Abstract
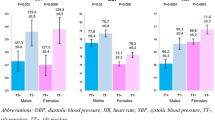
Two groups of patients who developed orthostatic hypotension (OH) after spinal cord injury (SCI) were studied. In the first group all patients (4 females and 6 males) were asymptomatic, whereas in the second group (1 female and 9 males) all had clinical manifestations of hypotension. All but 3 patients were tetraplegic, and these patients were paraplegic above the T6 level. For this study blood pressure (BP), heart rate and cerebral blood flow (CBF) velocity were measured simultaneously on a tilt table at 0, 30, 60, and 80 degrees. Cerebral blood flow in the middle cerebral artery was measured bilaterally utilising the transcranial Doppler technique. In asymptomatic patients the mean baseline (0 degrees) BP (110 ± 16/70 ± 77 mm Hg systolic/diastolic) was not significantly different from the BP (106 ± 16/68 ±11 mm Hg) of symptomatic patients. The mean maximal change in BP during tilting in the asymptomatic group (−23 ± 10/10 ± 7 mm Hg) was also not significantly different when compared to the symptomatic group (−29 ± 13/11 ± 6 mm Hg). CBF in the symptomatic group during the hypotensive reaction at 80 degrees was 32.5 ± 5 cm/sec, while at the same body position in the asymptomatic group it was 40.9 ± 8 cm/sec (significant at the p < 0.02). In addition, CBF decreased in the symptomatic group at 80 degrees to 55.5 ± 9.6% of baseline, while in the asymptomatic group the fall was 69.3 ±7.2% (p < 0.001). Our data suggests that autoregulation of CBF rather than systemic BP plays a dominant role in the adaptation to OH in patients with SCI.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Claus-Walker J, Halstead L S 1982 Metabolic and endocrine changes in spinal cord injury: II Partial decentralization of the autonomic nervous system. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 63: 576–601.
Corbet J L, Frankel H L, Harris P J 1971a Cardiovascular responses to tilting in tetraplegic man. Journal of Physiology 215: 411–431.
Corbet J L, Frankel H L, Harris P J 1971b Cardiovascular changes associated with skeletal muscle spasm in tetraplegic man. Journal of Physiology 215: 395–409.
DeWitt D L, Wechsler L R 1988 Transcranial doppler. Stroke 19: 915–921.
Downey J A, Chiodi H P, Miller J M 1966 The effect of inhalation of 5 per cent carbon dioxide in air on postural hypotension in quadriplegia. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 47: 422–426.
Engel P, Hildebrandt G 1976 Long term studies about orthostatic training after high spinal cord injury. Paraplegia 14: 159–164.
Figoni S F 1984 Cardiovascular and hemodynamic responses to tilting and to standing in tetraplegic patients: A Review. Paraplegia 22: 99–109.
Frankel H L, Hancock D P, Hyslop G et al. 1969 The value of postural reduction in the initial management of closed injury of the spine with paraplegia and tetraplegia. Paraplegia 7: 179–192.
Guttmann L, Munro A F, Robinson R, Walsh J J 1963 Effect of tilting on the cardiovascular responses and plasma catecholamine levels in spinal man. Paraplegia 1: 4–18.
Hogan R D, Hirschmann L 1984 Arteriolar proliferation in the rat cremaster muscle as a long term autoregulatory response to reduced perfusion. Microvascular Research 27: 290–296.
Johnson R H, Park D M 1973 Effect of change of posture on blood pressure and plasma rennin concentration in men with spinal transections. Clinical Science 44: 539–546.
Johnson R H, Park D M, Frankel H L 1971 Orthostatic hypotension and the renin-angiotensin system in paraplegia. Paraplegia 9: 146–152.
Johnson P C 1984 Autoregulation of blood flow. Circulation Research 59: 483–495.
Kamelhar D L, Steele J M, Schacht R G, Lowenstein J, Naftehi N E 1978 Plasma renin and serum dopamine beta hydroxylase during orthostatic hypotension in quadriplegic man. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 59: 212–216.
Knighton D R, Hunt T K, Schenenstuhl H, Holliday, B J, Werb Z, Banda M J 1983 Oxygen tension regulates the expression of angiogenesis factor by macrophages. Science 221: 1283–1285.
Lopes P, Figoni S 1981 Current literature on orthostatic hypotension and training in SCI patients. American Corrective Medical Therapy Journal 36: 56–59.
McCluer S 1968 A temporary method of controlling orthostatic hypotension in quadriplegia. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 49: 598–599.
Nanda R N, Wyper D J, Harper A M, Johnson R H 1974 Cerebral blood flow in paraplegia. Paraplegia 12: 212–218.
Spencer W A, Vallbona C, Carter R E 1969 Physiologic concept of immunobilization. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 89–100.
Sommers D K 1979 Reactivity of the cardiovascular system in the tetraplegic patient. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 26: 344–353.
Stainsby W N 1973 Local control of regional blood flow. Annual Review of Physiology 35: 151–168.
Vallbona C, Spencer W A, Cardus D, Dale J W 1963 Control of orthostatic hypotension of quadriplegic patients with a pressure suit. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 44: 7–18.
Vallbona C, Lipscomb H S, Carter R E 1966 Endocrine responses to orthostatic hypotension in quadriplegia. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilition 47: 412–421.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonzalez, F., Chang, J., Banovac, K. et al. Autoregulation of cerebral blood flow in patients with orthostatic hypotension after spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 29, 1–7 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.1991.1
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.1991.1
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A cerebral blood flow evaluation during cognitive tasks following a cervical spinal cord injury: a case study using transcranial Doppler recordings
Cognitive Neurodynamics (2015)
-
Cerebrovascular autoregulation: lessons learned from spaceflight research
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2013)
-
Effect of hypotensive challenge on systemic hemodynamics and cerebral blood flow in persons with tetraplegia
Clinical Autonomic Research (2009)
-
Relationships between physiological responses and presyncope symptoms during tilting up in patients with spinal cord injury
Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing (2008)
-
Development of a biofeedback tilt-table for investigating orthostatic syncope in patients with spinal cord injury
Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing (2007)