Abstract
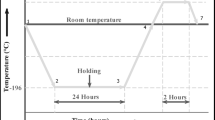
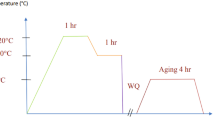
The manufacturing sector is under intense pressure to improve product quality and productivity while reducing production costs due to the rising cost of complex products. The performance of the cutting tool was much improved after the carbide inserts were coated with CVD. As it is customary in the industry, ISO P-20 coated insert grades were utilized for the studies. Cryogenic treatment was applied to the carbide inserts by bringing the temperature down to -186 °C. Frozen tungsten carbide inserts have a longer lifespan, according to the research. In order to determine the impact of cryogenic treatment on the toughness and tool life of coated and uncoated carbide inserts used to turn alloy steel, we utilised the Taguchi technique to consider both technical and economic aspects. The efficiency was tested using Taguchi orthogonal array L16, taking into account feed rate, cutting speed, insert coating, and tool type. While turning continuously, the effect of cutting speed was 18.01% and when facing intermittently, it was 9.45%. This was achieved using inserts coated with a sandwich layer of Al2O3 and TiC, with a thickness of 18.3 microns, on EN24 grade alloy steel with BHN values ranging from 234 to 236. While the feed rate contributed to 16.47% during intermittent facing operation, it was 21.66% in the continuous turning operation. When compared to untreated inserts, those that have been cryogenically treated had a 66.79% longer life during intermittent facing. At A2B2C1 parameters the inserts wear study shown that, the tool life of cryogenic treated coated carbide inserts found 42.81% higher than untreated coated carbide inserts for the same tool wear. Tempering of cryogenic-treated inserts at 200 °C for 150 min, resulted to 46.53% higher when compared to untreated coated carbide inserts in the continuous turning test and 71.44% higher in the intermittent facing trial compared to untreated coated carbide inserts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that supports the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Gopal, P. K. & Selvam, D. Effect of carbide inserts with titanium nitride coating of different thickness on machining mild steel. Int. J. Chemtech Res. 11 (2), 23–28 (2018).
Naveen Kumar Reddy, R. & Lokesh, S. A comparative study on physical vapor deposition- titanium carbide coated novel insert and uncoated carbide insert in CNC turning of EN24 for minimizing surface roughness and maximizing material removal rate. Mater. Today Proc. 69 858–862. (2022).
Shabani, M. M., Sacramento, J., Oliveira, F. J. & Silva, R. F. Multilayer CVD diamond coatings in the machining of an Al6061-15 Vol % Al2O3 composite. J. Coat. 7 (165), 01–13. (2017).
Charnnarong Saikaew, P., Paengchit, A. & Wisitsoraat Machining performances of TiN+AlCrN coated WC and Al2O3 + TiC inserts for turning of AISI 4140 steel under dry condition. J. Manuf. Process. 50, 412–420 (2020).
Prem Chand, R., Sreerama Reddy, T. V. & Omprakash, C. A. B. Abdul Razak, Anteneh Wogasso Wodajo, impact of cryogenic treatment on the performance of coated tungsten carbide inserts during machining of EN24 grade alloy steel. Eng. Rep. 6, e12839 (2024).
Akhtar & Khan Kalipada maity comparative study of some machinability aspects in turning of pure titanium with untreated and cryogenically treated carbide inserts. J. Manuf. Process. 28, 272–284 (2017).
Kumar, M. & Sidhu, H. S. Buta Singh Sidhu. Parametric and microstructural analysis of cryogenically treated austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Today Proc. 45 4511–4519. (2021).
Engin, N. A. S. & Nursel, A. L. T. O. N. O. Z. B. E. K. ‘Optimization the machining parameters in turning of hardened hot work tool steel using cryogenically treated tools. Surf. Rev. Lett. (2019).
Fuat Kara, M., Karabatak, M., Ayyildiz, E. & Nas Effect of machinability, microstructure and hardness of deep cryogenic treatment in hard turning of AISI D2 steel with ceramic cutting. Elsevier J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9 (1), 969–983 (2020).
Qin, Y. et al. Jinfeng Li b, Longqing Chen e, Jun Zhu, Microstructure and mechanical performance study of CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloys after cryogenic treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 942, 148663, 1-10. (Elsevier, 2025).
Jingwen Liu, L., Shi, R., Su, T., Liu, G. & Li Effect of deep cryogenic treatment on microstructure and properties of Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloy with RRA. J. Alloys Compd. 1020, 179574, 1-10. (Elsevier, 2025).
Ozbek, N. A. & Ozbek, O. Effect of cryogenic treatment holding time on mechanical and microstructural properties of Sverker 21 steel. Mater. Test. 64 (12), 1809–1817 (2022).
Onur Ozbek, N. A. & Ozbek Impact of deep cryogenic treatment on X210CrW12 steel’s wear behavior and microstructural characteristics. Materials 18, 879 (2025).
Yuan Gao, Y. et al. Influence of the cryogenic treatment on wear resistance and cutting performance of cemented carbide Elsevier. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 128, 107042 (2025).
Gopal Krishna, P. V., Kishore, Ramadevudu, G. & Sikandar Ali performance evaluation of cryogenic treated tools in turning. Adv. Prod. Eng. Manage. 7 (3), 187–194 (2012).
Priya Jadhav, S. & Kumar Arunkumar Bongale. Optimization of cutting forces by cryogenic treatment on tungsten carbide inserts during dry turning of the P 20 tool steel. Mater. Today Proc. 28 2485–2493. (2020).
Gill, S. S., Singh, J. & Singh, H. Rupinder Singh investigation on wear behaviour of cryogenically treated TiAlN coated tungsten carbide inserts in turning. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 51, 25–33 (2011).
Prem Chand, R. et al. Ankit Sharma & Raman Kumar, cutting force and surface roughness evaluation of cryogenic treated inserts for machining en24 grade alloy steel: RSM modelling approach. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 18, 3923–3934 (2024).
Fuat Kara, A. & Takmaz. Effect of cryogenic treatment applied to cutting toolon machining parameters and RSM optimization. 2024101057. (2024).
Swastik Pradhan, V. P. et al. Eldin performance investigation of cryogenic treated double tempered cutting inserts in dry turning of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 25, 2989–3006 (2023).
Sahoo, B. N., Mohanty, A., Gangopadhyay, S. & Vipindas, K. An insight into microstructure and machining performance of deep cryogenically treated cemented carbide inserts. J. Manuf. Process. 58, 819–831 (2020).
Upendra Kumar, P. & Senthil. Performance of cryogenic treated multi-layer coated WC insert in terms of machinability on titanium alloys Ti-6Al-4V in dry turning. Mater. Today Proc. 27, 2329–2333. (2020).
Butt, M. M. & Najar, K. A. Towseef Hussain Dar experimental evaluation of multilayered CVD- and PVD-coated carbide turning inserts in severe machining of AISI-4340 steel alloy. Jurnal Tribologi. 29, 117–143 (2021).
Mani lavanya, K., Suresh, R. K., Sushil Kumar Priya, A. & Diwakar Reddy, V. Optimization of process parameters in turning operation of AISI-1016 alloy steels with CBN using Taguchi method and Anova. IOSR J. Mech. Civil Eng. 7 (2), 24–27 (2013).
Bhaskar Mutyalu, K., Venkatrami Reddy, V., Uma Maheswara Reddy, S. & Lakshmi Prasad, K. Effect of machining parameters on cutting forces during turning of EN 08, EN 36 & mild steel on high speed lathe by using Taguchi orthogonal array. Mater. Today Proc. 80 2411–2415. (2023).
Li, Y., Chen, Y. & Xuejieo Volume, Effects of cryogenic treatment and tempering on mechanical properties and microstructure of 0.25 C-0.8Si-1.6Mn steel. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1501474, 8. (2020).
Gadekula, R. K., Potta, M., Kamisetty, D., Yarava, U. K. & Anand, P. Raja Sekhar Dondapati Investigation on parametric process optimization of HCHCR in CNC turning machine using Taguchi technique. Mater. Today Proc. 5 28446–28453. (2018).
Kara, M., Karabatak, M., Ayyıldız, E. & Nas Effect of machinability, microstructure and hardness of deep cryogenic treatment in hard turning of AISI D2 steel with ceramic cutting. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9 (1), 969–983 (2020).
Fuat Kara, A., Takmaz, O., Erkan, S. & Filiz. Response surface method optimization of hard machining with cryogenically treated cutting tools: surface roughness, cutting force, tool wear, rietveld analysis, and metallurgical properties, steel research international. (2024).
Gao, Y., Chen, Z. & Wang, Y. The effect of cryogenic treatment on the mechanical properties and cutting performance of coated cemented carbide tools with different Co. contents Elsevier. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 59, 18–33 (2025).
Fuat Kara, N. A., Ozbek, O. & Ozbek Effect of cryogenic treatment on the machinability of impax supreme steel and optimization of machining parameters. ES Mater. Manuf. 271457. (2025).
Carou, D., Rubio, E. M., Lauro, C. H. & Davim, J. P. Experimental investigation on surface finish during intermittent turning of UNS M11917 magnesium alloy under dry and near dry machining conditions measurement. 56 136–154. (2014).
Prakash Rao, C. R., Bhagyashekar, M. S. & Viswanath, N. Studies on intermittent facing of metal matrix composites using cryogenic treated carbide. Inserts Procedia Eng. 97, 930–940 (2014).
Henrik Persson, M., Agmell, V., Bushlya, J. E. & Stahl Experimental and numerical investigation of burr formation in intermittent turning of AISI 4140. Procedia CIRP. 58, 37–42 (2017).
Carou, D., Rubio, E. M., Lauro, C. H. & Davim, P. J. Experimental investigation on surface finish during intermittent turning of UNS M11917 magnesium alloy under dry and near dry machining conditions. Measurement 56, pp136–154 (2014).
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University, Saudi Arabia for funding this work through Small Research Group Program under Grant No. RGP. 1/84/46.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University, Saudi Arabia for funding this work through Small Research Group Program under Grant No. RGP. 1/84/46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, P.C.R, C.S.A; Writing—Review and Editing, C.R.P.R, V.K.C; Methodology, C.R.C, A.A.R; Formal analysis, A.A.D; Investigation, Y.D., M.K.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Chand, R.P., Shekar, A.C., Rao, C.R.P. et al. Effect of cryogenic treatment on coated and uncoated carbide inserts during turning and facing of alloy steel using Taguchi method. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-40235-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-40235-w