Abstract
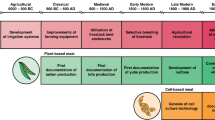
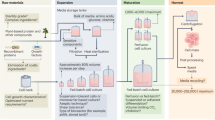
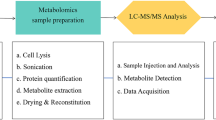
For commercial viability, cultivated meats require scientifically informed approaches to identify and manage hazards and risks. Here we discuss food safety in the rapidly developing field of cultivated meat as it shifts from lab-based to commercial scales. We focus on what science-informed risk mitigation processes can be implemented from neighbouring fields. We case-study pre-market safety assessments from UPSIDE Foods, GOOD Meat and Vow Group using publicly available dossiers. Quality control and safety assurance practices need to be established and standardized for cell lines and food-grade cell banks.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eat Just Inc. gets approval in Singapore for lab-grown chicken. Food Safety News https://www.foodsafetynews.com/2020/12/eat-just-inc-gets-approval-in-singapore-for-lab-grown-chicken/ (2020).
UPSIDE is approved for sale in the US! Here’s what you need to know. UPSIDE Foods https://upsidefoods.com/blog/upside-is-approved-for-sale-in-the-us-heres-what-you-need-to-know (2023).
GOOD Meat gets full approval in the U.S. for cultivated meat. GOOD Meat https://www.goodmeat.co/all-news/good-meat-gets-full-approval-in-the-us-for-cultivated-meat (2023).
Aleph Farms granted world’s first regulatory approval for cultivated beef. Aleph Farms https://aleph-farms.com/journals/aleph-farms-granted-worlds-first-regulatory-approval-for-cultivated-beef/ (2024).
Requirements for the Safety Assessment of Novel Foods and Novel Food Ingredients (SFA, 2023); https://www.sfa.gov.sg/docs/default-source/regulatory-standards-frameworks-and-guidelines/requirements-for-the-safety-assessment-of-novel-foods-and-novel-food-ingredients.pdf
Food Act 2014 (MPI, 2023); https://www.legislation.govt.nz/act/public/2014/0032/159.0/DLM2995811.html
Coecke, S. et al. Guidance on good cell culture practice: a report of the second ECVAM task force on good cell culture practice. Altern. Lab. Anim. 33, 261–287 (2005).
Hallman, W. K., Hallman, W. K. & Hallman, E. E. Cell-based, cell-cultured, cell-cultivated, cultured, or cultivated. What is the best name for meat, poultry, and seafood made directly from the cells of animals? npj Sci. Food 7, 62 (2023).
Premarket Notice for Integral Tissue Cultured Poultry Meat (UPSIDE Foods, 2021); https://www.fda.gov/media/163262/download
Dossier in Support of the Safety of Good Meat Cultured Chicken as a Human Food Ingredient (GOOD Meat, 2022); https://www.fda.gov/media/166346/download
Vow Cultured Quail: Novel Food Dossier Food Standards Australia New Zealand Update (Vow, 2023); https://consultations.foodstandards.gov.au/sas/a1269-cultured-quail-as-a-novel-food/user_uploads/application---cultured-quail-as-a-novel-food.docx.pdf
Food Safety Aspects of Cell-Based Meats (FAO and WHO, 2023); https://doi.org/10.4060/cc4855en
Valiant, W. G., Cai, K. & Vallone, P. M. A history of adventitious agent contamination and the current methods to detect and remove them from pharmaceutical products. Biologicals 80, 6–17 (2022).
McNamara, E. & Bomkamp, C. Cultivated meat as a tool for fighting antimicrobial resistance. Nat. Food 3, 791–794 (2022).
Whaley, D. et al. Cryopreservation: an overview of principles and cell-specific considerations. Cell Transplant. 30, 0963689721999617 (2021).
Ladics, G. S. et al. Bioinformatics and the allergy assessment of agricultural biotechnology products: industry practices and recommendations. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 60, 46–53 (2011).
Ong, K. J. et al. Food safety considerations and research priorities for the cultured meat and seafood industry. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 20, 5421–5448 (2021).
Peppou, G. Vow is officially on market. Medium https://medium.com/vow-food/vow-is-officially-on-market-f2b3028abb5e (2024).
Animal Products Regulations 2021 (MPI, 2021); https://www.legislation.govt.nz/regulation/public/2021/0400/latest/LMS520972.html
Animal Products Notice: Production, Supply and Processing (MPI, 2023). https://www.mpi.govt.nz/dmsdocument/50182-Animal-Products-Notice-Production-Supply-and-Processing
Hepburn, P. et al. The application of post-market monitoring to novel foods. Food Chem. Toxicol. 46, 9–33 (2008).
Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 November 2015 on Novel Foods, Amending Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 258/97 of the European Parliament and of the Council and Commission Regulation (EC) No 1852/2001 (European Parliament and the Council of the European Union, 2015); https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32015R2283
Review of Novel Food Standard (FSANZ, 2007); https://www.foodstandards.gov.au/sites/default/files/food-standards-code/proposals/Documents/P291%20Novel%20Food%20Review%20FAR%20FINAL.pdf
Recommendations for the Evaluation of Animal Cell Cultures as Substrates for the Manufacture of Biological Medicinal Products and for the Characterization of Cell Banks WHO Technical Report Series No. 978 (WHO, 2010); https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/biologicals/documents/trs_978_annex_3.pdf?sfvrsn=fe61af77_3&download=true
Guidance for Industry: Characterization and Qualification of Cell Substrates and Other Biological Materials Used in the Production of Viral Vaccines for Infectious Disease Indications (US Department of Health and Human Services, 2010); https://www.fda.gov/media/78428/download
Singh, J. International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 6, 185–187 (2025).
Ye, J., Liu, Z. & Pollard, D. in ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation Guide (eds Teasdale, A. et al.) 337–344 (John Wiley & Sons, 2017); https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118971147.ch11
Viral Safety Evaluation of Biotechnology Products Derived from Cell Lines of Human or Animal Origin Q5A(R1) (International Conference On Harmonisation, 1999); https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q5A%28R1%29%20Guideline_0.pdf
Horbach, S. P. J. M. & Halffman, W. The ghosts of HeLa: how cell line misidentification contaminates the scientific literature. PLoS ONE 12, e0186281 (2017).
Cell-Based Food: Its Safety and its Future Role (FAO, 2023); https://doi.org/10.4060/cc6967en
Ong, K. J. et al. Cultured meat safety research priorities: regulatory and governmental perspectives. Foods 12, 2645 (2023).
Cell-Based Food and Precision Fermentation—Products, Safety and the Future Role (FAO, 2024); https://doi.org/10.4060/cd0311en
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ministry of Business and Innovation Smart Ideas grant (Catalyst: Strategic – New Zealand-Singapore Future Foods Research programme), Marsden Fund managed by Royal Society Te Apārangi, A*STAR Biomedical Research Council, A*STAR Bioprocessing Technology Institute, National Research Foundation Singapore, A*STAR AME Programmatic Fund, Singapore Food Agency, Good Food Institution Research Program, IAF, SMART CAMP, WisDM, Mechanobiology Institute of Singapore, AGS, Biomolecular Interaction Centre and The Riddet Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.Z.B. and O.J.O. conceptualized the Perspective and wrote the original draft preparation. L.S.W.L., H.Z., S.K.N., A.J., H.J.F.T., A.W., L.J.D. and R.C.J.D provided feedback and edits. All authors contributed to editing and revising the paper. L.J.D., H.Y. and R.C.J.D. acquired research funding to allow this work to be carried out. All authors reviewed and approved the final paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
O.J.O. and L.J.D. are co-founders, shareholders and employees of Opo Bio Limited, a cell line development company that specializes in high-quality cell lines for cultivated meat. H.Y. is the non-executive chairman, co-founder, and shareholder of Ants Innovate Pte Ltd. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Food thanks Craig Hedberg, Andreas Kurtz, Dhruv Raina and Jin Wang for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bennie, R.Z., Ogilvie, O.J., Loo, L.S.W. et al. A risk-based approach can guide safe cell line development and cell banking for scaled-up cultivated meat production. Nat Food 6, 25–30 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-024-01085-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43016-024-01085-9