Abstract
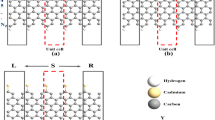
The variation in the properties of MgO Nanoribbons towards Arsenic (As) atoms is discussed in the current work. To evaluate the MgONRs behavior towards the As atoms, the first principles approach within the context of density functional theory is deployed to evaluate the electronic and transport characteristics of MgONRs. Results revealed that As-termination is found to improve the stability of the MgONRs compared to hydrogenated MgONRs (H–MgO–H). The electronic characteristics of MgONRs are significantly altered with As passivation. Further, the current–voltage (I–V) characteristics reveal a significantly enhanced current conductivity for the As-terminated MgONRs (As–MgO–As). This determines their transport characteristics are significantly enahnced with As termination. Further, the local device density of states showcase that the carrier transmission majorly occurs through the edges. From the acquired results, it can be concluded that MgONRs can be efficiently utilized as an effective material for the future nanoelectronic applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Zeng, S., Liu, C. & Zhou, P. Transistor engineering based on 2D materials in the post-silicon era. Nat. Rev. Electr. Eng. 1, 335–348 (2024).
Liu, Y. et al. Promises and prospects of two-dimensional transistors. Nature 591, 43–53 (2021).
Mir, S. H., Yadav, V. K. & Singh, J. K. Recent advances in the carrier mobility of two-dimensional materials: A theoretical perspective. ACS Omega 5, 14203–14211 (2020).
Shanmugam, V. et al. A review of the synthesis, properties, and applications of 2D materials. Part. Part. Syst. Character. 39, 2200031 (2022).
Zhang, Y. et al. Direct observation of the transition from indirect to direct bandgap in atomically thin epitaxial MoSe\(_2\). Nat. Nanotechnol. 9, 111–115 (2014).
Li, W., Yu, C., Tan, X., Wang, Z. & Qiu, J. Electric-field-triggered graphene production: From fundamental energy applications to perspectives. Acc. Mater. Res. 3, 175–186. https://doi.org/10.1021/accountsmr.1c00211 (2022).
Glavin, N. R. et al. Emerging applications of elemental 2D materials. Adv. Mater. 32, 1904302 (2020).
Novoselov, K. S. et al. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306, 666–669 (2004).
Lee, C., Wei, X., Kysar, J. W. & Hone, J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 321, 385–388 (2008).
Marmolejo-Tejada, J. M. & Velasco-Medina, J. Review on graphene nanoribbon devices for logic applications. Microelectron. J. 48, 18–38 (2016).
Nakada, K., Fujita, M., Dresselhaus, G. & Dresselhaus, M. S. Edge state in graphene ribbons: Nanometer size effect and edge shape dependence. Phys. Rev. B. 54, 17954 (1996).
Tian, C., Miao, W., Zhao, L. & Wang, J. Graphene nanoribbons: Current status and challenges as quasi-one-dimensional nanomaterials. Rev. Phys. 10, 100082 (2023).
Houtsma, R. K., de la Rie, J. & Stöhr, M. Atomically precise graphene nanoribbons: Interplay of structural and electronic properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 50, 6541–6568 (2021).
Ezawa, M. Peculiar width dependence of the electronic properties of carbon nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 73, 045432 (2006).
Lou, S. et al. Graphene nanoribbons: Current status, challenges and opportunities. Quantum Front. 3, 3 (2024).
Yagmurcukardes, M., Peeters, F. M., Senger, R. T. & Sahin, H. Nanoribbons: From fundamentals to state-of-the-art applications. Appl. Phys. Rev. 3 (2016).
Coston, J. A., Fuller, C. C. & Davis, J. A. Pb\(^{2+}\) and Zn\(^{2+}\) adsorption by a natural aluminum-and iron-bearing surface coating on an aquifer sand. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 59, 3535–3547 (1995).
Agrawal, A. & Sahu, K. Kinetic and isotherm studies of cadmium adsorption on manganese nodule residue. J. Hazard. Mater. 137, 915–924 (2006).
Van Benschoten, J. E., Reed, B. E., Matsumoto, M. R. & McGarvey, P. Metal removal by soil washing for an iron oxide coated sandy soil. Water Environ. Res. 66, 168–174 (1994).
Wang, Y.-H., Lin, S.-H. & Juang, R.-S. Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions using various low-cost adsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 102, 291–302 (2003).
Krasovska, M. et al. ZnO-nanostructure-based electrochemical sensor: Effect of nanostructure morphology on the sensing of heavy metal ions. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 9, 2421–2431 (2018).
Asl, M. A., Benam, M. R., Shahri, R. P., Feyzi, A. & Kafi, F. Two-dimensional quantum confinement effects on thermoelectric properties of MgO monolayers: A first principle study. Micro Nanostruct. 163, 107134 (2022).
Yeganeh, M. & Kafi, F. Effects of strain on the electronic and optical properties of MgO (111) nanosheet. Optik 186, 395–404 (2019).
Sagadevan, S. et al. Effect of synthesis temperature on the morphologies, optical and electrical properties of MgO nanostructures. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 20, 2488–2494 (2020).
Liu, P., Abdala, P. M., Goubert, G., Willinger, M.-G. & Copéret, C. Ultrathin single crystalline MgO (111) nanosheets. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 3254–3260 (2021).
Nilius, N. et al. Electronic and electrostatic properties of polar oxide nanostructures: MgO (111) islands on Au (111). Phys. Rev. B. 86, 205410 (2012).
Kiguchi, M., Entani, S., Saiki, K., Goto, T. & Koma, A. Atomic and electronic structure of an unreconstructed polar MgO (111) thin film on Ag (111). Phys. Rev. B 68, 115402 (2003).
Wu, P., Huang, M., Cheng, W. & Tang, F. First-principles study of B, C, N and F doped graphene-like MgO monolayer. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 81, 7–13 (2016).
Akhtar, A., Pilevarshahri, R. & Benam, M. R. Investigating and comparison of electronic and optical properties of MgO nanosheet in (100) and (111) structural directions based on the density functional theory. Phys. B Condens. Matter 502, 61–67 (2016).
Goniakowski, J., Giordano, L. & Noguera, C. Polarity compensation in low-dimensional oxide nanostructures: The case of metal-supported MgO nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. B 87, 035405 (2013).
Krishna, M. S., Singh, S. & Kaushik, B. K. Edge tailored MgO nanoribbon for negative differential resistance/nanointerconnect applications. Comput. Mater. Sci. 231, 112570 (2024).
Krishna, M. S., Singh, S. & Kaushik, B. K. Copper passivated zigzag MgO nanoribbons for potential nanointerconnect applications. IEEE Open J. Nanotechnol. 3, 220–226 (2022).
Krishna, M. S., Singh, S. & Mohammed, M. K. Carcinogenic heavy metals detection based on ZnO nanoribbons. IEEE Sens. J. 22, 16929–16937 (2022).
Brandbyge, M., Mozos, J.-L., Ordejón, P., Taylor, J. & Stokbro, K. Density-functional method for nonequilibrium electron transport. Phys. Rev. B 65, 165401 (2002).
Inge, S. V., Jaiswal, N. K. & Kondekar, P. N. Realizing negative differential resistance/switching phenomena in zigzag GaN nanoribbons by edge fluorination: A DFT investigation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 4, 1700400 (2017).
Živković, A. et al. Changes in CO\(_2\) adsorption affinity related to Ni doping in FeS surfaces: A DFT-D3 study. Catalysts 11, 486 (2021).
Aasi, A., Javahersaz, R., Mehdi Aghaei, S. & Panchapakesan, B. Novel green phosphorene as a superior gas sensor for dissolved gas analysis in oil transformers: Using DFT method. Mol. Simul. 48, 541–550 (2022).
Krishna, M. S., Singh, S. & Kaushik, B. K. Planar quasi-1D nano-interconnects based on selective edge passivated ZnO nanoribbons. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 22, 597–605 (2023).
Wu, H.-C., Chen, H.-H. & Zhu, Y.-R. Effects of Al-impurity type on formation energy, crystal structure, electronic structure, and optical properties of ZnO by using density functional theory and the Hubbard-U method. Materials 9, 647 (2016).
Baboukani, A. R. et al. Defects investigation of bipolar exfoliated phosphorene nanosheets. Surf. Sci. 720, 122052 (2022).
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Vellore Institute of Technology Chennai for providing us the computational resources.
Funding
Open access funding provided by Vellore Institute of Technology- AP University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M. Sankush Krishna has done the computational analysis and manuscript drafting. K. Srinivas has contributed by result analysis and graphical plotting. Aruru Sai kumar contributed by literature review and images. Anil kumar nayak is involved in reviewing and editing of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Krishna, M.S., Kumar, A.S., Kankanala, S. et al. First principles investigation of arsenic functionalized MgO nanoribbons. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-39119-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-39119-w