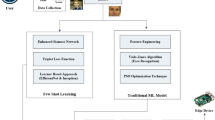
Abstract
This comprehensive study demonstrates an advanced machine learning framework for distinguishing identical twins using facial skin marks, achieving 96.62% cross-validation accuracy and 90.6% AUC score. The methodology incorporates four distinct hyperparameter optimization techniques (random search, Bayesian optimization, particle swarm optimization, and grid search), comprehensive statistical validation, and a robust preprocessing pipeline including PCA and SMOTE. Analysis of 74 twin pairs from 319 processed images using automated facial mark detection and multi-metric similarity assessment reveals spatial distribution patterns as the primary discriminating factor. The framework employs sophisticated feature engineering (32\(\rightarrow\)15\(\rightarrow\)6 dimensions) and achieves statistically significant performance (p < 0.001) with minimal overfitting. Random search optimization emerged as the optimal method, providing the best performance-efficiency trade-off with 90.6% AUC, 88.4% test accuracy, and the fastest execution time (31.8s). The system demonstrates production-ready computational efficiency and establishes a reliable foundation for forensic biometric applications with comprehensive statistical validation and deployment specifications. Figure 1 depicts the graphical abstract.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset used in this study, the ND-TWINS-2009-2010 database, is owned by a third party (the University of Notre Dame) and is subject to a specific license agreement. Therefore, the authors do not have the authority to share or distribute this data. Researchers interested in accessing the dataset must contact the original curators directly to obtain a license. Information on acquiring the dataset is available from the University of Notre Dame’s Computer Vision Research Laboratory (CVRL). Access to the ND-Twins-2009-2010 dataset requires a license agreement authorized by the university. The dataset can be requested through the following link: ND-Twins-2009-2010: [Online Access] - https://cvrl.nd.edu/projects/data/#nd-twins-2009-2010.
Abbreviations
- AAM:
-
Active appearance models
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- CNN:
-
Convolutional neural networks
- CV:
-
Cross-validation
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- FERET:
-
Facial recognition technology
- FPR:
-
False positive rate
- FRST:
-
Fast radial symmetry transform
- GLCM:
-
Gray level co-occurrence matrix
- Hog:
-
Histogram oriented of gradients
- LBP:
-
Local binary pattern
- LoG:
-
Laplacian-of-gaussian
- MBE:
-
Multi-biometric evaluation
- MRF:
-
Markov random field
- ND TWINS:
-
Notre dame-twins
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- PR:
-
Precision-recall
- PSO:
-
Particle swarm optimization
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- RNN:
-
Recurrent neural networks
- SIFT:
-
Scale invariant feature transform
- SMOTE:
-
Synthetic minority oversampling technique
- SMT:
-
Scars, marks and tattoos
- SURF:
-
Speeded up robust features
- ORB:
-
Oriented FAST and rotated BRIEF
- TAR:
-
True accept rate
- TPR:
-
True positive rate
- XGBoost:
-
eXtreme gradient boosting
References
Taskiran, M., Kahraman, N. & Erdem, C. E. Face recognition: Past, present, and future (a review). Digit. Signal Process. 106, 102809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2020.102809 (2020).
Kukharev, G. & Kaziyeva, N. Digital facial anthropometry: Application and implementation. Pattern Recognit. Image Anal. 30(3), 496–511 (2020).
Kasyanyuk, V. Monozygotic or dizygotic twins. Types of twins. https://www.dreamstime.comhttps://www.dreamstime.com/monozygotic-dizygotic-twins-types-image168628172
Jain, A. K., Prabhakar, S. & Pankanti, S. On the similarity of identical twin fingerprints. Pattern Recognit. 35(11), 2653–2663. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-3203(01)00218-7 (2002).
Sundaresan, V. & Shanthi, S. Monozygotic twin face recognition: An in-depth analysis and plausible improvements. Image Vision Comput. 116, 104331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2021.104331 (2021).
Rehkha, K. K. & Vinod, V. A literary survey on multimodal biometric identification of monozygotic twins. in Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, 385–398 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-8221-9_36
Thomas, N. S. E. S, B., Kizhakkethottam, J. J. & Kizhakkethottam, J. J. Analysis of effective biometric identification on monozygotic twins, In 2015 International Conference on Soft-Computing and Networks Security (ICSNS) (Coimbatore, India, Feb. 2015), https://doi.org/10.1109/icsns.2015.7292444.
Chijindu, A. T. & Chinagolum I. Machine learning-based digital recognition of identical twins to support global crime investigation. Int. J. Latest Technol. Eng. Manag. Appl. Sci. (IJLTEMAS), 7, 18–25 (2018).
Share, C., Williams, L. & Graham, J. Identical twins arrested following rare coin shop burglary, car chase, Orange County Register (Nov. 19, 2017). https://www.ocregister.com/2017/11/19/two-burglary-suspects-fleeing-police-on-55-freeway-are-caught-hiding-in-a-ditch/
Abubakar, S. Nigeria’s Boko Haram leader is dead, say rival militants, News, Jun. 07, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-57378493
Sundaresan, V. & Amala Shanthi, S. Monozygotic twin face recognition: An in-depth analysis and plausible improvements. Image Vision Comput. 116, 104331 (2021).
Zeinstra, C. G., Meuwly, D., Ruifrok, A. C. C., Veldhuis, R. N. J. & Spreeuwers, L. J. Forensic face recognition as a means to determine the strength of evidence: A survey. Forensic Sci. Rev. 30(1), 21–32 (2018).
Phillips, P. J. et al. Distinguishing identical twins by face recognition. In 2011 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG) (IEEE, Mar. 2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/fg.2011.5771395.
Klare, B., Paulino, A. A. & Jain, A. K. Analysis of facial features in identical twins. In 2011 International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB) (IEEE, Oct. 2011), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/ijcb.2011.6117548.
Bowyer, K. W. & Flynn, P. J. Biometric identification of identical twins: A survey. In IEEE 8th International Conference on Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS) (IEEE, Sep. 2016), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/btas.2016.7791176.
Sanil, G., Prakash, K., Prabhu, S., Nayak, V. C. & Sengupta, S. 2D-3D Facial image analysis for identification of facial features using machine learning algorithms with hyper-parameter optimization for forensics applications. IEEE Access 11, 82521–82538 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3298443
Sanil, G., Prakasha, K., Prabhu, S. & Nayak, V. Facial similarity measure for recognizing monozygotic twins utilizing 3D facial landmarks, efficient geodesic distance computation, and machine learning algorithms. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3439572.
Sanil, G., Prakash, K., Prabhu, S. & Nayak, V. C. Effectiveness of the use of golden ratio in identifying similar faces using ensemble learning. In Communications in Computer and Information Science, 62–80, (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-1166-8_6.
Mousavi, S., Charmi, M. & Hassanpoor, H. Recognition of identical twins based on the most distinctive region of the face: Human criteria and machine processing approaches. Multimedia Tools and Applications 80(10), 15765–15802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10360-3 (2021).
Sanil, G., Prakasha, K., Prabhu, S. & Nayak, V. C. Region-wise landmarks-based feature extraction employing SIFT, SURF, and ORB feature descriptors to recognize monozygotic twins from 2D/3D facial images. F1000Research. 14, 444. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.162911.1 (2025).
Sanil, G., Prakasha, K., Prabhu, S. & Nayak, V. C. Area-based face curve characteristic analysis to recognize multimodal 2D/3D monozygotic twins using Simpson’s rule and machine learning. Syst. Soft Comput., 23, 200267 (2025).
Sami, S. M., McCauley, J., Soleymani, S., Nasrabadi, N. M. & Dawson, J. Benchmarking human face similarity using identical twins. IET Biometrics 11(5), 459–484. https://doi.org/10.1049/bme2.12090 (2022).
Mousavi, S., Charmi, M. & Hassanpoor, H. A distinctive landmark-based face recognition system for identical twins by extracting novel weighted features. Comput. Electr. Eng. 94, 107326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2021.107326 (2021).
Nahar, K. M. O., Abul-Huda, B., Bataineh, A. Al. & Al-Khatib, R. M. Twins and similar faces recognition using geometric and photometric features with transfer learning. Int. J. Comput. Digit. Syst. 11(1), 129–139. https://doi.org/10.12785/ijcds/110110 (2022).
Rehkha, K. K. Differentiating monozygotic twins by facial features. Turkish J. Comput. Math. Educ. (TURCOMAT) 12(10), 1467–1476. https://doi.org/10.17762/turcomat.v12i10.4468 (2021).
Sudhakar, K., & Nithyanandam, P. Facial identification of twins based on fusion score method. J. Ambient Intell. Humanized Comput. 15(8), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03012-3 (2021).
Vengatesan, K., Kumar, A., Karuppuchamy, V., Shaktivel, R. & Singhal, A. Face recognition of identical twins based on support vector machine classifier. In 2019 Third International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) (I-SMAC), 577–580. https://doi.org/10.1109/I-SMAC47947.2019.9032548 (2019).
Nafees, M. & Uddin, J. A twin prediction method using facial recognition feature. In 2018 International Conference on Computer, Communication, Chemical, Material and Electronic Engineering (IC4ME2). https://doi.org/10.1109/ic4me2.2018.8465615
Afaneh, A., Noroozi, F. & Toygar, Ö. Recognition of identical twins using a fusion of various facial feature extractors. Eurasip J. Image Video Process. 2017(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13640-017-0231-0 (2017).
Monnappa, D. S. & Maheshappa, S. Twin-based face differentiation using facial marks. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Commun. Eng. 4(6), 302–306 (2015).
Guo, Y., Wang, H., Wang, L., Lei, Y., Liu, L., & Bennamoun, M. 3D face recognition: Two decades of progress and prospects. ACM Comput.Surv. 56(3), 54. https://doi.org/10.1145/3615863 (2024).
Jain, A. K. & Park, U. Facial marks: Soft biometric for face recognition. In ICIP’09: Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, vol. 2, 37–40 (Nov. 2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/icip.2009.5413921
Lee, J.-E., Jain, A. K. & Jin, R. Scars, marks and tattoos (SMT): Soft biometrics for suspect and victim identification. In Proc. 2008 Biometrics Symposium (Tampa, FL, USA, 2008), 1–8.
Prema, R. & Shanmugapriya, P. Facial marks are soft biometric for identification of identical twins, similar faces, and siblings in face recognition. Int. J. Sci. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. (IJSRSET) 5(1), 64–69 (2018).
Srinivas, N., Aggarwal, G., Flynn, P. J. & Bruegge, R. W. V. Analysis of facial marks to distinguish between identical twins. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 7(5), 1536–1550. https://doi.org/10.1109/tifs.2012.2206027 (2012).
Suresh, K. Feature extraction techniques for identical twins fraud detection using machine learning. International Research Journal of Modernization in Engineering Technology and Science 6(4), 5190–5198 (2024).
Zhang, L. Explainable AI for biometric twin differentiation: Interpretable deep learning with visual attention maps. IEEE Trans. Biometrics Behav. Identity Sci. 7(1), 45–58 (2025).
Ahmad, B., Usama, M., Lu, J., Xiao, W., Wan, J. & Yang, J. Deep convolutional neural network using triplet loss to distinguish the identical twins. In 2019 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps) (IEEE, 2019), 1–6.
Yuan, Y. & Bowyer, K.W. A siamese network to detect if two iris images are monozygotic. arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.09749 (2025).
Abed, M. H. & Sztahó, D. Effect of identical twins on deep speaker embeddings based forensic voice comparison. Int. J. Speech Technol. 27(2), 341–351 (2024).
Ferreira, F. R., do Couto, L. M., de Melo Baptista Domingues, G. Comparing the efficiency of YOLO-M for face recognition in images and videos degraded by compression artifacts. Evolv. Syst. 16(2), 70 (2025).
Negi, A., Kumar, K., Chauhan, P. & Rajput, R. S. Deep neural architecture for face mask detection on simulated masked face dataset against covid-19 pandemic. In 2021 International Conference on Computing, Communication, and Intelligent Systems (ICCCIS), 595–600 (Feb. 2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/icccis51004.2021.9397196
Negi, A., Chauhan, P., Kumar, K. & Rajput, R. S. Face mask detection classifier and model pruning with keras-surgeon. In 2020 5th IEEE International Conference on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering (ICRAIE) (Dec. 2020), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/icraie51050.2020.9358337
Negi, A. & Kumar, K. Face mask detection in real-time video stream using deep learning. Computat. Intell. Healthcare Inf. 7, 255–68 (2021).
Stefanik, R. ND-TWINS-2009-2010. 2013. [Online]. https://cvrl.nd.edu/projects/data/
Kittipongdaja, P. Skin-Problem-Detection-Multiple-Clean Dataset. [Online]. Available: https://universe.roboflow.com/parin-kittipongdaja-vwmn3/skin-problem-detection-multiple-clean Accessed: Jun. 18, 2025.
Fabian, P. et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2825–2830 (2011).
B. Jason, Hyperparameter optimization with random search and grid search. Machine Learning Mastery, 2020, [Online]. Available: https://machinelearningmastery.com/hyperparameter-optimization-with-random-search-and-grid-search/
N. V, A Hands-On discussion on hyperparameter optimization Techniques. Analytics Vidhya, Oct. 2021, [Online]. Available: https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2021/09/a-hands-on-discussion-on-hyperparameter-optimization-techniques/
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the University of Notre Dame, United States (UND), for sharing the ND-TWINS-2009–2010 Dataset.
Funding
Open access funding provided by Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal. The author(s) declare that no agency has funded this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mr. Khush Jay Brahmbhatt: Writing—Original draft preparation; Dr. Gangothri Sanil: Writing—Reviewing and Editing; Dr. Krishna Prakasha: Supervision; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study involved the analysis of a third-party, controlled-access dataset: the ND-TWINS-2009-2010 database, collected and curated by the University of Notre Dame (UND). The original data collection was conducted with ethical approval and informed consent from participants and/or their legal guardians, as detailed by the data source. Our research team’s use of the dataset was performed in strict accordance with a signed license agreement with UND, which governs data privacy and security protocols. This agreement is attached for the editor’s reference.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Brahmbhatt, K.J., Prakasha, K. & Sanil, G. Facial mark based biometric differentiation of identical twins using dynamic feature enhancement. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-39470-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-39470-y