Abstract
Study design:
A case report of fibrocartilaginous embolism (FCE) presenting as acute myelopathy.
Objectives:
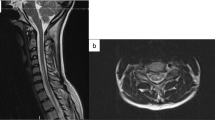
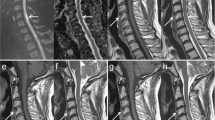
To illustrate the clinical presentation and magnetic resonance imaging features of FCE.
Setting:
Johns Hopkins Transverse Myelitis Center.
Case report:
A 16-year-old boy was diagnosed with ischemic myelopathy secondary to FCE 2 years after symptom onset. Diagnosis was delayed because the clinical and radiological characteristics were not recognized initially. After rehabilitation, the patient made a modest recovery.
Conclusions:
Diagnosis of FCE can be made by recognition of the characteristic clinical and radiological features and a high index of suspicion.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Nance JR, Golomb MR . Ischemic spinal cord infarction in children without vertebral fracture. Pediatr Neurol 2007; 36: 209–216.
Han JJ, Massagli TL, Jaffe KM . Fibrocartilaginous embolism—an uncommon cause of spinal cord infarction: a case report and review of the literature. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2004; 85: 153–157.
Transverse Myelitis Consortium Working Group. Proposed diagnostic criteria and nosology of acute transverse myelitis. Neurology 2002; 59: 499–505.
Duprez TP, Danvoye L, Hernalsteen D, Cosnard G, Sindic CJ, Godfraind C . Fibrocartilaginous embolization to the spinal cord: serial MR imaging monitoring and pathologic study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2005; 26: 496–501.
Tosi L, Rigoli G, Beltramello A . Fibrocartilaginous embolism of the spinal cord: a clinical and pathogenetic reconsideration. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1996; 60: 55–60.
Toro G, Roman GC, Navarro-Roman L, Cantillo J, Serrano B, Vergara I . Natural history of spinal cord infarction caused by nucleus pulposus embolism. Spine 1994; 19: 360–366.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, K., Hammond, E., Kerr, D. et al. Fibrocartilaginous embolism: a cause of acute ischemic myelopathy. Spinal Cord 47, 643–645 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2008.135
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2008.135
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pediatric fibrocartilaginous embolism inducing paralysis
Child's Nervous System (2020)