Abstract
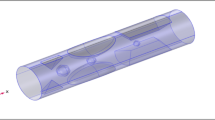
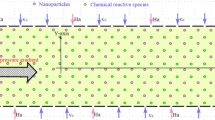
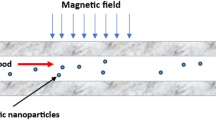
Magnetic drug targeting (MDT) offers a non-invasive and localized approach for improving therapeutic delivery in vascular diseases, but its efficiency is strongly affected by age-related hemodynamic changes. In this study, a computational framework was employed to compare MDT performance in young and old patient-specific aortic models reconstructed from clinical imaging. Blood was modeled using non-Newtonian Carreau, Power-law, and Casson-Papanastasiou rheologies, while nanoparticle motion was simulated under external magnetic fields ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 T. Across all rheological models, capture efficiency (CE) increased with particle size and magnetic field intensity. Importantly, older patients consistently exhibited slightly higher CE than younger patients, a trend driven by their reduced flow velocity, enlarged aortic lumen, and lower wall shear stress, which collectively prolonged nanoparticle residence time and reduced hydrodynamic drag opposing magnetic capture. For example, under a 1.5 T field using the Carreau model, CE reached 8.7% for 1000 nm particles in both young and old patients, but at intermediate intensities (0.5–1.25 T), older patients showed higher CE (e.g., 2.4% vs. 2.1% at 0.5 T, and 7.3% vs. 6.6% at 1.25 T). Newtonian rheology consistently over-predicted CE relative to non-Newtonian models. All applied magnetic field strengths remained within clinically acceptable safety thresholds, and field localization coincided with the target region of interest. These findings demonstrate that vascular aging enhances magnetophoretic drug capture under realistic hemodynamic conditions and underscore the need for age-aware optimization in patient-specific MDT strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets produced and evaluated throughout the present work are available from the corresponding author for reasonable requests. For ethical reasons and patient confidentiality, we cannot share individual-level medical imaging data publicly; thus, it is not available. Notwithstanding, processed simulation data along with the scripts to evaluate and support the findings of this study are available from the authors for reasonable requests.
References
Buja, L. M., Zhao, B., Vela, D., Segura, A. & Narula, N. Pathobiology of aortic aneurysms and dissections: synthesis of recent investigations and evolving insights. JACC: Adv. 4, 101682 (2025).
Ferrer, M., Altadill, F., Tabilo, J. & Barros, A. Impact of age-related arterial degeneration and inflammation on the presentation and etiopathogenesis of acute aortic syndrome. Eur. Heart Journal: Acute Cardiovasc. Care. 13, zuae036 (2024).
Alcorn, H. G., Wolfson, S. K. Jr, Sutton-Tyrrell, K., Kuller, L. H. & O’Leary, D. Risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysms in older adults enrolled in the cardiovascular health study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 16, 963–970 (1996).
Maleszewski, J. J. Inflammatory ascending aortic disease: perspectives from pathology. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 149, S176–S183 (2015).
Czerny, M. et al. Current options and recommendations for the use of thoracic endovascular aortic repair in acute and chronic thoracic aortic disease: an expert consensus document of the European society for cardiology (ESC) working group of cardiovascular surgery, the ESC working group on aorta and peripheral vascular Diseases, the European association of percutaneous cardiovascular interventions (EAPCI) of the ESC and the European association for Cardio-Thoracic surgery (EACTS). Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 59, 65–73 (2021).
Organization, W. H. World health organization fact sheets on cardiovascular diseases. World Health Organ. Fact. Sheet N 317 (2015).
Ferreira, J. P. et al. World heart federation roadmap for heart failure. Global Heart. 14, 197–214 (2019).
Le Huu, A. et al. Endovascular therapy for patients with heritable thoracic aortic disease. Annals Cardiothorac. Surg. 11, 31 (2022).
Afilalo, J. et al. Addition of frailty and disability to cardiac surgery risk scores identifies elderly patients at high risk of mortality or major morbidity. Circulation: Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes. 5, 222–228 (2012).
Tu, L. et al. Targeted drug delivery systems for atherosclerosis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 23, 306 (2025).
Lübbe, A. S., Alexiou, C. & Bergemann, C. Clinical applications of magnetic drug targeting. J. Surg. Res. 95, 200–206 (2001).
Shirvalilou, S. et al. Development of a magnetic nano-graphene oxide carrier for improved glioma-targeted drug delivery and imaging: in vitro and in vivo evaluations. Chemico-Biol. Interact. 295, 97–108 (2018).
Xu, Z., Mousavi, T. & Ainslie, M. Numerical simulation of magnetic drug targeting for lung cancer therapy using a bulk superconducting magnet. Drug Deliv. 32, 2490836 (2025).
Hua, M. Y. et al. Magnetic-nanoparticle-modified Paclitaxel for targeted therapy for prostate cancer. Biomaterials 31, 7355–7363 (2010).
Issa, B., Qadri, S., Obaidat, I. M., Bowtell, R. W. & Haik, Y. PEG coating reduces NMR relaxivity of Mn0. 5Zn0. 5Gd0. 02Fe1. 98O4 hyperthermia nanoparticles. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 34, 1192–1198 (2011).
Furlani, E. & Ng, K. Analytical model of magnetic nanoparticle transport and capture in the microvasculature. Phys. Rev. E—Statistical Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 73, 061919 (2006).
Ardalan, A., Aminian, S., Seyfaee, A. & Gharehkhani, S. Effects of geometrical parameters on the capture efficiency of nanoparticles under the influence of the magnetic field in a stenosed vessel. Powder Technol. 380, 39–46 (2021).
Sodagar, H., Sodagar-Abardeh, J., Shakiba, A. & Niazmand, H. Numerical study of drug delivery through the 3D modeling of aortic arch in presence of a magnetic field. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 20, 787–802 (2021).
Barnsley, L. C., Carugo, D., Aron, M. & Stride, E. Understanding the dynamics of superparamagnetic particles under the influence of high field gradient arrays. Phys. Med. Biol. 62, 2333 (2017).
Hewlin, R. L. Jr & Tindall, J. M. Computational assessment of magnetic nanoparticle targeting efficiency in a simplified circle of Willis arterial model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 2545 (2023).
Hewlin, R. L. Jr, Smith, M. & Kizito, J. P. Computational assessment of unsteady flow effects on magnetic nanoparticle targeting efficiency in a magnetic stented carotid bifurcation artery. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 14, 694–712 (2023).
Alizadeh, A. et al. Numerical investigation of the injection angle of carrier nanoparticles under the effect of different magnetic fields. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 578, 170836 (2023).
Jalali, S., Jalali, S. & Barati, E. Pulsatile blood flow simulations of magnetic drug targeting (MDT) for drug particles dispersion through stenosis asymmetric and symmetric vessels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 590, 171649 (2024).
Sharma, B. K., Khanduri, U., Kumawat, C. & Duraihem, F. Z. Simulation of Magnetically Targeted Drug Delivery for Two-Phase Blood Flow in Stenotic Arteries Under Hall and Ion Influence. Advanced Theory and Simulations, e00208 (2025).
Hussain, M. A., Kar, S. & Puniyani, R. R. Relationship between power law coefficients and major blood constituents affecting the whole blood viscosity. J. Biosci. 24, 329–337 (1999).
Boyd, J., Buick, J. M. & Green, S. Analysis of the Casson and Carreau-Yasuda non-Newtonian blood models in steady and oscillatory flows using the lattice Boltzmann method. Physics Fluids 19, 93–103 (2007).
Aminian, S., Najafi, M., Saadat, H. & Ashjaee, M. Computational study of halbach-array-driven magnetic targeting for aortic tumor using Non-Newtonian blood flow models. Comput. Biol. Med. 195, 110580 (2025).
Papanastasiou, T. C. Flows of materials with yield. J. Rheol. 31, 385–404 (1987).
Könözsy, L. Z. & Multiphysics CFD modelling of incompressible flows at low and moderate Reynolds numbers. (2012).
Ranjbari, L., Zarei, K., Alizadeh, A., Hosseini, O. & Aminian, S. Three-dimensional investigation of capturing particle considering particle-RBCs interaction under the magnetic field produced by an Halbach array. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 79, 104046 (2023).
Tamboli, N. K. & Murallidharan, J. S. Numerical studies on magnetic driven targeted drug delivery in human vasculature. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 104, 111–145 (2024).
Turton, R. & Levenspiel, O. A short note on the drag correlation for spheres. Powder Technol. 47, 83–86 (1986).
Xia, Y. et al. Hemodynamic characteristics of dilated ascending aorta in patients with bicuspid aortic valve. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 20, 354 (2025).
Takeda, S., Mishima, F., Terazono, B., Izumi, Y. & Nishijima, S. Development of magnetic force-assisted gene transfer system using biopolymer-coated ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 7, 308–314 (2006).
Van Ooij, P. et al. Age-related changes in aortic 3D blood flow velocities and wall shear stress: implications for the identification of altered hemodynamics in patients with aortic valve disease. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 43, 1239–1249 (2016).
Pagoulatou, S. & Stergiopulos, N. Evolution of aortic pressure during normal ageing: A model-based study. PLoS One. 12, e0182173 (2017).
Bina, A., Siavashi, M. & Beigzadeh, B. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of magnetic drug delivery in carotid artery with Eulerian-Lagrangian method: injection point and magnetic field performance analysis. Journal Magnetism Magn. Materials, 628, 164–173 (2025).
Fanelli, C., Kaouri, K., Phillips, T. N., Myers, T. G. & Font, F. Magnetic nanodrug delivery in non-Newtonian blood flows. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 26, 74 (2022).
Yadeta, H. B. & Shaw, S. Unsteady fractional dispersion under controlled targeted drug elimination and non-Newtonian rheology. Nonlinear Dynamics, 113, 21181–21197 (2025).
Manshadi, M., Mohammadi, M. & Sanati-Nezhad, A. Investigation of non-Newtonian blood effects on magnetic drug delivery for chemotherapy applications in an artery vessel. Anal. Comput. Theor. Chem. Lett. 1, 8–14 (2018).
Bose, S., Datta, A., Ganguly, R. & Banerjee, M. Implant assisted magnetic drug targetting for non-Newtonian blood flow. (2023).
Lunnoo, T. & Puangmali, T. Capture efficiency of biocompatible magnetic nanoparticles in arterial flow: A computer simulation for magnetic drug targeting. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 10, 426 (2015).
Kenjereš, S. & Righolt, B. Simulations of magnetic capturing of drug carriers in the brain vascular system. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow. 35, 68–75 (2012).
Aryan, H., Beigzadeh, B. & Siavashi, M. Euler-Lagrange numerical simulation of improved magnetic drug delivery in a three-dimensional CT-based carotid artery bifurcation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 219, 106778 (2022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Seyed Majid Hosseini: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. Wala Almosawy: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing; Rasoul Karimi Takrami: Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources; Negar Abdi: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing; Saman Aminian: Conceptualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseini, S.B., Almosawy, W., Takrami, R.K. et al. Age-dependent efficiency of magnetic drug targeting in young and old patient-specific aortic models. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-39486-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-39486-4