Abstract
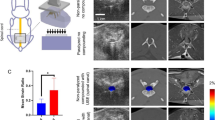
In the absence of an adequate description of the response of spinal cord to dynamic insult, work is in hand to determine the dynamic characteristics of canine spinal cord tissue. In-vitro experimentation is described. A vibration technique using a low amplitude (0.5 mm), variable frequency (0-40 Hz) forcing frequency is used to describe the resonant property of the tissue in a supporting environment.
The canine spinal cord is demonstrated to respond as a non-linear, soft, visco-elastic element suceptible in the frequency range 14-22 Hz.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Barbenel, J C, Evans, J H & Finlay, J B (1972). Stress-strain-time relations of soft connective tissues. Perspectives in Biomedical Engineering, ed. Kenedi, 165–172.
Breig, A (1960). Biomechanics of the central nervous system. Almqvist and Wiksell, Stockholm.
Breig, A (1972). The therapeutic possibilities of surgical bio-engineering in incomplete spinal cord lesions. Paraplegia, 9, 173–182.
Comninov, M & Yannas, I V (1976). Dependence of stress-strain non-linearity of connective tissues on the geometry of collagen fibres. J. Biomechanics, 9, 427.
Ewing, C L & Thomas, D J (1973). Torque versus angular displacement response of human head to — Gx impact acceleration. SAE Paper 730976. Proc. 17th Stapp. Car Crash Conf. November, 1973, 309–342.
Ewing, C L et al. (1976). The effect of duration, rate of onset and peak sled acceleration on the dynamic response of the human head and neck. SAE Paper 760800, Proc. 20th Stapp Car Crash Conf., October, 1976, 3–41.
Galford, J E & Mcelhaney, J H (1970). A viscoelastic study of scalp, brain and dura. J. Biomechanics, 3, 111–124.
Haut, R C & Little, R W (1972). A constitutive equation for collagen fibres. J. Biomech., 5, 423–430.
Melvin, J W et al. (1971). Deployable head restraints—a feasibility study. SAE Paper 710853. Procs. 15th Stapp Car Crash Conf., November, 1971, 158–189.
Mertz, H J & Patrick, L M (1967). Investigation of the kinematics and kinetics of whiplash. SAE Paper 670919, Proc. 11th Stapp. Car Crash Conf. October, 1967, 267–317.
Parks, R L (1962). Defining human reaction to whole body vibration. Human Factors, 4, 305–314.
Prasad, P et al. (1975). Dynamic response of the spine during + Gx accelaration. SAE Paper 751172. Procs., 19th Stapp car crash Conf., November, 1975, 869–897.
Reid, J D (1960). Effects of flexion-extension movements of the head and spine upon the spinal cord and nerve roots. J. Neural. Neurosurg. and Psych., 23, 214–221.
Smith, C G (1956). Changes in length and position of the segments of the spinal cord with changes in posture in the monkey. Radiology, 66, 259–266.
Tarriere, C & Sapin, C (1969). Biokinetic study of the head to thorax linkage. SAE paper 690315, Proc. 13th Stapp. Car Crash Conf. December, 1969, 369–380.
Tunturi, A R (1977). Elasticity of the spinal cord dura in the dog. J. Neurosurg., 47, 391–396.
Von Gierke, H E & Coermann, R R (1963). The biodynamics of human response to vibration and impact. Incl. Med and Surg., 52, 30–32.
Yamada, H & Evans, F G (1970) Strength of biological materials. Williams & Wilkins Co., Baltimore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scull, E. The dynamic mechanical response characteristics of spinal cord tissue: a preliminary report. Spinal Cord 17, 222–232 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.1979.45
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.1979.45