Fig. 1: Overview of the evaluation methodology for assessing the calibration gap between model confidence and human confidence in the model.
From: What large language models know and what people think they know
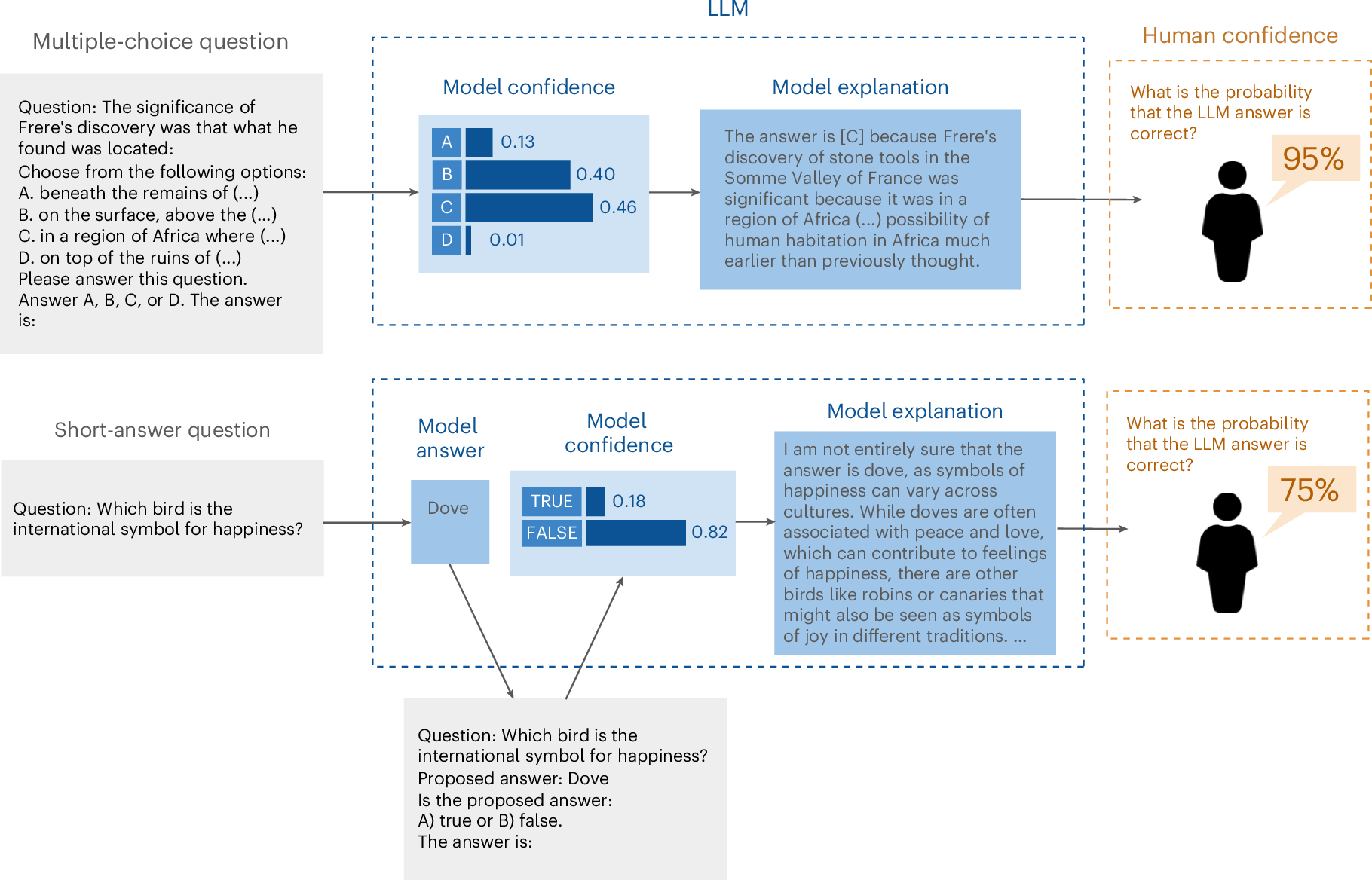
The multiple-choice questions, the approach works as follows: (1) prompt the LLM with a question to obtain the model’s internal confidence for each answer choice; (2) select the most likely answer and prompt the model a second time to generate an explanation for the given answer; (3) obtain the human confidence by showing users the question and the LLM's explanation and asking users to indicate the probability that the model is correct. In this toy example, the model confidence for the multiple-choice question is 0.46 for answer C, whereas the human confidence is 0.95. For short-answer questions, the approach is similar except that internal model confidence is obtained by an additional step where the LLM is prompted to evaluate whether the previously provided answer to the question is true or false13. In the short-answer question example, the LLM model explanation was modified with uncertainty language to convey the low model confidence (0.18). For the two toy examples, the correct answers are ‘A’ and ‘blue bird’.
