Abstract
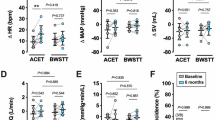
As part of the assessment of the Odstock functional electrical stimulation (FES) standing system for mid to low thoracic lesion spinal cord injured (SCI) subjects, cardiac output, thigh blood flow and quadriceps muscle thickness were measured before and following an electrical stimulation muscle retraining programme. The same parameters were also measured in a group of uninjured subjects and in SCI subjects. It was found that there was no difference in cardiac output between the groups. However thigh blood flow was found to be around 65% of normal values in the spinally injured group. This returned to normal values following the retraining programme. The quadriceps muscle wasted to approximately 50% of its original thickness in the first 3 weeks following spinal cord injury. The retraining programme increased the muscle thickness to near normal values.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ewins D J, Taylor P N, Crook S E, Lipcyznski R T, Swain I D (1988) Practical low cost stands/sit system for mid-thoracic paraplegics. J Biomed Eng 10(2): 184–188.
Ewins D J, Taylor P N, Swain I D (1990) A functional closed-loop stand/sit system for mid-low thoracic paraplegics. In: D Popovic, D editor. Advances in External Control of Human Extremities 10. Nauka, Belgrade: 261–264.
Nash R S W, Davy M S, Orpwood R, Swain I D (1990) Development of a wheelchair mounted folding standing frame. J Biomed Eng 12(3): 189–192.
Taylor P N, Fox B A, Ewins D J, Biss S J, Swain I D (1989) Exercise procedure and treatment routine for preparation of paraplegics prior to standing using FES. In: F Clifford Rose, R Jones, G Vrbova, editors. Neuromuscular Stimulation: Basic Concepts and Clinical Implications. Demos Publications, New York: 245–251.
Barr F M D, Bayley J I L, Midleton F R I, Moffat B (1987) Functional electrical stimulation: practical experience in the clinical setting. In: D Popovic, editor. Advances In External Control Of Human Extremities 9. Taujug, Belgrade: 181–192.
Kubicek W G, Karnegis J N, Patterson R P, Witsoe D A, Mattson R H (1966) Development and evaluation of an impedance cardiac output system. Aerospace Med 37(12): 1208–1212.
Porter J M, Swain I D, Shakespeare P G (1985) Measurement of limb blood flow by electrical impedance plethysmography. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 67: 169–172.
Naggar C Z, Dobnik D B, Flessas A P, Kripke B J, Ryan T J (1975) Accuracy of stroke index as determined by the tranthoracic electrical impedance method. Anaesthesiology 42(2): 46–56.
Van de Water J M, Dmochowski J R, Dove G B, Couch N P (1979) Evaluation of an impedance flow meter in arterial surgery. Surgery 3: 132–137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor, P., Ewins, D., Fox, B. et al. Limb blood flow, cardiac output and quadriceps muscle bulk following spinal cord injury and the effect of training for the Odstock functional electrical stimulation standing system. Spinal Cord 31, 303–310 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.1993.54
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.1993.54