Abstract
Study design:
Cross-sectional study.
Objective:
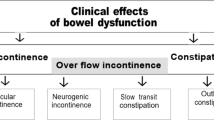
To analyze the predictors of severe neurogenic bowel dysfunction (NBD) in persons with spinal cord injury (SCI).
Setting:
The Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Taiwan.
Methods:
Two questionnaires—the NBD score and the Beck Depression Inventory second edition—were sent to 232 persons with SCI by mail. The demographic factors and injury-related factors were recorded to evaluate any relationships with severe NBD. The associations between the severity of NBD and psychological condition were also measured.
Results:
In all, 39.4% of the respondents suffered from severe NBD. Multiple logistic regression analysis showed that those with a cervical injury (odds ratios (OR)=10.5, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.6–67.7) or a thoracic injury (OR=7.1, 95% CI 1.2–40.3) had a higher risk of severe NBD than those with a lumbar injury. Persons with American Spinal Injury Association (ASIA) A had a 12.8-fold higher risk of severe NBD than persons with ASIA D (OR=12.8, 95% CI 3.3–50.1). Longer duration of injury (⩾10 years) was another risk factor of severe NBD. Moderate-to-severe depression was associated with reduced bowel function.
Conclusions:
This study showed that high level of cord lesion, completeness of cord injury and longer duration of injury (⩾10 years) could predict the severity of NBD in patients with SCI.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Krogh K, Nielsen J, Djurhuus JC, Mosdal C, Sabroe S, Laurberg S . Colorectal function in patients with spinal cord lesions. Dis Colon Rectum 1997; 40: 1233–1239.
Faaborg PM, Christensen P, Finnerup N, Laurberg S, Krogh K . The pattern of colorectal dysfunction changes with time since spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2008; 46: 234–238.
Gore RM, Mintzer RA, Calenoff L . Gastrointestinal complications of spinal cord injury. Spine 1981; 6: 538–544.
Glickman S, Kamm MA . Bowel dysfunction in spinal-cord-injury patients. Lancet 1996; 347: 1651–1653.
Vaizey CJ, Carapeti E, Cahill JA, Kamm MA . Prospective comparison of fecal incontinence grading systems. Gut 1999; 44: 77–80.
Agachan F, Chen T, Pfeiffer J, Reisman P, Wexner SD . A constipation scoring system to simplify evaluation and management of constipated patients. Dis Colon Rectum 1996; 39: 681–685.
Krogh K, Christensen P, Sabroe S, Laurberg S . Neurogenic bowel dysfunction score. Spinal Cord 2006; 44: 625–631.
Liu CW, Huang CC, Yang YH, Chen SC, Weng MC, Huang MH . Relationship between neurogenic bowel dysfunction and health-related quality of life in persons with spinal cord injury. J Rehabil Med 2009; 41: 35–40.
Krause JS, Kjorsvig JM . Mortality after spinal cord injury: a four-year prospective study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1992; 73: 558–563.
Furlan JC, Urbach DR, Fehlings MG . Optimal treatment for severe neurogenic bowel dysfunction after chronic spinal cord injury: a decision analysis. Br J Surg 2007; 94: 1139–1150.
Steer RA, Ball R, Ranieri WF, Beck AT . Dimensions of the Beck Depression Inventory-II in clinically depressed outpatients. J Clin Psychol 1999; 55: 117–128.
Ditunno JF, Young W, Donovan WH, Creasey G . The international standards booklet of neurological and functional classification of spinal cord injury. Paraplegia 1994; 32: 70–80.
Fajardo NR, Pasiliao RV, Modeste-Duncan R, Creasey G, Bauman WA, Korsten MA . Decreased colonic motility in persons with chronic spinal cord injury. Am J Gastroenterol 2003; 98: 128–134.
De Looze D, Van Laere M, De Muynck M, Beke R, Elewaut A . Constipation and other chronic gastrointestinal problems in spinal cord injury patients. Spinal Cord 1998; 36: 63–66.
Lynch AC, Antony A, Dobbs BR, Frizelle FA . Bowel dysfunction following spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2001; 39: 193–203.
Brading AF, Ramalingam T . Mechanisms controlling normal defecation and the potential effects of spinal cord injury. Prog Brain Res 2006; 152: 345–358.
Kirshblum SC, Gulati M, O’Connor KC, Voorman SJ . Bowel care practices in chronic spinal cord injury patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1998; 79: 20–23.
Scivoletto G, Morganti B, Ditunno P, Ditunno JF, Molinari M . Effects on age on spinal cord lesion patients′ rehabilitation. Spinal Cord 2003; 4: 457–464.
Madsen JL, Graff J . Effects of ageing on gastrointestinal motor function. Age Ageing 2004; 33: 154–159.
Ng C, Prott G, Rutkowski S, Li Y, Hansen R, Kellow J et al. Gastrointestinal symptoms in spinal cord injury: relationships with level of injury and psychologic factors. Dis Colon Rectum 2005; 48: 1562–1568.
Acknowledgements
We thank the National Science Council for their financial support. We also thank Mr James Fenton for his assistance with editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, CW., Huang, CC., Chen, CH. et al. Prediction of severe neurogenic bowel dysfunction in persons with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 48, 554–559 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2009.181
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2009.181
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effective bowel management in spinal cord injury during inpatient rehabilitation: data from the Dutch spinal cord injury database
Spinal Cord (2023)
-
Retrospective trends in length of stay and bowel management at discharge from inpatient rehabilitation among individuals with spinal cord injury
Spinal Cord (2022)
-
Are micro enemas administered with a squeeze tube and a 5 cm-long nozzle as good or better than micro enemas administered with a 10 cm-long catheter attached to a syringe in people with a recent spinal cord injury? A non-inferiority, crossover randomised controlled trial
Spinal Cord (2022)
-
Guideline for the management of neurogenic bowel dysfunction in spinal cord injury/disease
Spinal Cord (2022)
-
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth as a cause of protracted wound healing and vitamin D deficiency in a spinal cord injured patient with a sacral pressure sore: a case report
BMC Gastroenterology (2020)