Fig. 1: Association between the cumulative adherence to dietary patterns and the yearly rate of total chronic disease accumulation during a 15-year follow-up (N = 2,473).
From: Dietary patterns and accelerated multimorbidity in older adults
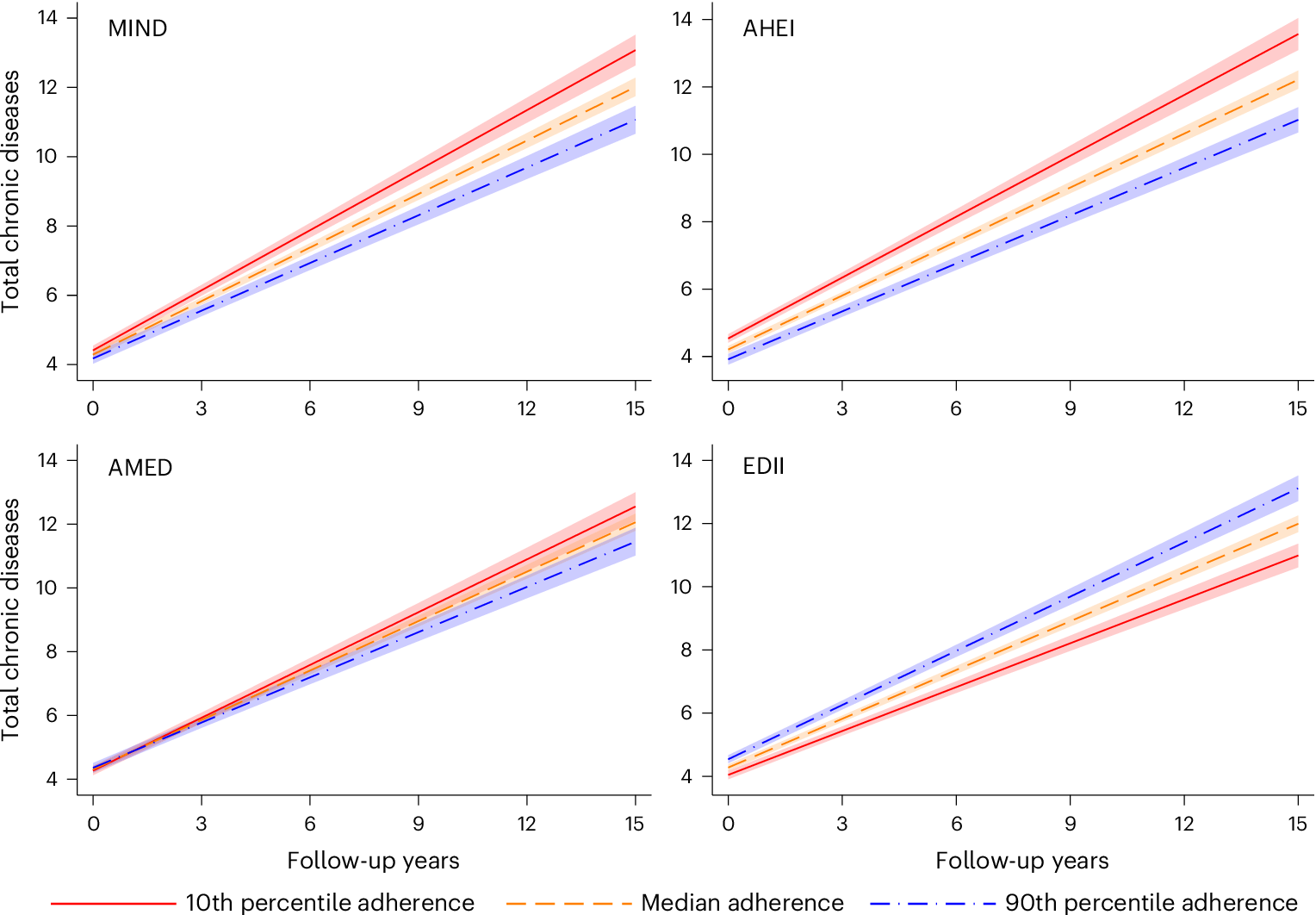
MIND: baseline range: 2–12; 1 s.d. = 1.74. AHEI: baseline range: 29.9–91.7; 1 s.d. = 9.82. AMED: baseline range: 0–9; 1 s.d. = 1.76. EDII: baseline range: −1.36 to 2.70; 1 s.d. = 0.30. Model: linear mixed model with random intercept and slope, adjusted by age (years), sex (male or female), living arrangements (alone or not), previous occupation (manual or non-manual worker), education (elementary, high school or university), tobacco smoking (never, former smoker, current smoker or unknown), physical activity (inadequate, health-enhancing, fitness-enhancing or unknown) and energy intake (kcal d−1). Data are presented as average predicted number of chronic diseases ± 95% CIs (shaded area).
