Abstract
Study design:
Case report.
Objective:
To describe a role for breathing in maintenance for blood pressure in a tetraplegic man.
Setting:
Veterans Administration Hospital, USA.
Methods/Results:
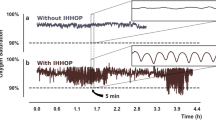
A 60-year-old man, tetraplegic for 14 years, was successfully treated for orthostatic hypotension (OH) by raising the head of his bed in the mornings before transfer to his wheelchair. To test the role of breathing in the compensation for OH, we monitored the nasal airflow with a thermistor clipped onto a naris and pulse pressure was measured with a transducer held against a supraorbital artery with an elastic band. On raising the head of the bed to 30° the pulse pressure fell and breathing effort increased. Within 1 min, however, pulse pressure rose to baseline levels whereas increased breathing effort continued. On transfer to his wheelchair OH was avoided and medication was unnecessary.
Conclusion:
For the tetraplegic subject the partial raising of the head of the bed for a period of time to be determined individually will recruit increased breathing effort and venous return to the chest, preventing OH on transfer to an upright position in a wheelchair.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Mathias CJ, Christensen NJ, Corbett JL, Frankel HL, Goodwin TJ, Peart WS . Plasma catecholamines, plasma renin activity and plasma aldosterone in tetraplegic man, horizontal and tilted. Clin Sci Mol Med 1975; 49: 291–299.
Adkins RH, Milic-Emili J . Lung mechanics in individuals with spinal cord injury: effects of injury level and posture. J Appl Physiol 2001; 90: 405–411.
Frisbie JH . Salt wasting, hypotension, polydipsia, and hyponatremia and the level of spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2007; 43: 563–568.
Kogan I, McCool FD, Leiberman SL, Garshick E, Shannon K, Frisbie JH et al. The diaphragm hypertrophies during inspiratory muscle training in quadriplegia. Am J Resp Critical Care Med 1996; 153: A2528.
Frisbie JH . Breathing pattern in tetraplegic patients. Spinal Cord 2002; 40: 424–425.
Acknowledgements
This paper is the result of a study supported with the resources and the use of facilities at the VA Boston Healthcare System, Boston, MA, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frisbie, J. Correction of orthostatic hypotension by respiratory effort. Spinal Cord 48, 434–435 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2009.148
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2009.148