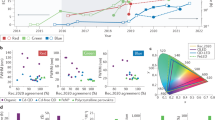
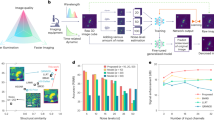
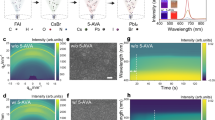
Abstract
Metal halide perovskites could form the basis of future display technology due to their powerful optical properties. However, the commercialization of electroluminescent perovskites has been hindered by key challenges, including limited operational lifetime and instability in blue emission. Here we highlight the potential of perovskites in colour conversion displays. We examine the particular advantages of perovskite materials as colour conversion layers: narrow emission spectrum, high absorption coefficients, high-brightness operation, photon recycling and ease of manufacturing. We provide a framework for the development of RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances)-compliant and colour-filter-free perovskite-based colour conversion displays and offer guidelines for commercialization. We also explore the potential of using perovskite colour conversion layers to create advanced augmented reality and virtual reality technologies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Zhu, R., Luo, Z., Chen, H., Dong, Y. & Wu, S.-T. Realizing Rec. 2020 color gamut with quantum dot displays. Opt. Express 23, 23680–23693 (2015).
Dai, X., Deng, Y., Peng, X. & Jin, Y. Quantum-dot light-emitting diodes for large-area displays: towards the dawn of commercialization. Adv. Mater. 29, 1607022 (2017).
Shirasaki, Y., Supran, G. J., Bawendi, M. G. & Bulović, V. Emergence of colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting technologies. Nat. Photon. 7, 13–23 (2013).
Chen, J., Hardev, V., Hartlove, J., Hofler, J. & Lee, E. 66.1: Distinguised paper: A high-efficiency wide-color-gamut solid-state backlight system for LCDs using quantum dot enhancement film. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 43, 895–896 (2012).
Yin, M. et al. Color-stable WRGB emission from blue OLEDs with quantum dots-based patterned down-conversion layer. Org. Electron. 62, 407–411 (2018).
Hu, Z. et al. Inkjet printed uniform quantum dots as color conversion layers for full-color OLED displays. Nanoscale 12, 2103–2110 (2020).
Xuan, T., Shi, S., Wang, L., Kuo, H.-C. & Xie, R.-J. Inkjet-printed quantum dot color conversion films for high-resolution and full-color micro light-emitting diode displays. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11, 5184–5191 (2020).
Li, Y. et al. Microfluidics-based quantum dot color conversion layers for full-color micro-LED display. Appl. Phys. Lett. 118, 173501 (2021).
Han, T.-H. et al. A roadmap for the commercialization of perovskite light emitters. Nat. Rev. Mater. 7, 757–777 (2022).
Wu, X.-G., Ji, H., Yan, X. & Zhong, H. Industry outlook of perovskite quantum dots for display applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 813–816 (2022).
Lu, M. et al. Metal halide perovskite light-emitting devices: promising technology for next-generation displays. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1902008 (2019).
Protesescu, L. et al. Nanocrystals of cesium lead halide perovskites (CsPbX3, X = Cl, Br, and I): novel optoelectronic materials showing bright emission with wide color gamut. Nano Lett. 15, 3692–3696 (2015).
Li, G. et al. Color-conversion displays: current status and future outlook. Light Sci. Appl. 13, 301 (2024).
Sadhukhan, P., Kim, M. S., Baek, S.-D. & Myoung, J.-M. Super-bright green perovskite light-emitting diodes using ionic liquid additives. Small Methods 7, 2201407 (2023).
Liu, A. et al. Optimizing perovskite surfaces to enhance post-treatment for efficient blue mixed-halide perovskite light-emitting diodes. Adv. Mater. 36, 2414788 (2024).
Li, N. et al. Diammonium-mediated perovskite film formation for high-luminescence red perovskite light-emitting diodes. Adv. Mater. 34, 2202042 (2022).
Yuan, F. et al. Color-pure red light-emitting diodes based on two-dimensional lead-free perovskites. Sci. Adv. 6, eabb0253 (2020).
Jiang, X., Fan, Z., Luo, L. & Wang, L. Advances and challenges in heavy-metal-free InP quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Micromachines 13, 709 (2022).
Rabouw, F. T. & de Mello Donega, C. Excited-state dynamics in colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals. Top. Curr. Chem. 374, 58 (2016).
Wolf, M. & Berezovsky, J. Homogeneous and inhomogeneous sources of optical transition broadening in room temperature CdSe/ZnS nanocrystal quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 143105 (2014).
Xie, B. et al. Precise optical modeling of quantum dots for white light-emitting diodes. Sci. Rep. 7, 16663 (2017).
Osinski, J. & Palomaki, P. Quantum dot design criteria for colour conversion in microLED displays. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 50, 34–37 (2019).
Dey, A. et al. State of the art and prospects for halide perovskite nanocrystals. ACS Nano 15, 10775–10981 (2021).
De Roo, J. et al. Highly dynamic ligand binding and light absorption coefficient of cesium lead bromide perovskite nanocrystals. ACS Nano 10, 2071–2081 (2016).
Herz, L. M. Charge-carrier dynamics in organic–inorganic metal halide perovskites. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 67, 65–89 (2016).
Song, H. et al. A universal perovskite nanocrystal ink for high-performance optoelectronic devices. Adv. Mater. 35, 2209486 (2023).
Liu, X.-K. et al. Metal halide perovskites for light-emitting diodes. Nat. Mater. 20, 10–21 (2021).
Wei, Q. et al. Recent progress in metal halide perovskite micro- and nanolasers. Adv. Opt. Mater. 7, 1900080 (2019).
Manser, J. S. & Kamat, P. V. Band filling with free charge carriers in organometal halide perovskites. Nat. Photon. 8, 737–743 (2014).
Zhao, B. et al. High-efficiency perovskite–polymer bulk heterostructure light-emitting diodes. Nat. Photon. 12, 783–789 (2018).
Cho, C. et al. The role of photon recycling in perovskite light-emitting diodes. Nat. Commun. 11, 611 (2020).
Cho, C., Sun, Y., You, J., Cui, L.-S. & Greenham, N. C. Enhanced photon recycling enables efficient perovskite light-emitting diodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34, 2411556 (2024).
Murray, C. B., Norris, D. J. & Bawendi, M. G. Synthesis and characterization of nearly monodisperse CdE (E = sulfur, selenium, tellurium) semiconductor nanocrystallites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115, 8706–8715 (1993).
Vighnesh, K., Wang, S., Liu, H. & Rogach, A. L. Hot-injection synthesis protocol for green-emitting cesium lead bromide perovskite nanocrystals. ACS Nano 16, 19618–19625 (2022).
Zhang, F. et al. Brightly luminescent and color-tunable colloidal CH3NH3PbX3 (X = Br, I, Cl) quantum dots: potential alternatives for display technology. ACS Nano 9, 4533–4542 (2015).
Al-Milaji, K. N. & Zhao, H. New perspective of mitigating the coffee-ring effect: interfacial assembly. J. Phys. Chem. C 123, 12029–12041 (2019).
Park, H. et al. Efficient quantum dot color conversion layer with mixed spherical/rod-shaped scattering particles. ACS Appl. Opt. Mater. 1, 289–297 (2023).
Fink, Y. et al. A dielectric omnidirectional reflector. Science 282, 1679–1682 (1998).
Ooi, Z. Y. et al. Strong angular and spectral narrowing of electroluminescence in an integrated Tamm-plasmon-driven halide perovskite LED. Nat. Commun. 15, 5802 (2024).
Pourdavoud, N. et al. Room-temperature stimulated emission and lasing in recrystallized cesium lead bromide perovskite thin films. Adv. Mater. 31, 1903717 (2019).
McGroddy, K. et al. Directional emission control and increased light extraction in GaN photonic crystal light emitting diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 103502 (2008).
Kumar, S. et al. Anisotropic nanocrystal superlattices overcoming intrinsic light outcoupling efficiency limit in perovskite quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nat. Commun. 13, 2106 (2022).
Sim, S. et al. Color gamut change by optical crosstalk in high-resolution organic light-emitting diode microdisplays. Opt. Express 30, 24155–24165 (2022).
Directive 2011/65/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 8 June 2011 on the Restriction of the Use of Certain Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment (Recast) Text with EEA Relevance EUR-Lex Document 32011L0065 (European Union, 2011); https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2011/65/oj/eng
Kong, Q. et al. Phase engineering of cesium manganese bromides nanocrystals with color-tunable emission. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 19653–19659 (2021).
Han, D. et al. Tautomeric mixture coordination enables efficient lead-free perovskite LEDs. Nature 622, 493–498 (2023).
Lu, Q. et al. A review on encapsulation technology from organic light emitting diodes to organic and perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2100151 (2021).
Chen, S. et al. Trapping lead in perovskite solar modules with abundant and low-cost cation-exchange resins. Nat. Energy 5, 1003–1011 (2020).
Chen, B. et al. Recycling lead and transparent conductors from perovskite solar modules. Nat. Commun. 12, 5859 (2021).
Samsung Display introduces innovative quantum dot ink regeneration technology. Samsung Display Newsroom https://global.samsungdisplay.com/31318 (2024).
Alberola-Borràs, J.-A. et al. Perovskite photovoltaic modules: life cycle assessment of pre-industrial production process. iScience 9, 542–551 (2018).
Zhang, M. et al. Towards sustainable perovskite light-emitting diodes. Nat. Sustain. 8, 315–324 (2025).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to K. Kang (Seoul National University) for his comments and suggestions during the overall review of this paper. This work was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grants funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (RS-2025-00523067, NRF-2022R1A2C4002248, 2021M3H4A1A02049006, 2022H1D3A3A01077343 and RS-2024-00337375). This work was partly supported by a Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) grant funded by the Korea Government (MOTIE) (RS-2024-00418086, HRD Program for Industrial Innovation). C.C. also acknowledges the Korea Basic Science Institute (National Research Facilities and Equipment Center) (RS-2024-00403574) funded by the Korea government (Ministry of Science and ICT). This work received funding from the Engineering and Physical Science Research Council (EPSRC), UK, through projects EP/V061747/1 and EP/V06164X/1. It was also supported by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics under projects SRFC-TC2103-04 and SRFC-MA2302-02.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.K., E.D.J. and B.R.L. conceived of the project and wrote the initial draft of the paper. J.K. and J.Y. drew the figures. J.Y. conducted the optical simulations and collected the relevant data for Supplementary Information. J.L. provided overall feedback and helped improve the clarity of the paper. B.C.P. supported literature research. H.J.S. and R.H.F. provided scientific advice and critical discussion throughout the project. C.C. and B.R.L. supervised the project and led the overall research direction. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final version of the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
H.J.S. and R.H.F. are co-founders of Helio Display Materials Ltd, a company commercializing perovskite nanocrystals for colour conversion applications in displays.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Electronics thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Note 1, Figs. 1–4 and Table 1.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Jung, E.D., You, J. et al. Perovskites for next-generation colour conversion displays. Nat Electron 8, 886–894 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-025-01456-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-025-01456-5