Abstract
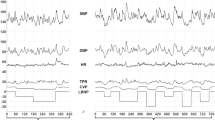
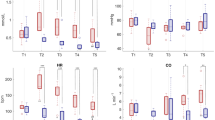
The arterial blood pressure, heart rate and electrocardiograph were recorded, and plasma electrolytes, arterial blood gases and pH, and plasma catecholamines were estimated in seven patients with physiologically complete cervical spinal cord transections who needed intermittent positive pressure ventilation (I.P.P.V.) or were undergoing urological surgery under general anaesthesia.
In the tetraplegics on I.P.P.V., bradycardia, and in two patients even cardiac arrest, occurred during tracheal suction, especially in the presence of hypoxia. In one tetraplegic being anaesthetised, cardiac arrest occurred during endotracheal intubation. This reflex bradycardia and cardiac arrest appeared to be due to a vago-vagal reflex, unopposed by sympathetic activity or by the pulmonary (inflation) vagal reflex. Atropine was effective in preventing this reflex.
In the tetraplegics undergoing urological surgery, severe hypertension resulting from visceral stimulation was effectively reduced by halothane. In these patients, control of arterial blood pressure with lower concentrations of halothane may also be achieved with I.P.P.V.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Angell-James, Jennifer & Daly, M De Burgh (1969). Cardiovascular responses in apnoeic asphyxia: role of arterial chemoreceptors and the modification of their effects by a pulmonary vagal inflation reflex. J. Physiol. (Lond.), 201, 87–104.
Bahlman, S H, Eger, E I, Jr., Halsey, M J, Stevens, W C, Shakespeare, T F, Smith, N T, Cromwell, T H & Fourcade, H (1972). The cardiovascular effects of halothane in man during spontaneous ventilation. Anesthesiol. 36, 494–502.
Burn, J H & Epstein, H G (1959). Hypotension due to halothane. Brit. J. Anaesth. 31, 199–204.
Burnstein, C L, Lo Pinto, F J & Newman, W (1950). Electrocardiographic studies during endotracheal intubation, 1: Effects during usual routine techniques. Anesthesiol. 11, 224–237.
Christensen, N J (1973). Plasma noradrenaline and adrenaline in patients with thyrotoxicosis and myxoedema. Clin. Sci. and Mol. Med. 45, 163–171.
Corbett, J L, Frankel, H L & Harris, P J (1971). Cardiovascular reflex responses to cutaneous and visceral stimuli in spinal man. J. Physiol. (Lond.), 215, 395–409.
Corbett, J L, Kerr, J H & Prys-Roberts, C (1969). Cardiovascular responses to aspiration of secretions from the respiratory tract in man. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 201, 41P–43P.
Daly, M de Burgh (1972). Interaction of cardiovascular reflexes. In Scientific Basis of Medicine, Eds. Gilliland, I. and Francis, J., pp. 307–332. Athlone Press.
Daly, M de Burgh & Scott, Mary J (1958). The effects of stimulation of the carotid body chemoreceptors on heart rate in the dog. J. Physiol. (Lond.), 144, 148–166.
Debarge, O, Christensen, N J, Corbett, J L, Eidelman, B H, Frankel, H L & Mathias, C J (1974). Plasma catecholamines in tetraplegics. Paraplegia, 12, 44–49.
Forbes, A M & Dally, F G (1970). Acute hypertension during induction of anaesthesia and endotracheal intubation in normotensive man. Brit. J. Anaesth. 42, 618–624.
Frankel, H L, Mathias, C J & Walsh, J J (1974). Blood pressure, plasma catecholamines and prostaglandins during artificial erection in a male tetraplegic. Paraplegia, 12, 205–211.
Gersh, B J, Prys-Roberts, C & Baker, A B (1972). The effects of halothane on the interactions between myocardial contractility, aortic impedance, and left ventricular performance, II: Aortic input impedance and the distribution of energy during ventricular ejection. Brit. J. Anaesth. 44, 767–1005.
Guttmann, L & Whitteridge, D (1947). Effects of bladder distension on autonomic mechanisms after spinal cord injuries. Brain, 70, 361–404.
Johnson, R H, Smith, A C & Spalding, J M K (1969). Blood pressure response to standing and to Valsalva's manoeuvre: independence of the two mechanisms in neurological diseases including cervical cord lesions. Clin. Sci. 36, 77–86.
King, B D, Harris, L C, Jr., Greifenstein, F E, Elder, J D & Dripps, R D (1951). Reflex circulatory responses to direct laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation performed during general anaesthesia. Anesthesiol. 12, 556–566.
MaCmillan, A L & Stott, F D (1968). Continuous intra-arterial blood pressure measurement. Bio-med. Engineering, 3, 20–27.
Mathias, C J, Christensen, N J, Corbett, J L, Frankel, H L, Goodwin, T J & Peart, W S (1975). Plasma catecholamines, plasma renin activity and plasma aldosterone in tetraplegic man, horizontal and tilted. Clin. Sci. and Mol. Med. (in press).
Nieder, R M, O'Higgins, J W & Aldrete, J A (1970). Autonomic hyperreflexia in urologic surgery. J.A.M.A. 213, 867–869.
Prys-Roberts, C, Lloyd, J W, Fisher, A, Kerr, J H & Patterson, T J S (1974). Deliberate profound hypotension induced with halothane: studies of haemodynamics and pulmonary gas exchange. Brit. J. Anaesth. 46, 105–116.
Raventos, J (1956). The action of Fluothane—a new volatile anaesthetic. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 11, 394–410.
Rosner, S, Newman, W & Burstein, C L (1953). Electrocardiographic studies during endotracheal intubation, VI: effects during anaesthesia with thiopental sodium combined with a muscle relaxant. Anesthesiol. 14, 591–595.
Stephenson, H E, Jr. (1969). Cardiac Arrest and Resuscitation, 3rd edition. C. V. Mosby Company, St. Louis.
Takeshima, K, Noda, K & Higaki, M (1964). Cardiovascular response to rapid anaesthesia induction and endotracheal intubation. Anaesth. Analg. (Cleveland), 43, 201–208.
Tomori, Z & Widdicombe, J G (1969). Muscular, bronchomotor and cardiovascular reflexes elicited by mechanical stimulation of the respiratory tract. J. Physiol. (Lond.), 200, 24–49.
Weiss, S & Ferris, E B (1934). Adams-Stokes Syndrome with transient complete heart block of vagovagal reflex origin. Arch. Int. Med. 54, 931–951.
Welply, N (1975). Unpublished observations.
Winsor, T & Burch, G W (1946). Use of phlebomanometer. Amer. Heart J. 31, 387–406.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Welply, N., Mathias, C. & Frankel, H. Circulatory reflexes in tetraplegics during artificial ventilation and general anaesthesia. Spinal Cord 13, 172–182 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.1975.28
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.1975.28
This article is cited by
-
Bradycardia and cardiac arrest during tracheal suction ?Mechanisms in tetraplegic patients
European Journal of Intensive Care Medicine (1976)