Press, Laguna Hills, 1982).
Sarwate, D. V. & Pursley, M. B. Crosscorrelation properties of pseudorandom and related sequences. Proc. IEEE 68, 593–619. https://doi.org/10.1109/PROC.1980.11697 (1980).
Sklar, B. & Kumar Ray, P. Digital Communications: Fundamentals and Applications, 2 edn. (Pearson, Dorling Kindersley, India, 2014)
Proakis, J. G. & Manolakis, D. K. Digital Signal Processing: Principles, Algorithms, and Applications, 4 edn. (Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, 2006)
Mengali, U. & D’Andrea, A. N. Synchronization Techniques for Digital Receivers (Springer, New York, 1997).
Funding
The research was co-funded with the financial support of the European Union under the REFRESH - Research Excellence For REgion Sustainability and High-tech Industries project number CZ.10.03.01/00/22_003/0000048 via the European Just Transition Fund, next by the project TAČR FW10010287 “KITR - Comprehensive Transceiver Module Innovation for Wireless Mesh Networks and Global Competitiveness” and next by the project of the Ministry of Education of the Czech Republic under project SP2026/025, “Development of Algorithms and Systems for Control, Measurement and Safety Applications XII” of Student Grant System, VSB-TU Ostrava.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.V., M.S., and R.H. conceived and designed the experiments. R.H. and J.V. performed the experiments. M.S. analysed the data. R.H. contributed materials and analytical tools. M.S. processed the state of the art. M.S. and M.P. wrote the paper. R.H. and M.P. supervised the entire research and ensured the publication of the scientific article. The manuscript was drafted by M.S. and J.V. and reviewed and edited by all co-authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Skula, M., Pies, M., Hajovsky, R. et al. Multi-criteria selection of a synchronisation word for low-power IoT receivers based on the IQRF standard. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-38142-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-38142-1