Abstract
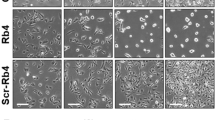
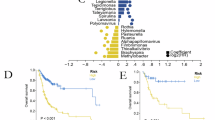
Tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC) is a common type of oral mucosal epithelial malignancy that can severely affect patient quality of life. Therefore, novel therapeutic strategies for TSCC are needed. This study aimed to investigate the role and mechanism of action of retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4) in TSCC progression and its effect on tumor-associated macrophages. To this end, TSCC cell lines with RBP4 overexpression and knockdown were constructed, and effects of RBP4 expression on the proliferation and invasive abilities of TSCC cells were verified using ex vivo experiments. Furthermore, a tumor cell-macrophage co-culture model was established to assess the effect of RBP4 on macrophage polarization. RBP4 overexpression reduced the phosphorylation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and inhibited tumor cell proliferation by regulating Snail levels; RBP4 inhibited TSCC cells from undergoing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. In addition, RBP4 promoted the activation of NF-κB signaling pathway, leading to macrophage polarization toward M1 type and inhibiting TSCC growth. We found for the first time that RBP4 affects the proliferation and migration of TSCC cells by inhibiting the activation of the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, and that RBP4 promotes the M1-type polarization of tumor-associated macrophages, which contributes to their antitumor effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available in the GEO repository, GSE301618. (The following secure token has been created to allow review of record GSE301618 while it remains in private status: onqrusgezjcflch.) Five OSCC microarrays (i.e., GSE13601, GSE52915, GSE34105, GSE31056 and GSE78060) were downloaded from the GEO database and are available at the following URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi? acc=GSE13601, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi? acc=GSE52915, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi? acc=GSE34105, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi? acc=GSE31056, and https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi? acc=GSE78060. The Hallmark gene set was obtained from the MSigDB database (https://www.gsea-msigdb.org/gsea/msigdb). TSCC as well as HNSCC data were downloaded from the TCGA database (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov).
References
Anneroth, G., Batsakis, J. & Luna, M. Review of the literature and a recommended system of malignancy grading in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Scand. J. Dent. Res. 95, 229–249. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0722.1987.tb01836.x (1987).
Lorkova, L. et al. Decreased concentrations of retinol-binding protein 4 in Sera of epithelial ovarian cancer patients: a potential biomarker identified by proteomics. Oncol. Rep. 27, 318–324. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2011.1513 (2012).
Kinoshita, M. & Miyata, M. Underexpression of mRNA in human hepatocellular carcinoma focusing on eight loci. Hepatology 36, 433–438. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhep.2002.34851 (2002).
Fei, W. et al. RBP4 and THBS2 are serum biomarkers for diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 8, 92254–92264. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21173 (2017).
Glaviano, A. et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies in cancer. Mol. Cancer. 22, 138. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-023-01827-6 (2023).
Fresno Vara, J. A. et al. PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 30, 193–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2003.07.007 (2004).
Zheng, L. et al. NQO1 drives glioblastoma cell aggressiveness through EMT induction via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR/Snail pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 63 https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2023.5558 (2023).
Vitale, I., Manic, G., Coussens, L. M., Kroemer, G. & Galluzzi, L. Macrophages and metabolism in the tumor microenvironment. Cell. Metab. 30, 36–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.06.001 (2019).
Christofides, A. et al. The complex role of tumor-infiltrating macrophages. Nat. Immunol. 23, 1148–1156. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-022-01267-2 (2022).
Gao, J., Liang, Y. & Wang, L. Shaping polarization of Tumor-Associated macrophages in cancer immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 13, 888713. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.888713 (2022).
Cornice, J. et al. NF-kappaB: governing macrophages in cancer. Genes (Basel). 15 https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15020197 (2024).
Rask, L. et al. The retinol-binding protein. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. Suppl. 154, 45–61 (1980).
Kanehisa, M., Furumichi, M., Sato, Y., Matsuura, Y. & Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG: biological systems database as a model of the real world. Nucleic Acids Res. 53, D672–D677. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkae909 (2025).
Hussein, A. A. et al. A review of the most promising biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognosis prediction of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer. 119, 724–736. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-018-0233-4 (2018).
Karatas, O. F., Oner, M., Abay, A. & Diyapoglu, A. MicroRNAs in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma: from pathogenesis to therapeutic implications. Oral Oncol. 67, 124–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.02.015 (2017).
Steinhoff, J. S., Lass, A. & Schupp, M. Biological functions of RBP4 and its relevance for human diseases. Front. Physiol. 12, 659977. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.659977 (2021).
Chen, Y. et al. Identification of host-immune response protein candidates in the Sera of human oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. PLoS One. 9, e109012. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0109012 (2014).
Noy, N., Li, L., Abola, M. V. & Berger, N. A. Is retinol binding protein 4 a link between adiposity and cancer? Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 23, 39–46. https://doi.org/10.1515/hmbci-2015-0019 (2015).
Yu, L., Wei, J. & Liu, P. Attacking the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway for targeted therapeutic treatment in human cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 85, 69–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.06.019 (2022).
Huang, Y., Hong, W. & Wei, X. The molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of EMT in tumor progression and metastasis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 15, 129. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-022-01347-8 (2022).
Saitoh, M. Transcriptional regulation of EMT transcription factors in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 97, 21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.10.001 (2023).
Wang, Y., Shi, J., Chai, K., Ying, X. & Zhou, B. P. The role of snail in EMT and tumorigenesis. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets. 13, 963–972. https://doi.org/10.2174/15680096113136660102 (2013).
Retracted. 14-3-3zeta promotes gliomas cells invasion by regulating snail through the PI3K/AKT signaling. Cancer Med. 12, 15761. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.6192 (2023).
Zarkesh, M. et al. Utilizing the Circulating tumor markers in diagnosis and management of medullary thyroid cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 229, 153694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2021.153694 (2022).
Cassetta, L. & Pollard, J. W. Targeting macrophages: therapeutic approaches in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 17, 887–904. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2018.169 (2018).
Li, Y. et al. Qing-Xue-Xiao-Zhi formula attenuates atherosclerosis by inhibiting macrophage lipid accumulation and inflammatory response via TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB pathway regulation. Phytomedicine 93, 153812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153812 (2021).
Gu, M. & Pang, Z. Luteolin inhibits inflammation and M1 macrophage polarization in the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced acute pneumonia through suppressing EGFR/PI3K/AKT/NF-kappaB and EGFR/ERK/AP-1 signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 141, 156663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156663 (2025).
Acknowledgements
Our thanks should go to Editage [www.editage.cn] for editing the English language.
Funding
The present study was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 8167110215).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.Y. wrote the main manuscript text and prepared figures. N.M. performed manuscript editing and ethical review. Xf.W. provided funding support. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Y., Miao, N. & Wang, X. RBP4 interferes with tongue squamous cell carcinoma progression by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and promoting macrophage M1-type polarization. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-39915-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-39915-4