Abstract
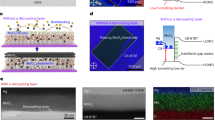
Amorphous oxide semiconductors could be used as thin channel materials in future back-end-of-line-compatible electronics. However, thin body amorphous materials suffer from Joule heating due to the strong scattering of electrons and phonons from extensive local disorder, which can lead to device failure in high-speed power-intensive applications. Here we show that the electrical and thermal transport properties of amorphous indium tin oxide can be enhanced using a silicon carbide substrate. Using this approach, we create top-gate transistors that have a channel length of 120 nm and exhibit negligible performance degradation under high electric fields and temperatures of up to 125 °C. We show that the devices can offer a cutoff frequency of 103 GHz and a maximum oscillation frequency of 125 GHz. Furthermore, our indium tin oxide power amplifiers provide a high output power density of 0.69 W mm−1 and a power-added efficiency of 24.1% at 12 GHz.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the plots within this paper are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Li, S. et al. Nanometre-thin indium tin oxide for advanced high-performance electronics. Nat. Mater. 18, 1091–1097 (2019).
Li, Q. et al. BEOL-compatible high-performance a-IGZO transistors with record high Ids,max = 1,207 μA/μm and on-off ratio exceeding 1011 at Vds = 1 V. In Proc. 2022 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 42–45 (IEEE, 2022).
Hu, Q. et al. True nonvolatile high-speed DRAM cells using tailored ultrathin IGZO. Adv. Mater. 35, 2210554 (2023).
Ye, H. et al. Double-gate W-doped amorphous indium oxide transistors for monolithic 3D capacitorless gain cell eDRAM. In Proc. 2020 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 613–616 (IEEE, 2020).
Belmonte, A. et al. Tailoring IGZO-TFT architecture for capacitorless DRAM, demonstrating >103 s retention, >1011 cycles endurance and Lg scalability down to 14 nm. In Proc. 2021 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 226-229 (IEEE, 2021).
Duan, X. et al. Novel vertical channel-all-around (CAA) IGZO FETs for 2T0C DRAM with high density beyond 4F2 by monolithic stacking. In Proc. 2021 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 222–225 (IEEE, 2021).
Hu, Q. et al. Optimized IGZO FETs for capacitorless DRAM with retention of 10 ks at RT and 7 ks at 85 °C at zero Vhold with sub-10 ns speed and 3-bit operation. In Proc. 2022 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 619–622 (IEEE, 2022).
Wang, C. et al. Extremely scaled bottom gate a-IGZO transistors using a novel patterning technique achieving record high Gm of 479.5 μS/μm (VDS of 1 V) and fT of 18.3 GHz (VDS of 3 V). In Proc. 2022 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology 294–295 (IEEE, 2022).
Zheng, D. et al. Ultrathin atomic-layer-deposited In2O3 radio-frequency transistors with record high fT of 36 GHz and BEOL compatibility. In Proc. 2023 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology T11-1 (IEEE, 2023).
Hu, Q. et al. Ultrashort 15-nm flexible radio frequency ITO transistors enduring mechanical and temperature stress. Sci. Adv. 8, eade4075 (2022).
Chasin, A. et al. Understanding and modelling the PBTI reliability of thin-film IGZO transistors. In Proc. 2021 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 657–660 (IEEE, 2021).
Kong, Q. et al. New insights into the impact of hydrogen evolution on the reliability of IGZO FETs: experiment and modeling. In Proc. 2022 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 699–702 (IEEE, 2022).
Zhang, J. et al. Back-end-of-line-compatible scaled InGaZnO transistors by atomic layer deposition. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 69, 147–151 (2023).
Shen, Y. et al. Gate stack engineering in MoS2 field-effect transistor for reduced channel doping and hysteresis effect. Adv. Electron. Mater. 7, 2000395 (2021).
Si, M., Lin, Z., Chen, Z. & Ye, P. D. High-performance atomic-layer-deposited indium oxide 3-D transistors and integrated circuits for monolithic 3-D integration. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 68, 6605–6609 (2021).
Wahid, S. et al. First-demonstration of top-gated ITO transistors: effect of channel passivation. In Proc. 2022 Device Research Conference (DRC) 1–2 (2022).
Gu, C. et al. High-performance short-channel top-gate indium-tin-oxide transistors by optimized gate dielectric. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 44, 837–840 (2023).
Liao, P. et al. Thermal studies of BEOL-compatible top-gated atomically thin ALD In2O3 FETs. In Proc. 2022 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology 322–323 (IEEE, 2022).
Jeong, C., Datta, S. & Lundstrom, M. Thermal conductivity of bulk and thin-film silicon: a Landauer approach. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 093708 (2012).
Kwon, S., Wingert, M. C., Zheng, J., Xiang, J. & Chen, R. Thermal transport in Si and Ge nanostructures in the ‘confinement’ regime. Nanoscale 8, 13155–13167 (2016).
Zhou, W. et al. Thermal conductivity of amorphous materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 1903829 (2020).
Scott, E. A. et al. Simultaneous thickness and thermal conductivity measurements of thinned silicon from 100 nm to 17 μm. Appl. Phys. Lett. 118, 202108 (2021).
Jugdersuren, B. et al. The effect of ultrasmall grain sizes on the thermal conductivity of nanocrystalline silicon thin films. Commun. Phys. 4, 169 (2021).
Yoshikawa, T. et al. Thermal conductivity of amorphous indium-gallium-zinc oxide thin films. Appl. Phys. Express 6, 021101 (2013).
Kim, C. K. et al. Electrothermal annealing (ETA) method to enhance the electrical performance of amorphous-oxide-semiconductors (AOS) thin-film transistors (TFTs). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 23820–23826 (2016).
Olson, D. H. et al. Size effects on the cross-plane thermal conductivity of transparent conducting indium tin oxide and fluorine tin oxide thin films. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 9, 51–57 (2019).
Cai, L. et al. Investigation of self-heating effect on stacked nanosheet GAA transistors. In Proc. 2018 International Symposium on VLSI Technology, Systems and Application (VLSI-TSA) 1–2 (2018).
Charnas, A. et al. Record RF performance of ultra-thin indium oxide transistors with buried-gate structure. In Proc. 2022 Device Research Conference (DRC) 1–2 (2022).
Khanna, A. et al. BEOL compatible ferroelectric routers for rum-time reconfigurable compute-in-memory accelerators. In Proc. 2022 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology 240–241 (IEEE, 2022).
Liao, P., Si, M., Zhang, Z., Lin, Z. & Ye, P. D. Realization of maximum 2 A/mm drain current on top-gate atomic-layer-thin indium oxide transistors by thermal engineering. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 69, 147–151 (2021).
Liao, P. et al. Transient thermal and electrical co-optimization of BEOL top-gated ALD In2O3 FETs on various thermally conductive substrate including diamond. In Proc. 2022 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 286–289 (IEEE, 2022).
Yu, X. et al. High-voltage β-Ga2O3 RF MOSFETs with a shallowly-implanted 2DEG-like channel. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 44, 1060–1063 (2023).
Pop, E., Dutton, R. & Goodson, K. Thermal analysis of ultra-thin body scaling. In Proc. 2003 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 883–886 (IEEE, 2003).
Qian, X., Zhou, J. & Chen, G. Phonon-engineered extreme thermal conductivity materials. Nat. Mater. 20, 1188–1201 (2021).
Salamin, S., Santen, V. M. V., Rapp, M., Henkel, J. & Amrouch, H. Minimizing excess timing guard banding under transistor self-heating through biasing at zero-temperature coefficient. IEEE Access 9, 30687–30697 (2021).
Hu, Q. et al. First demonstration of top-gate indium-tin-oxide RF transistors with record high cut-off frequency of 48 GHz, Id of 2.32 mA/μm and gm of 900 μS/μm on SiC substrate with superior reliability at 85 °C. In Proc. 2023 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 39.6 (IEEE, 2023).
Teppati, V., Ferrero, A. & Sayed, M. Modern RF and Microwave Measurement Techniques (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2013).
Liao, L. et al. High-speed graphene transistors with a self-aligned nanowire gate. Nature 467, 305–308 (2010).
Shi, H. et al. Radiofrequency transistors based on aligned carbon nanotubes arrays. Nat. Electron. 4, 405–415 (2021).
Wu, Y. et al. 200 GHz maximum oscillation frequency in CVD graphene radio frequency transistors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 25645–25649 (2016).
Zheng, D. et al. First demonstration of BEOL-compatible ultrathin atomic-layer-deposited InZnO transistors with GHz operation and record high bias-stress stability. In Proc. 2022 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 78–81 (IEEE, 2022).
Green, A. J. et al. β-Ga2O3 MOSFETs for radio frequency operation. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 38, 790–793 (2017).
Chabak, K. W. et al. Sub-micron gallium oxide radio frequency field-effect transistors. In Proc. 2018 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on Advanced Materials and Processes for RF and THz Applications (IMWS-AMP) 1–3 (IEEE, 2018).
Zhang, Y. et al. Demonstration of high mobility and quantum transport in modulation-doped β-(AlxGa1−x)2O3/Ga2O3 heterostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 112, 173502 (2018).
Zhang, Y. et al. Evaluation of low-temperature saturation velocity in β-(AlxGa1−x)2O3/Ga2O3 modulation-doped field-effect transistors. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 66, 1574–1578 (2019).
Lv, Y. et al. Oxygen annealing impact on β-Ga2O3 MOSFETs: Improved pinch-off characteristic and output power density. Appl. Phys. Lett. 117, 133503 (2020).
Moser, N. et al. Toward high voltage radio frequency devices in β-Ga2O3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 117, 242101 (2020).
Saha, C. N. et al. Scaled β-Ga2O3 thin channel MOSFET with 5.4 MV/cm average breakdown field and near 50 GHz fMAX. Appl. Phys. Lett. 122, 182106 (2023).
Yu, X. et al. Heterointegrated Ga2O3-on-SiC RF MOSFETs with fT/fmax of 47/51 GHz by ion-cutting process. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 44, 1951–1954 (2023).
Singh, M. et al. Pulsed large signal RF performance of field-plated Ga2O3 MOSFETs. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 39, 1572–1575 (2018).
Moser, N. A. et al. Pulsed power performance of β-Ga2O3 MOSFETs at L-band. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 41, 989–992 (2020).
Schwierz, F. & Liou, J. J. Modern Microwave Transistors: Theory, Design and Performance (Wiley, 2003).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant no. 2020AAA0109005) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 62425402, 92364203 and 62090034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.W. proposed and supervised the project. Q.H. fabricated the devices and carried out the electrical measurements. S.Z., Y.Z. and C.G. contributed to the d.c. characterizations. S.L. contributed to the device structure characterizations. Q.H., Y.W. and R.H. analysed the data. Q.H. and Y.W. co-wrote the paper. All authors contributed to discussions on the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Electronics thanks Tiangui You and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–8, Notes 1–10 and Tables 1–3.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Q., Zhu, S., Zhu, Y. et al. Amorphous indium tin oxide transistors for power amplification above 10 GHz. Nat Electron 8, 803–809 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-025-01447-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-025-01447-6