Abstract
Thirteen paraplegias after decompression have been treated in the 5 centres of Lyons, Geneva, Mulhouse, Basel and Strasbourg.
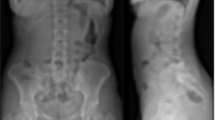
All these cases are somehow comparable: 12 males, 1 female, skilled and well-trained divers are involved from 27 to 50 years. Submersion between 30 and 42 metres, during 15 to 30 minutes. Ascension with or without decompression stops. Beginning with sudden posterior thoracic, 4 feeling sick, 2 becoming briefly unconscious, paralysis after a while (until 1 hour). All have received hyperbaric oxygenation (from 1 to 5 hours later), with an improvement for 10.
Neurological findings. 5 tetraplegics, 7 para-(5 with Brown-Sequard), and one L1. Quickly, the tetraplegics improved to a thoracic level. In two cases, paraplegia remained complete at thoracic level. The others had a better evolution; the paralysis improved slowly, with marked spasticity, impaired sensation did not improve to such an extent, often localised at a lower level, with sexual impotence. Micturitions became normal but with often urine leakages.
This rather favourable evolution allowed 11 to go back to work.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Belaich E (1975). Approche thérapeutique des accidents de plongée en scaphandre autonome.Thèse Marseille, 1975, 176 réf.
Bert, P (1978). La pression barométrique, Masson Paris. English translation by Hitchcock (1943). Columbers College Book Company.
Boycott, A E, Damant, G & Haldane, J S (1908). The prevention of compressed-air illness. J. Hyg. 8, 342–343.
Force, L, Esvan, J, Barthelemy L, Michaud, A, Joly, R & Gilly R (1974). Aspects cliniques d'une série d'accidents de plongée. Maroc Méd. 54, 38–39.
Frankel, H L (1975). Aqualung diving for the paralysed. Paraplegia, 13, 128–132.
Frankel, H L (1977). Paraplegia due to decompression sickness. Paraplegia, 14, 306–311.
Girard, R, Minaire P, Berard, E & Bourret J (1979). Les paraplégies par plongée sous-marine. Arch Mal. Prof. 40, 744–747.
Hallenbeck, J M, Bove, A A & Elliot, D M (1975). Mechanisms undulying spinal cord damage in decompression sickness. Neurology Minneapolis 25, 4, 308–315.
Langlois, M & Veyrat, J G (1960). La paraplégie par accident de décompression chez le plongeur. Étude clinique et anatomo-physiologique. Rev. Neurol., 103, 582–589.
Ohresser, P h, Tassy, J, Amorus, J F & Dor, J (1972). Les accidents de plongée à propos de 75 observations recueillies en trois ans, Maroc Méd. 52, 445–447.
Pannier, S, Piera, J B, Bourgeois-Gavardin, Th & Grossiord, A (1975). Para et tétraplégies par accident de décompression. 9 observations. Ann. Méd. Interne, 126, 331–338.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Girard, R. Paraplegia during skin-diving (13 cases). Spinal Cord 18, 123–126 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.1980.20
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.1980.20