Abstract
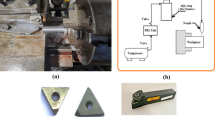
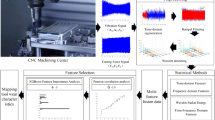
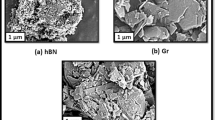
This study explores the implementation of artificial intelligence (AI)–based predictive frameworks for the precise evaluation of tool wear in the sustainable machining of Hastelloy X using PVD TiAlN-coated carbide inserts. To improve lubrication effectiveness and restrain excessive tool degradation under severe thermo-mechanical cutting conditions, a minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) strategy aided with a carbon nanotube (CNT)-based nanofluid was adopted. Tool wear evolution was modelled using advanced machine learning approaches, including Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), Deep Neural Networks (DNN), and Support Vector Regression (SVR), with key machining parameters serving as the primary input variables. Experimental investigations demonstrated that CNT-based MQL substantially reduced tool wear, with an optimal nanoparticle concentration of 0.6%, attributed to improved heat dissipation and superior tribological behaviour at the machining zone. Among the implemented models, XGBoost exhibited the highest predictive accuracy, attaining an R² of 0.9924 along with minimal error indices, including MAE of 0.0017, RMSE of 0.002, and MAPE of 0.6%. In contrast, DNN and SVR showed comparatively poor predictive capability for the evaluated dataset split, reflected by low or negative R² values, highlighting the importance of model selection and data sensitivity in tool wear prediction tasks. Sensitivity analysis based on Spearman correlation revealed that cutting speed exerted the most dominant impact on tool wear (correlation coefficient = 0.94), followed by feed rate and depth of cut. Overall, the outcomes indicate that CNT-based nano-MQL combined with appropriately selected AI models—particularly XGBoost—provides a robust pathway for extending tool life, enhancing machinability, and enabling intelligent tool condition monitoring aligned with Industry 4.0 and sustainable manufacturing paradigms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data supporting this study’s findings are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Murali, T., Devendiran, S. & Venkatesan, K. A hybrid algorithm-based comparative analysis of a newly designed tool holder during the machining of Hastelloy-B3 with MQL. Arab. J. Sci. Eng., 1–24. (2024).
Li, X. et al. Active thermography non-destructive testing going beyond camera’s resolution limitation: A heterogenous Dual-band single-pixel approach. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. https://doi.org/10.1109/tim.2025.3545520 (2025).
Ambhore, N., Naranje, V. & Shelke, S. Machining performance evaluation in turning of hardened steel using machine learning. Mater. Manuf. Process. 40(14), 1935–1942 (2025).
Yan, X., Hu, J., Zhang, X. & Xu, W. Obtaining superior low-temperature wear resistance in Q&p-processed medium Mn steel with a low initial hardness. Tribol. Int. 175, 107803 (2022).
Kumar, G., Sen, B., Ghosh, S. & Rao, P. V. Strategic enhancement of machinability in nickel-based superalloy using eco-benign hybrid nano-MQL approach. J. Manuf. Process. 127, 457–476 (2024).
Wan, A. et al. A novel GA-PSO-SVM model for compound fault diagnosis in gearboxes with limited data. IEEE Sens. J. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2025.3576761 (2025).
Ambhore, N., Kamble, D. & Chinchanikar, S. Evaluation of cutting tool vibration and surface roughness in hard turning of AISI 52100 steel: An experimental and ANN approach. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 8(3), 455–462 (2020).
Wang, Z. et al. A mutual cross-attention fusion network for surface roughness prediction in robotic machining process using internal and external signals. J. Manuf. Syst. 82, 284–300 (2025).
Sen, B., Yadav, S. K., Kumar, G., Mukhopadhyay, P. & Ghosh, S. Performance of eco-benign lubricating/cooling mediums in machining of superalloys: A comprehensive review from the perspective of Triple Bottom Line theory. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 35, e00578 (2023).
Liu, H., Zhang, D. & Geng, D. Design of a self-excited vibration tool bar for cutting difficult-to-machine alloys. Int. J. Mech. Sci., 110456. (2025).
Hao, W. Q. et al. Multi-mode fatigue life prediction using machine learning inspired by damage physics. Int. J. Mech. Sci., 110723. (2025).
Sen, B. et al. Exploring cryo-MQL medium for hard machining of hastelloy C276: a multi-objective optimization approach 1–14 (International Journal on Interactive Design and Manufacturing (IJIDeM), 2024).
Zeng, L. et al. Study on dynamic wear evolution of modified gear rack considering the real-time variation of contact characteristics. Wear https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2025.205845 (2025).
Ambhore, N. & Kamble, D. Experimental investigation of tool wear and induced vibration in turning high hardness AISI52100 steel using cutting parameters and tool acceleration. Facta Univ. Ser. Mech. Eng. 18(4), 623–637 (2020).
Zhu, J., Wang, X. & Mu, Y. Uncertain constitutive model for metals in the presence of inherent defects. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 447, 118355 (2025).
Cai, W., Zhang, W., Hu, X. & Liu, Y. A hybrid information model based on long short-term memory network for tool condition monitoring. J. Intell. Manuf. 31, 1497–1510 (2020).
Zhu, J., Wang, X., Cao, G., Xu, L. & Cao, Y. Quantum interval neural network for uncertain structural static analysis. Int. J. Mech. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2025.110646 (2025).
Ambhore, N., Kamble, D. & Chinchanikar, S. Behaviour of cutting tool vibrations with the progress of tool wear in turning hardened AISI 52100 steel: An approach to tool condition monitoring system. In IOP Conference Series. Materials Science and Engineering 455 (1), 012062 (2018).
Xie, W. T., Song, D. N., Tang, W. C., Ma, J. W. & Li, J. H. Auxiliary support path planning for robot-assisted machining of thin-walled parts with non-uniform thickness and closed cross-section based on a neutral surface. J. Manuf. Process. 147, 16–28 (2025).
Xu, H. et al. ESMNet: An enhanced YOLOv7-based approach to detect surface defects in precision metal workpieces. Measurement 235, 114970 (2024).
Ambhore, N., Kamble, D. & Chinchanikar, S. Analysis of tool vibration and surface roughness with tool wear progression in hard turning: An experimental and statistical approach. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 14 (1), 6461–6472 (2020).
Wang, M., Zhou, J., Gao, J., Li, Z. & Li, E. Milling tool wear prediction method based on deep learning under variable working conditions. IEEE Access 8, 140726–140735 (2020).
Nouri, M., Fussell, B. K., Ziniti, B. L. & Linder, E. Real-time tool wear monitoring in milling using a cutting condition independent method. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 89, 1–13 (2015).
Zhu, K. & Yu, X. The monitoring of micro milling tool wear conditions by wear area estimation. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 93, 80–91 (2017).
Stavropoulos, P., Papacharalampopoulos, A., Vasiliadis, E. & Chryssolouris, G. Tool wear predictability estimation in milling based on multi-sensorial data. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 82, 509–521 (2016).
Shankar, S., Mohanraj, T. & Rajasekar, R. Prediction of cutting tool wear during milling process using artificial intelligence techniques. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 32 (2), 174–182 (2019).
Alhadeff, L. L., Marshall, M. B., Curtis, D. T. & Slatter, T. Protocol for tool wear measurement in micro-milling. Wear 420, 54–67 (2019).
Kong, D. et al. Tool wear estimation in end milling of titanium alloy using NPE and a novel WOA-SVM model. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 69(7), 5219–5232 (2019).
Lei, Z. et al. A GAPSO-enhanced extreme learning machine method for tool wear estimation in milling processes based on vibration signals. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 8, 745–759 (2021).
Kong, D., Chen, Y. & Li, N. Hidden semi-Markov model-based method for tool wear estimation in milling process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 92, 3647–3657 (2017).
Kong, D., Chen, Y. & Li, N. Force-based tool wear estimation for milling process using Gaussian mixture hidden Markov models. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 92, 2853–2865 (2017).
Liu, H., Liu, Z., Jia, W., Lin, X. & Zhang, S. A novel transformer-based neural network model for tool wear estimation. Meas. Sci. Technol. 31 (6), 065106 (2020).
Zhang, C. & Zhang, H. Modelling and prediction of tool wear using LS-SVM in milling operation. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 29 (1), 76–91 (2016).
Yang, W. A., Zhou, Q. & Tsui, K. L. Differential evolution-based feature selection and parameter optimisation for extreme learning machine in tool wear estimation. Int. J. Prod. Res. 54(15), 4703–4721 (2016).
Li, W. & Liu, T. Time varying and condition adaptive hidden Markov model for tool wear state estimation and remaining useful life prediction in micro-milling. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 131, 689–702 (2019).
Zhang, J., Starly, B., Cai, Y., Cohen, P. H. & Lee, Y. S. Particle learning in online tool wear diagnosis and prognosis. J. Manuf. Process. 28, 457–463 (2017).
Kilickap, E., Yardimeden, A. & Hışman Çelik, Y. Mathematical modelling and optimization of cutting force, tool wear and surface roughness by using artificial neural network and response surface methodology in milling of Ti-6242S. Appl. Sci. 7 (10), 1064 (2017).
Zhang, X., Han, C., Luo, M. & Zhang, D. Tool wear monitoring for complex part milling based on deep learning. Appl. Sci. 10(19), 6916 (2020).
Hesser, D. F. & Markert, B. Tool wear monitoring of a retrofitted CNC milling machine using artificial neural networks. Manuf. Lett. 19, 1–4 (2019).
Bhattacharyya, P., Sengupta, D. & Mukhopadhyay, S. Cutting force-based real-time estimation of tool wear in face milling using a combination of signal processing techniques. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 21 (6), 2665–2683 (2007).
Sen, B., Mia, M., Mandal, U. K. & Mondal, S. P. GEP-and ANN-based tool wear monitoring: A virtually sensing predictive platform for MQL-assisted milling of Inconel 690. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 105(1), 395–410 (2019).
Khajavi, M. N., Nasernia, E. & Rostaghi, M. Milling tool wear diagnosis by feed motor current signal using an artificial neural network. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 30, 4869–4875 (2016).
García-Nieto, P. J., García-Gonzalo, E., Vilán Vilán, J. A. & Segade Robleda, A. A new predictive model based on the PSO-optimized support vector machine approach for predicting the milling tool wear from milling runs experimental data. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 86, 769–780 (2016).
Guo, J., Li, A. & Zhang, R. Tool condition monitoring in milling process using multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis and support vector machine. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 110, 1445–1456 (2020).
Kothuru, A., Nooka, S. P. & Liu, R. Audio-based tool condition monitoring in milling of the workpiece material with the hardness variation using support vector machines and convolutional neural networks. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 140(11), 111006 (2018).
Gomes, M. C., Brito, L. C., da Silva, M. B. & Duarte, M. A. V. Tool wear monitoring in micromilling using support vector machine with vibration and sound sensors. Precis. Eng. 67, 137–151 (2021).
Kong, D., Chen, Y. & Li, N. Gaussian process regression for tool wear prediction. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 104, 556–574 (2018).
Zhang, C., Wang, W. & Li, H. Tool wear prediction method based on symmetrized dot pattern and multi-covariance Gaussian process regression. Measurement 189, 110466 (2022).
Wang, G., Qian, L. & Guo, Z. Continuous tool wear prediction based on Gaussian mixture regression model. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 66, 1921–1929 (2013).
Ying, S., Sun, Y., Fu, C., Lin, L. & Zhang, S. Grey wolf optimization based support vector machine model for tool wear recognition in fir-tree slot broaching of aircraft turbine discs. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 36(12), 6261–6273 (2022).
Chuo, Y. S. et al. Artificial intelligence enabled smart machining and machine tools. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 36(1), 1–23 (2022).
Zhao, J. W., Guo, S. J., Ma, L., Kong, H. Q. & Zhang, N. Tool wear monitoring based on an improved convolutional neural network. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 37(4), 1949–1958 (2023).
Liao, C. W., Lee, M. T. & Liu, Y. C. A thermal deformation estimation method for high precision machine tool spindles based on the convolutional neural network. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 37(6), 3151–3162 (2023).
Sanjeevi, B. & Loganathan, K. Synthesis of multi wall carbon nanotubes nanofluid by using two step method. Therm. Sci. 24 (1 Part B), 519–524 (2020).
Srivastava, A. & Sahai, P. Vegetable oils as lube basestocks: A review. Afr. J. Biotechnol., 12(9). (2013).
Patel, N. S., Parihar, P. L. & Makwana, J. S. Parametric optimization to improve the machining process by using Taguchi method: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 47, 2709–2714 (2021).
Karna, S. K. & Sahai, R. An overview on Taguchi method. Int. J. Eng. Math. Sci. 1(1), 1–7 (2012).
Sun, S., Jiang, Z., Li, L., Wang, J. & Song, S. DEM analysis on rock-breaking impact effect of shield disc cutter in typical soft and hard composite strata. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.3991 (2025).
Yeo, C., Kim, B. C., Cheon, S., Lee, J. & Mun, D. Machining feature recognition based on deep neural networks to support tight integration with 3D CAD systems. Sci. Rep. 11 (1), 22147 (2021).
Dhumal, A., Kulkarni, A., Ambhore, N. & Karvinkoppa, M. Investigating Thermal Performance of Substrate Board through Forced Convection and Machine Learning.
Sun, S. Q. et al. Prediction model for rock-breaking force and wear of large‐diameter shield disc cutters in hard rock stratum. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 49(17), 4076–4090 (2025).
Wang, M., Zhou, D. & Chen, M. Hybrid variable monitoring: An unsupervised process monitoring framework with binary and continuous variables. Automatica 147, 110670 (2023).
Manikanta, J. E., Abdullah, M., Ambhore, N. & Kotteda, T. K. Analysis of machining performance in turning with trihybrid nanofluids and minimum quantity lubrication. Sci. Rep. 15(1), 12194 (2025).
Cheng, M. et al. Prediction and evaluation of surface roughness with hybrid kernel extreme learning machine and monitored tool wear. J. Manuf. Process. 84, 1541–1556 (2022).
Song, D. N., Tang, W. C., Zhao, Y. N., Zhong, Y. G. & Ma, J. W. Convolution-based velocity-smoothing principle and its application to real-time parametric curve interpolation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. https://doi.org/10.1109/tase.2025.3625244 (2025).
Liu, G., Su, Z., Luo, B. & Zhu, Y. GSLI-RTMdet: An automatic nondestructive detection method for internal defects in gas-insulated switchgear X‐DR images. High Voltage https://doi.org/10.1049/hve2.70044 (2025).
Cao, C. et al. Prediction and optimization of surface roughness for laser-assisted machining SiC ceramics based on improved support vector regression. Micromachines 13 (9), 1448 (2022).
Arun, M. & Gopan, G. Effects of natural light on improving the lighting and energy efficiency of buildings: Toward low energy consumption and CO2 emission. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 20, 1047–1056 (2025).
Asilturk, I., Kahramanli, H. & Mounayri, H. E. Prediction of cutting forces and surface roughness using artificial neural network (ANN) and support vector regression (SVR) in turning 4140 steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 28(8), 980–986 (2012).
Maheshwary, P. B., Handa, C. C. & Nemade, K. R. A comprehensive study of effect of concentration, particle size and particle shape on thermal conductivity of titania/water based nanofluid. Appl. Therm. Eng. 119, 79–88 (2017).
Sarıkaya, M. & Güllü, A. Multi-response optimization of minimum quantity lubrication parameters using Taguchi-based grey relational analysis in turning of difficult-to-cut alloy Haynes 25. J. Clean. Prod. 91, 347–357 (2015).
Mia, M., Gupta, M. K., Singh, G., Królczyk, G. & Pimenov, D. Y. An approach to cleaner production for machining hardened steel using different cooling-lubrication conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 187, 1069–1081 (2018).
Marquardt, E. D., Le, J. P. & Radebaugh, R. Cryogenic material properties database. Cryocoolers 11, 681–687 (2002).
Bhatt, A., Attia, H., Vargas, R. & Thomson, V. Wear mechanisms of WC coated and uncoated tools in finish turning of Inconel 718. Tribol. Int. 43 (5–6), 1113–1121 (2010).
Boothroyd, G. Fundamentals of metal machining and machine tools Vol. 28 (Crc, 1988).
Gopan, G., Arun, M. & Vembu, S. Comparison of dimple tube with flat plate collector for solar water heater by using carbon nanofluid. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 20, 820–833 (2025).
Das, S. R., Kumar, A. & Dhupal, D. Surface roughness analysis of hardened steel using TiN coated ceramic inserts. Int. J. Mach. Mach. Mater. 17(1), 22–38 (2015).
Arun, M., Barik, D. & Chandran, S. S. Exploration of material recovery framework from waste–A revolutionary move towards clean environment. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 18, 100589 (2024).
Sen, B., Mia, M., Mandal, U. K., Dutta, B. & Mondal, S. P. Multi-objective optimization for MQL-assisted end milling operation: An intelligent hybrid strategy combining GEP and NTOPSIS. Neural Comput. Appl. 31, 8693–8717 (2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author Contributions: Omar Almomani and B. Venkatesh conceived the study, formulated the research objectives, and supervised the overall research work. Shivam P. Chaudhary and Akanksha Mishra were responsible for data curation, statistical analysis, and interpretation of results. Sujai S and Shahbaz Juneja carried out the experimental investigations and contributed to data acquisition. Premananda Pradhan and S. P. Venkatesan prepared the initial draft of the manuscript and assisted in result validation. Abhijit Bhowmik contributed to methodological development, technical guidance, and critical evaluation of the study. Yalew Tamene was involved in the review of related literature, manuscript editing, and refinement. All authors critically reviewed the manuscript, contributed intellectually to the discussion, and approved the final version for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent for publication
All authors have given their consent for the publication of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Almomani, O., Venkatesh, B., Chaudhary, S.P. et al. Intelligent tool wear monitoring using XGBoost, SVR, and DNN models in NMQL environment. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-40968-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-40968-8