Abstract
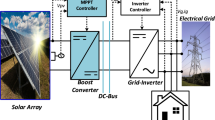
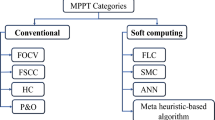
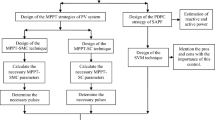
This paper introduces an improved current-sensorless maximum power point tracking (MPPT) approach, coupled with a battery charging unit, specifically designed for single-phase standalone photovoltaic (PV) power systems. An interleaved hybrid DC-DC boost converter with high voltage gain, previously developed by the authors, is used to boost the low and non-linear voltage output of the PV array to the usable DC grid voltage level. Since the energy yield of PV systems is highly sensitive to variations in solar irradiance, fast and accurate tracking of the maximum power point (MPP) is essential. Unlike conventional MPPT techniques that rely on both voltage and current measurements, the proposed method estimates the input current using only the inductor voltage observed during the switch ON-state, thus removing the need for direct current sensing. This sensorless approach simplifies hardware design and reduces implementation costs, particularly in experimental environments where current sensors may introduce complexity and noise susceptibility. In addition, the proposed system includes a battery charging unit which ensures effective energy transfer to the battery in isolated operating conditions for single-phase AC off-grid power applications. The control structure regulates charging dynamics based on voltage behavior and operating constraints, contributing to stable performance under changing environmental conditions. The system’s effectiveness is verified through MATLAB/Simulink simulations under dynamic irradiance profiles. Predicted and actual current values are compared to validate estimation accuracy. Furthermore, experimental validation using a digital signal processor (DSP) demonstrates reliable real-time operation, confirming the practical applicability of the proposed method in cost-sensitive, off-grid solar energy systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available because a standalone dataset was not created for the simulation outputs; however, the simulation data can be provided by the corresponding author on reasonable request. The experimental results are reported as oscilloscope outputs, and no separate dataset is available for these.
References
Sahu, B., Nema, R. & Shrivastava, S. Renewable and sustainable energy reviews on energy demand, policy and global emissions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 138, 110551 (2022).
Guo, L., Zeng, D. & Liu, J. Environmental performance of fossil fuel and renewable energy systems: a comparative analysis. Energy Policy. 119, 300–310 (2018).
Zhang, J. & Li, J. Revolution in renewables: integration of green hydrogen for a sustainable future. Energies 17, 4148. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17164148 (2024).
Yilmaz, M. & Tascıkaraoglu, O. A review of the integration of renewable energy systems with electric vehicles. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 94, 501–516 (2018).
Kocaarslan, A. et al. Energy demand and renewable sources integration. Energy Sources Part. A. 41(2), 181–194 (2019).
Yang, H., Wei, Z. & Chengzhi, L. Optimal design and techno-economic analysis of a hybrid solar–wind power generation system. Appl. Energy. 86(2), 163–169 (2009).
Ko, D. et al. Performance analysis of PV modules in various climates. Sol. Energy. 114, 145–155 (2020).
Kotti, H. & Shireen, W. A comparative study of MPPT techniques for PV systems. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 30(2), 813–821 (2015).
Naderipour, M. et al. A review on MPPT methods for photovoltaic systems under partial shading conditions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 100, 356–373 (2019).
Rabaia, M. K. H. M. et al. Environmental impacts of solar energy systems: a review. Sci. Total Environ. 754, 141989 (2021).
Irmak, E. & Güler, N. A model predictive control-based hybrid MPPT method for boost converters. Int. J. Electron. 107(1), 1–16 (2019).
Kumar, N. B. et al. Performance measurement of high gain landsman converter with ANFIS based MPPT and cascaded H-bridge thirty-one multilevel inverter in a single-phase grid-connected PV system. Sci. Rep. (2025).
Karafil, A., Ozbay, H. & Oncu, S. Design and analysis of Single-Phase Grid-Tied inverter with PDM MPPT-Controlled converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 35(5), 4756–4766 (2020).
Esram, T. & Chapman, P. L. Comparison of photovoltaic array maximum power point tracking techniques. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 22(2), 439–449 (2007).
Villalva, M. G., Gazoli, J. R. & Filho, E. R. Comprehensive approach to modeling and simulation of PV arrays. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 24(5), 1198–1208 (2009).
Ghazi, G. A. et al. Circle search algorithm-based super twisting sliding mode control for MPPT of different commercial PV modules. IEEE Access. 12, 33109–33128 (2024).
Li, X., He, Y. & Li, M. Research on photovoltaic maximum power point tracking control based on improved tuna swarm algorithm and adaptive perturbation observation method. Energies 17, 2985. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122985 (2024).
Kim, I., Kim, H. & Kim, K. High-Performance Sensor-Based MPPT control for photovoltaic systems. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 66(11), 8732–8742 (2019).
Melhaoui, M. et al. Hybrid fuzzy logic approach for enhanced MPPT control in PV systems. Sci. Rep. 15, 19235 (2025).
Abdel-Rahman, E. M. et al. Advanced MPPT techniques using adaptive and predictive control. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy. 11(4), 2491–2502 (2020).
Bhusan, J. et al. Sensorless techniques in photovoltaic systems: a review. Energy Procedia. 158, 3502–3507 (2019).
De Brito, M. A. G., Martines, G. M. S., Volpato, A. S., Godoy, R. B. & Batista, E. A. Current sensorless MPPT algorithms for photovoltaic systems. Sensors 23(10), 4587 (2023).
Mishra, S., Ahmad, R. & Srivastava, A. A comprehensive review of sensorless and intelligent MPPT techniques. Sci. Rep. 15, 96247 (2025).
Belghiti, H. et al. A novel adaptive FOCV algorithm with robust IMRAC control for sustainable and high-efficiency MPPT in standalone PV systems: experimental validation and performance assessment. Sci. Rep. 14, 31962 (2024).
Akter, K., Motakabeer, S. M. A., Zahirul Alam, A. H. M. & Yusoff, S. H. B. A novel MPPT approach for photovoltaic system using pelican optimization and high-gain DC–DC converter. Sci. Rep. 15, 40451 (2025).
Belghiti, H., Kandoussi, K., Harrison, A., Moustaine, F. Z. & Sadek, E. M. Simplified control algorithm for stable and efficient standalone PV systems: an assessment based on real Climatic conditions. Comput. Electr. Eng. 120, 109695 (2024).
Moustaine, F. Z. et al. A novel MPPT approach based on dichotomous search for solar PV systems: Design, Implementation, and performance evaluation under variable Climatic conditions. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-025-10502-5 (2025).
Ashwini, M. et al. Design and comprehensive analysis of adjustable step MPPT controllers for solar PV systems under stochastic atmospheric conditions. Sci. Rep. 15, 10369 (2025).
Almalaq, A. et al. A reduced sensor-based efficient and robust MPPT nonlinear controller for grid-integrated photovoltaic energy systems operating under rapidly changing Climatic conditions. Sci. Rep. 15, 41473 (2025).
Necaibia, S., Necaibia, A. & Bouraiou, A. A new adaptive MPPT design for photovoltaic system under real outdoor conditions. J. Renew. Energies. 1(1), 189–197 (2022).
Bayrak, G. & Ghaderi, D. An improved step-up converter with a developed real-time fuzzy-based MPPT controller for PV-based residential applications. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 29, e12140 (2019).
Zhang, X. et al. Sensorless control for DC–DC boost converter via generalized parameter Estimation-Based observer. Appl. Sci. 11, 7761. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11167761 (2021).
Ertekin, D. A high gain Switched-Inductor-Capacitor DC-DC boost converter for Photovoltaic-Based Micro-Grid applications. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 10(6), 2398–2410 (2024).
Iskender, I. & Genc, N. Design and analysis of a novel zero-voltage-transition interleaved boost converter for renewable power applications. Int. J. Electron. 97(9), 1051–1070 (2010).
Tian, T. et al. Boost converter topologies for PV systems: analysis and performance comparison. IEEE J. Photovolt. 9(1), 219–227 (2019).
Rex, A. & Praba, T. Design and analysis of high efficiency DC-DC converter for solar energy systems. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 11(1), 143–152 (2020).
Abdelmalek, A., Boudour, M. & Chadli, M. Modeling and simulation of SEPIC converter for PV energy systems. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 45(55), 30745–30754 (2020).
Kumar, M., Panda, K. P., Rosas-Caro, J. C., Valderrabano-Gonzalez, A. & Panda, G. Comprehensive review of conventional and emerging maximum power point tracking algorithms for uniformly and partially shaded solar photovoltaic systems. IEEE Access. 11, 31778–31812 (2023).
Celik, M. A., Genc, N. & Uzmus, H. Experimental verification of interleaved hybrid DC/DC boost converter. J. Power Electron. 22(10), 1665–1675 (2022).
Yahduo, X., Cheng, Y. & Mei, S. Advanced perturb and observe method for MPPT of PV systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 32(7), 5585–5594 (2017).
Uzmus, H., Genc, N. & Celik, M. A. The modified MPPT for PV system with interleaved hybrid DC-to-DC boost converter. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 51(1), 46–58 (2022).
Huba, M., Chamraz, S., Bisták, P. & Vrančić, D. Making the PI and PID controller tuning inspired by Ziegler and Nichols precise and reliable. Sensors 21(18), 6157 (2021).
Funding
This research was funded by THE SCIENCE COMMITTEE OF THE MINISTRY OF SCIENCE AND HIGHER EDUCATION OF THE REPUBLIC OF KAZAKHISTAN under Grant No. AP23488947.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, H.U. and N.G.; methodology, H.U., N.G. and M.A.C.; software, H.U., N.G., Z.K.; validation, H.U. and M.A.C.; formal analysis, N.G., Z.K.; investigation, H.U., N.G., Z.K.; writing—S.R., Z.K.; visualization, S.R. and Z.K.; funding acquisition, S.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Genc, N., Uzmus, H., Kalimbetova, Z. et al. Current sensorless MPPT method with battery management for PV based single phase standalone system. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-40097-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-40097-2