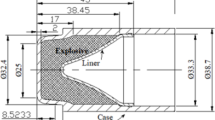
Abstract
An ideal jet that does not deviate from the charge axis is unrealistic due to manufacturing imperfections and jet fracture. At a large stand-off, the penetration depth of the jet particles that deviate from the charge axis is significantly reduced. The penetration process of a shaped charge jet into spaced plates with large spacings can be thought of as the residual jet passing through the front plate into the subsequent plate at various stand-off distances. Ideal jet theory significantly overestimates the penetration performance of shaped charge jets into spaced plates. This study systematically investigated the drift velocity and gap effects that govern shaped charge jet penetration through spaced plate configurations. A novel theoretical penetration model that incorporates non-ideal flow characteristics has been developed to quantitatively describe the interactions of a shaped charge jet with multiple spaced plates. Due to the combined effects of a high drift velocity and a large stand-off distance, it is impossible for low-velocity jet particles to traverse through spaced plates and reach the witness plate. Experimental results indicated that the tail of a shaped charge jet with a low velocity does not contribute to the penetration process and has no impact on the penetration depth of the witness plate. The non-ideal jet penetration model can accurately predict the velocity range of the shaped charge jet as it passes through spaced plates as well as the penetration depth of the residual jet on the witness plate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Sun, T. et al. Penetration-deflagration coupling damage performance of rod-like reactive shaped charge penetrator impacting thick steel plates. Def. Technol. (2025) (in press).
Żochowski, P. & Warchoł, R. Experimental and numerical study on the influence of shaped charge liner cavity filing on jet penetration characteristics in steel targets. Def. Technol. 23, 60–74 (2023).
Yin, X. X. et al. Mechnism and maximum interference model of functionally graded concrete with liquid composite aggregates subjected to shaped charge jet penetration. Constr. Build. Mater. 476, 141183 (2025).
Xu, H. Q. et al. Significantly improved penetration performance of intermetallic-compound-contained Ti–Al–Nb alloy shaped charge liner against reinforced concrete targets. Mater. Des. 221, 110997 (2022).
Gu, Y. C. et al. Formation characteristics and penetration performance of an underwater shaped charge jet. Ocean Eng. 258, 111695 (2022).
Cao, C. et al. Study on the formation characteristics of underwater hemispherical shaped charge jet and its penetration performance into concrete. Def. Technol. 47, 180–196 (2025).
Galante, E., Haddad, A. & Marques, N. Application of explosives in the oil industry. Int. J. Oil Gas Coal Eng. 1 (2), 16–22 (2013).
Bi, G. et al. Dynamic simulation of double-cased perforation in deepwater high temperature and high-pressure oil and gas wells. Pet. Sci. 21 (5), 3482–3495 (2024).
Fedorov, S. V. et al. Combined shaped-charge liners for explosion formation of aluminum particles with velocities up to 16km/s. Acta Astronaut. 190, 231–240 (2022).
Kolpakov, V. I. et al. Selection of shaped charge parameters for producing aluminum particle with velocities in the range of 2.5-16km/s. Def. Technol. 38, 126–135 (2024).
Fedorov, S. V. & Bolotina, I. A. & Merzlyakova, P. V. Producing compact copper elements in the velocity range of 5-9.5km/s using shaped charges with modified combined hemisphere-cylinder liners. J. Space Saf. Eng.
Held, M. Characterizing shaped charge performance by stand-off behavior. In 7th International Symposium on Ballistics, The Hague, The Netherlands, April 19–23, 331–339 (1983).
Liu, B. B. et al. Spaced armor effects on shaped charge jet penetration.Propellants Explosives Pyrotech. 40, 127–132 (2015).
Zu, X. D. et al. Theoretical study on equivalent target of ceramic composite armor. Propellants Explosives Pyrotech. 40, 576–582 (2015).
Segletes, S. B. Drift Velocity Computations for Shaped-Charge Jets. Ballistic Research Laboratory, Memorandum Report ARBRL-MR-003306 (1983).
Coppinger, M. J. & Uhlig, W. C. Simulating lateral drift of a shaped charge jet in ALEGRA. Int. J. Impact Eng. 136, 103415 (2020).
Chou, P. C. & Flis, W. J. Recent developments in shaped charge technology. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 11 (4), 99–114 (1986).
Hancock, S. L. An extension of the Umin model for cutoff of high precision jets. Int. J. Impact Eng. 26, 289–298 (2001).
Xiao, Q. Q. et al. Influence of drift velocity and distance between jet particles on the penetration depth of shaped charges. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 41, 76–83 (2016).
Xiao, Q. Q. et al. Shaped charge penetration into high- and ultrahigh-strength steel-fiber reactive powder concrete targets. Def. Technol. 16, 217–224 (2020).
Zheng, Z. M. Stability of jet produced by shaped charge. Explos. Shock Wave. 1, 6–17 (1981). (in Chinese).
Xiao, Q. Q. et al. Calculation of depth and crater diameter for the supersonic penetration of shaped charge jet into concrete. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 38(2), 224–231 (2013).
Xiao, Q. Q. et al. Shaped charge penetrator into soil-concrete double-layered target. Int. J. Impact Eng. 109, 302–310 (2017).
Xiao, Q. Q. et al. Penetration research of jacketed jet into concrete. Int. J. Impact Eng. 54, 246–253 (2013).
Funding
This work was supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Nanjing University of Science and Technology (CN) through Grant No. 30924010803 and the Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.12302471).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.X.; methodology, Q.X. and X.Z.; software, X.J.; validation, T.C. and Y.T.; formal analysis, Q.X. and X.Z.; investigation, T.C. and Y.C.; data curation, X.J.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.X.; writing—review and editing, Z.W., X.Z. and Z.H.; supervision, Z.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Q.Q., Zu, X.D., Huang, Z.X. et al. Non-ideal penetration of shaped charge jet into spaced plate based on drift velocity and gap effects. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-39841-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-39841-5