Abstract
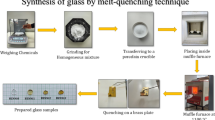
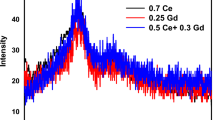
This investigation is to explore how CeO2 affects the physical, structural, and spectroscopic characteristics of tellurium soda-borate glasses for potential applications in optoelectronics. The conventional melt quenching technique was used to produce the necessary glasses by adding different amounts of CeO2 to the components of the tellurium soda-borate glasses. The non-crystalline nature of the samples was validated by the X-ray diffraction patterns. The density of glass samples was determined by Archimedes principle, and hence other physical properties like polaron radius, oxygen packing density, and average boron-boron separation were calculated. The FTIR spectra demonstrated the presence of fundamental structural groups of borate (BO3 and BO4) and tellurite (TeO4 and TeO3) in both the undoped and doped samples. FTIR also demonstrated the presence of the unique structural group of cerium tetrahedral CeO4 when the B2O3 level was decreased. The optical properties were analysed for the glass samples by the UV-Visible spectroscopy method. Refractive index (RI) of the glasses was found by using suitable mathematical approaches, and the highest RI value was found for BTNC5. Metallization criterion, optical basicity, electronegativity, and optical properties are determined with the help of the obtained RI and optical energy bandgap. The values of direct and indirect energy gaps, optical basicity, and refractive index were all impacted by the variation of CeO2 content. The CeO2-doped BTNC glasses allowed 5d → 4f transitions of Ce3+ ions and gave a wide green emission at 512 nm. The CIE diagram showed that CeO2-doped BTNC glasses lie in the green to yellowish region. The CCT values are > 5000 K, indicating a cool CCT. The obtained results of optical and luminescence properties indicate that the BTNC glasses are potential candidates for light-emitting devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request by corresponding author.
References
Gökçe, M., Burgaz, G. & Gökçe, A. G. Cerium doped glasses containing reducing agent for enhanced luminescence. J. Lumin. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2020.117175 (2020).
Tekin, H. O. et al. Cadmium oxide reinforced 46V2O5–46P2O5–(8 − x)B2O3–xCdO semiconducting oxide glasses and resistance behaviors against ionizing gamma rays. J. Mater. Res. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.06.020 (2021).
Ma, W. et al. Cerium oxide (CeO2-x) nanoparticles with high Ce3 + proportion synthesized by pulsed plasma in liquid. Ceram Int 46, (2020).
Al-Ghamdi, H. et al. An examination of synthesis, physical, optical, and radiation safety features of Ce/Yb-doped borate glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10296-y (2023).
Park, J. M. et al. Luminescence properties of Ce3 + doped gadolinium-calcium-silicaborate glass scintillator. Radiat Meas 90, (2016).
Rajaramakrishna, R., Kaewjaeng, S., Kaewkhao, J. & Kothan, S. Investigation of XANES study and energy transport phenomenon of Gd3 + to Ce3 + in CaO–SiO2–B2O3 glasses. Opt. Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2020.109826 (2020).
Sayyed, M. I. et al. X-ray shielding characteristics of P2O5–Nb2O5 glass doped with Bi2O3 by using EPICS2017 and Phy-X/PSD. Appl Phys. Mater. Sci. Process 127, (2021).
Rammah, Y. S. et al. FTIR, UV–Vis–NIR spectroscopy, and gamma rays shielding competence of novel ZnO-doped vanadium borophosphate glasses. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics 31, (2020).
Kilic, G. et al. Ytterbium (III) oxide reinforced novel TeO2–B2O3–V2O5 glass system: Synthesis and optical, structural, physical and thermal properties. Ceram Int 47, (2021).
Kavaz, E., Tekin, H. O., Kilic, G. & Susoy, G. Newly developed Zinc-Tellurite glass system: An experimental investigation on impact of Ta2O5 on nuclear radiation shielding ability. J Non Cryst. Solids 544, (2020).
Shams, M. S., Rammah, Y. S., El-Agawany, F. I. & Elsad, R. A. Synthesis, structure, physical, dielectric characteristics, and gamma-ray shielding competences of novel P2O5–Li2O–ZnO–CdO glasses. Journal Mater. Science: Mater. Electronics 32, (2021).
Tekin, H. O. et al. In-silico monte carlo simulation trials for investigation of V2O5 reinforcement effect on ternary zinc borate glasses: nuclear radiation shielding dynamics. Mater. 2021. 14, 1158 (2021).
Shelby, J. E. Introduction to Glass Science and Technology. Introduction to Glass Science and Technology (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/9781839169229
Varshneya, A. Fundamentals of Inorganic Glasses. (2013).
Yano, T., Kunimine, N., Shibata, S. & Yamane, M. Structural investigation of sodium borate glasses and melts by Raman spectroscopy. III. Relation between the rearrangement of super-structures and the properties of glass. J Non Cryst. Solids 321, (2003).
Yano, T., Kunimine, N., Shibata, S. & Yamane, M. Structural investigation of sodium borate glasses and melts by Raman spectroscopy. I. Quantitative evaluation of structural units. J Non Cryst. Solids 321, (2003).
Kaky, K. M. et al. Bismuth oxide effects on optical, structural, mechanical, and radiation shielding features of borosilicate glasses. Opt Mater. (Amst) 155, (2024).
Alawaideh, S. E. et al. Effect of different metal oxides on the Radiation shielding features of borate glasses. Radiation Phys. Chemistry 220, (2024).
Boubata, N., Roula, A. & Moussaoui, I. Thermodynamic and relative approach to compute glass-forming ability of oxides. Bulletin Mater. Science 36, (2013).
El-Mallawany, R. A., El-Deen, S. & Elkholy, M. M. L. M. Dielectric properties and polarizability of molybdenum tellurite glasses. J Mater. Sci 31, (1996).
Manning, S., Ebendorff-Heidepriem, H. & Monro, T. M. Ternary tellurite glasses for the fabrication of nonlinear optical fibres. Opt Mater. Express 2, (2012).
Wang, J. S., Vogel, E. M. & Snitzer, E. Tellurite glass: a new candidate for fiber devices. Opt Mater. (Amst) 3, (1994).
Mhareb, M. H. A. et al. Improving structural, optical, and ionizing absorption features of G-T-B glass system by doping different concentration of Sm2O3. Ceram Int 51, (2025).
Al-Ghamdi, H. et al. Impact of TiO2-Doped Bismuth-Boro-tellurite glasses: fabrication, physical and optical properties, and γ-Ray protection competence for optical and radiation shielding applications. J Electron. Mater 54, (2025).
Sidek, H. A. A., Rosmawati, S., Azmi, B. Z. & Shaari, A. H. Effect of ZnO on the thermal properties of tellurite glass. Advances in Condensed Matter Physics (2013). (2013).
Kassab, L. R. P. & Bell, M. J. V. Rare-earth-doped germanate and tellurite glasses: Laser, waveguide, and ultrafast device applications. in Lanthanide-Based Multifunctional Materials: From OLEDs to SIMs (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813840-3.00008-9
Sakida, S., Hayakawa, S. & Yoko, T. Part 2.125Te NMR study of M2O-TeO2 (M = Li, Na, K, Rb and Cs) glasses. J Non Cryst. Solids 243, (1999).
Rammah, Y. S. et al. Physical, optical, thermal, and gamma-ray shielding features of fluorotellurite lithiumniobate glasses: TeO2-LiNbO3-BaO-BaF2-La2O3. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 3743–3752 (2021).
Tekin, H. O. et al. A Systematical Characterization of TeO2–V2O5 Glass System Using Boron (III) Oxide and Neodymium (III) Oxide Substitution: Resistance Behaviors against Ionizing Radiation. Appl. Sci. 2021. 11, Page 3035 (11), 3035 (2021).
Kilic, G. et al. Novel zinc vanadyl boro-phosphate glasses: ZnO–V2O5– P2O5–B2O3: Physical, thermal, and nuclear radiation shielding properties. Ceram. Int. 46, 19318–19327 (2020).
Rammah, Y. S. et al. B2O3-Bi2O3-Li2O3-Cr2O3 glasses: Fabrication, structure, mechanical, and gamma radiation shielding qualities. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 57, 1057–1069 (2021).
Kilic, G., Issever, U. G. & Ilik, E. Synthesis, characterization and crystalline phase studies of TeO2–Ta2O5–ZnO/ZnF2 oxyfluoride semiconducting glasses. J Non Cryst. Solids 527, (2020).
Weber, M. J. Nonradiative decay from 5d states of rare earths in crystals. Solid State Commun 12, (1973).
Marzouk, S. Y. & Ezz-Eldin, F. M. Optical study of Ce3 + ion in gamma-irradiated binary barium-borate glasses. Physica B Condens. Matter 403, (2008).
Aloraini, D. A., Almuqrin, A. H., Kaky, K. M., Sayyed, M. I. & Elsafi, M. Radiation shielding capability and exposure buildup factor of cerium(IV) oxide-reinforced polyester resins. E-Polymers 23, (2023).
Rejisha, S. R., Anjana, P. S. & Gopakumar, N. Effect of cerium(IV) oxide on the optical and dielectric properties of strontium bismuth borate glasses. Journal Mater. Science: Mater. Electronics 27, (2016).
Ibrahim, S. E., El-Mallawany, R. & Abouhaswa, A. S. Structural, optical and dielectric properties of tellurite borate glasses doped with cerium oxide. J Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater 33, (2023).
Shiva Kumar B․N. Implications of silver nitrate doping on the physical, structural, and optical attributes of Na2O – ZnO–Borate glasses. J. Mol. Struct. 1325, 140985 (2025).
Vinay, D. et al. Investigation of physical, structural, optical, and luminescence properties of nickel oxide doped alkali zinco-borate glasses. Scientific Reports 2025 15:1 15, 1–20 (2025).
Dimitrov, V. & Sakka, S. Linear and nonlinear optical properties of simple oxides. II. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 1741–1745 (1996).
Dimitrov, V. & Komatsu, T. Classification of simple oxides: A polarizability approach. J. Solid State Chem. 163, 100–112 (2002).
Siddalingeshwara, B. P. et al. Structural correlation to linear and non-linear optical properties of Bi3 + ion doped Li2O–SrO–B2O3 glasses: Optical switching and limiting applications. Ceram. Int. 50, 37880–37899 (2024).
Gowda, G. V. J. et al. Exploration of physical, structural, thermal, and optical properties of alkali zinc boro tellurite glasses doped with europium trioxide. Appl. Phys. A 130, 1–15 (2024).
Devaraja, C. et al. Structural, conductivity and dielectric properties of europium trioxide doped lead boro-tellurite glasses. https://doi org/10 1016/j jallcom 2021 162967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162967 (2021).
Kaur, R. et al. Thermoluminescence, structural and optical properties of Ce3 + doped borosilicate doped glasses. Journal Mater. Science: Mater. Electronics 32, (2021).
Gomaa, H. M., Saudi, H. A., Yahia, I. S. & Zahran, H. Y. Enhanced the optical, electrical, and shielding properties of some alkali-borate glasses doped with lanthanide cerium oxide, CeO2. Journal Mater. Science: Mater. Electronics 33, (2022).
Malik, M., Khatri, A., Hooda, A., Dahiya, M. S. & Khasa, S. Structural, spectroscopic and electrical properties of iron doped oxyfluoride bismuth borate glasses. Mater Res. Bull 162, (2023).
Thakur, S., Thakur, V., Kaur, A. & Singh, L. Structural, optical and thermal properties of nickel doped bismuth borate glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids. 512, 60–71 (2019).
Devaraja, C., Gowda, J., Eraiah, G. V. & Keshavamurthy, K. B. FTIR and Raman studies of Eu3 + ions doped alkali boro tellurite glasses. in AIP Conference Proceedings vol. 2115 (2019).
Ahlawat, J. et al. Structural and optical characterization of IR transparent sodium-modified zinc borate oxide glasses. Appl. Phys. A 128, 1–14 (2022).
Sharma, V., Singh, S. P., Mudahar, G. S. & Thind, K. S. Synthesis and characterization of cadmium containing sodium borate glasses. New J. Glass Ceram. https://doi.org/10.4236/njgc.2012.24022 (2012).
Sekiya, T., Mochida, N. & Ogawa, S. Structural study of WO3-TeO 2 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(94)90067-1 (1994).
Elkhoshkhany, N., Khatab, M. A. & Kabary, M. A. Thermal, FTIR and UV spectral studies on tellurite glasses doped with cerium oxide. Ceram. Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.11.019 (2018).
Gomaa, H. M., Saudi, H. A., Yahia, I. S., Ibrahim, M. A. & Zahran, H. Y. Influence of exchanging CeO2 with Cu2O3 on structural matrix, shielding, and linear/nonlinear optical parameters of the cerium-sodium borate glass. Optik https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.168267 (2022).
Pattar, V. et al. Investigation of structural, physical and optical properties of sodium boro-tellurite glasses doped with iron oxide. Ceram. Int. 50, 30434–30444 (2024).
Vinay, D. et al. Silver oxide embedded alkali zinc boro tellurite glasses: Physical, structural and optical properties for possible optical switching applications. J. Mol. Struct. 1339, 142388 (2025).
B N, S. K., C, D. & Gedam, R. S. Implications of Ho3+-ions on physical, structural, optical, and spectroscopic features of Na2O-PbO-borotellurite glass system for feasible applications in optical and laser technology. Sci. Rep. 15, 1–24 (2025).
Kamitsos, E. I., Karakassides, M. A. & Chryssikos, G. D. Vibrational spectra of magnesium-sodium-borate glasses. 2. Raman and mid-infrared investigation of the network structure. J. Phys. Chem. 91, 1073–1079 (1987).
Deshpande, V. K. & Taikar, R. N. Effect of cerium oxide addition on electrical and physical properties of alkali borosilicate glasses. Materials Science and Engineering: B 172, 6–8 (2010).
El-Damrawi, G. & El-Egili, K. Characterization of novel CeO2-B2O3 glasses, structure and properties. Phys. B Condens. Matter https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-4526(00)00593-7 (2001).
Gedam, R. S. & Ramteke, D. D. Influence of CeO2 addition on the electrical and optical properties of lithium borate glasses. J. Phys. Chem. Solids https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2013.04.022 (2013).
Pal Singh, G., Kaur, P., Kaur, S. & Singh, D. P. Investigation of structural, physical and optical properties of CeO2–Bi2O3–B2O3 glasses. Phys. B Condens. Matter 407, 4168–4172 (2012).
Devaraja, C., Gowda, G. V. J., Keshavamurthy, K. & Eraiah, B. The optical and physical properties of holmium (Ho3+) ions doped bismuth-tellurite glasses. in AIP Conference Proceedings vol. 2162 (2019).
Alharshan, G. A. et al. CeO2 additive to bismo-borate glasses: synthesis, structure, physical characteristics, and radiation protection competence. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics 2024 35:12 35, 862- (2024).
Shwetha, M. & Eraiah, B. Influence of Er3 + ions on the physical, structural, optical, and thermal properties of ZnO–Li2O–P2O5 glasses. Appl. Phys. A https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2481-4 (2019).
Jagadeesha Gowda, G. V. et al. Structural, physical, and optical properties of lead boro-tellurite glasses doped with europium trioxide. Rasayan J. Chem. 16, 692 (2023).
Devaraja, C., Gowda, G. V. J., Eraiah, B. & Keshavamurthy, K. Optical properties of bismuth tellurite glasses doped with holmium oxide. Ceram. Int. 47, 7602–7607 (2021).
Kumar, V. & Singh, J. K. Model for calculating the refractive index of different materials. Indian J. Pure Appl. Physics 48, (2010).
Hervé, P. J. L. & Vandamme, L. K. J. Empirical temperature dependence of the refractive index of semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.359248 (1995).
Reddy, R. R., Nazeer Ahammed, Y., Rama Gopal, K. & Raghuram, D. V. Optical electronegativity and refractive index of materials. Opt. Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-3467(97)00171-7 (1998).
Barde, R. V. Influence of CeO2 content on complex optical parameters of phosphovanadate glass system. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 153, 160–164 (2016).
Siddalingeshwara, B. P., Reddy, S., ·, N., Jagannathan, · Abhiram. & The effect of NiO on the structural and optical properties of lithium strontium borate glasses. J. Opt. 2024, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12596-024-02008-4 (2024).
Roopa & Eraiah, B. Experimental and theoretical approach on the physical, structural and optical properties of ZrO2 - Na2O - B2O3 glasses doped with Dy2O3. J. Non Cryst. Solids. 551, 120394 (2021).
Marzouk, M. A., ElBatal, F. H. & Morsi, R. M. M. Optical and FTIR absorption spectra of CeO2 – doped cadmium borate glasses and effects of gamma irradiation. Silicon 9(1), 105–110 (2016).
Herzfeld, K. F. On atomic properties which make an element a metal. Phys. Rev. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.29.701 (1927).
Kashif, I., Ratep, A. & Adel, G. Polarizability, optical basicity and optical properties of SiO2B2O3Bi2O3TeO2 glass system. Appl. Phys. A https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1904-y (2018).
Dimitrov, V. & Komatsu, T. An Interpretation of optical properties of oxides and oxide glasses in terms of the electronic ion polarizability and average single bond strength. Journal Univ. Chem. Technol. Metallurgy 45, (2010).
Ali, A. A., Rammah, Y. S., El-Mallawany, R. & Souri, D. FTIR and UV spectra of pentaternary borate glasses. Meas. (Lond.). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2017.04.010 (2017).
Alsaif, N. A. M. et al. Development of CeO2-doped borophosphate glasses: fabrication, structure and linear/nonlinear optical characteristics for optical purposes. Optical and Quantum Electronics 2024 56:6 56, 950- (2024).
Chen, Q., Qiao, Y., Wang, H. & Chen, Q. Spectra and magneto optical behavior of CeO2 doped heavy metal diamagnetic glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 470, 70–77 (2017).
Alsaif, N. A. M. et al. Dielectric, optical properties, γ-ray/neutron shielding capacity of bismo-borate glasses reinforced with CeO2. Applied Physics A 2024 131:1 131, 45- (2024).
Tichá, H. & Tichý, L. Semiempirical relation between non-linear susceptibility (refractive index), linear refractive index and optical gap and its application to amorphous chalcogenides. Journal Optoelectron. Adv. Materials 4, (2002).
Chen, Q. Optical linear & nonlinearity and Faraday rotation study on V2O5 nanorod doped glass and glass-ceramic: Impact of optical basicity. J. Alloys Compd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155490 (2020).
Negm, H. H., Abdo, M. A. & Sadeq, M. S. Impact of Y2O3 on the structural, linear and nonlinear optical parameters of Na2O-Fe2O3-B2O3 glass. Optik https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2023.170923 (2023).
Qu, M. Y., Li, T. Q. & Liu, Q. L. Photoluminescence properties of cyan-emitting Lu3GaxAl5 − xO12: Ce3 + garnet phosphors synthesized in nonreducing atmosphere and at different temperature for high quality w-LEDs. Materials https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196817 (2022).
Song, Z. et al. After-glow, luminescent thermal quenching, and energy band structure of Ce-doped yttrium aluminum-gallium garnets. J. Lumin. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2017.09.008 (2017).
Rodríguez Chialanza, M. et al. Optical properties of lead diborate glass ceramics doped with Ce and Eu. J. Non-Cryst. Solids https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2013.11.026 (2014).
Kaur, S., Singh, G. P., Kaur, P. & Singh, D. P. Cerium luminescence in borate glass and effect of aluminium on blue green emission of cerium ions. J. Lumin. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2013.04.027 (2013).
Neto, O. C. S. et al. Tunable luminescence of Ce3+-doped calcium boroaluminate glasses for light emitting devices. J Electron. Mater 50, (2021).
Ramakrishna, P. et al. Structural and optical properties of cerium and dysprosium coactivated borophosphate glasses for cool white light application. J. Non-Cryst. Solids https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2021.120883 (2021).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank and acknowledge Manipal Institute of Technology Bengaluru and Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, for their great encouragement and support towards research.
Funding
Open access funding provided by Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
**SKBN** : Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing—original draft.**V D** : Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft.**C D** : Writing—review & editing, Validation, Supervision, Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Shiva Kumar, B.N., Vinay, D. & Devaraja, C. Effect of cerium oxide on physical, structural, and spectroscopic properties of tellurium-borate glasses for cool greenish light emitting devices. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-40883-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-40883-y