Abstract
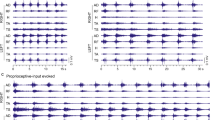
Propriospinal myoclonus is a rare and relatively little studied complication of spinal cord injury. We report two patients with an extension-producing myoclonus presenting with tetraplegia caused by cervical trauma. Rhythmic extension jerks of the trunk and lower limbs appeared several weeks after their injury in a context of severe spasticity. The characteristics of these jerks were determined by polymyography of 12 muscles. They lasted between 306 and 1127 ms with a frequency of 0.3 to 0.5 Hz. By comparing latencies their origin was found to be in the lumbar cord from which there was a slow (2 ms-1) upward and downward spread. Oral treatment with baclofen and sodium valproate was partially successful in one patient, but ineffective in the other. Intrathecal 75 or 100 μg baclofen produced a striking, complete disappearance of myoclonus prompting the implantation and successful use of a baclofen pump in one patient. These two new cases suggest the existence of a lumbar generator in which myoclonic extension jerks originate, and demonstrate a new therapeutic alternative in intrathecal baclofen for patients resistant to oral medication.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Lhermitte J . La Section Totale de la Moelle Dorsale. Tardy Pigelet: Bourges, 1919, 30 and 110.
Bussel B et al. Myoclonus in a patient with spinal cord transection. Brain 1988; 111: 1235–1245.
Brown P, Rothwell J C, Thompson P D, Marsden C D . Proprio-spinal myoclonus. Evidence for spinal pattern generators in humans. Movement Disord 1994; 9: 571–576.
Brown P et al. Axial myoclonus of propriospinal origin. Brain 1991; 114: 119–214.
Chokzoverty S, Walter A, Zimmerman T, Picone M . Propriospinal myoclonus: a neurophysiologic analysis. Neurology 1992; 42: 1591–1595.
Djindjian R, Mamo H, Saimot G, Houdart R . Contractures tétaniformes paroxystiques au cours de l'artériographie sélective de l'arière d'Adamkiewicz. Presse Médícale 77: 1311–1314.
Kapoor R, Brown P, Thompson P D, Miller D H . Propriospinal myoclonus in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1992; 55: 1086–1088.
Grillner S . Locomotion in vertebrates: central mechanisms and reflex interaction. Physiol Rev 1975 55: 247–304.
Jankovik J, Pardo R . Segmental myoclonus clinical and pharmacologic study. Arch Neurol 1986; 43: 1025–1031.
Jeon B, Lee M, Erickson D . Successful treatment of medically unresponsive spinal myoclonus with continuous intrathecal morphine administration (abstract). Neurology 1991; 41: 416.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fouillet, N., Wiart, L., Arne, P. et al. Propriospinal myoclonus in tetraplegic patients: clinical, electrophysiological and therapeutic aspects. Spinal Cord 33, 678–681 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.1995.142
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.1995.142
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Treatment of Myoclonus
Neurotherapeutics (2014)