Abstract
Study design:
To develop a method for the study of spinal cord injury (SCI) that can visualize the blood vessels and is compatible with hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining and immunohistochemical techniques.
Objective:
Visualization of the vascular changes is important for the study of SCI. The original ferric tannate method can stain the spinal cord vasculature to its terminals, but the diffuse tannate precipitates spoil the delicacy of the picture. More importantly, it is incompatible with HE staining and immunohistochemical techniques, which is crucial for the study of SCI. We thus aimed to develop a modified ferric tannate method that could meet the requirement for the study of SCI.
Setting:
This study was carried out in China.
Methods:
The original ferric tannate method involves a two-step procedure: intravascular perfusion of tannic acid, followed by soaking the tissue sections in a solution of ferric chloride. In the modified method both chemicals were delivered through perfusion.
Results:
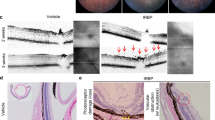
In the original method, diffuse ferric tannate precipitates blurred the profile of the vessels. More importantly, it was incompatible with either HE or immunostaining methods. Our modified method stained the blood vessels with clean background and was compatible with both HE staining and immunohistochemical techniques.
Conclusion:
The modified method is far superior to the original method and meets the requirement for the study of SCI.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Balentine JD . Pathology of experimental spinal cord trauma. I. The necrotic lesion as a function of vascular injury. Lab Invest 1978; 39: 236–253.
Mautes AE, Weinzierl MR, Donovan F, Noble LJ . Vascular event after spinal cord injury contribution to secondary pathogenesis. Phys Ther 2000; 80: 673–687.
Tator CH . Review of experimental spinal cord injury with emphasis on the local and systemic circulatory effects. Neurochirurgie 1991; 37: 291–302.
Li CH, Pan LH, Li CY, Zhu CL, Xu WX . Localization of ANP-synthesizing cells in rat stomach. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12: 5674–5679.
Li CH, Yang ZW, Yin ZR, Jin Z, Xing DG, Piao LH et al. Relationship between atrial natriuretic peptide-immunoreactive cells and microvessels in rat gastric mucosa. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2006; 27: 205–211.
Nakashima Y, Sueishi K . Alteration of elastic architecture in the lathyritic rat aorta implies the pathogenesis of aortic dissecting aneurysm. Am J Pathol 1992; 140: 959–969.
Kwo S, Young W, Decrescito V . Spinal cord sodium, potassium, calcium, and water concentration changes in rats after graded contusion injury. J Neurotrauma 1989; 6: 13–24.
Shu SY, Ju G, Fan LZ . The glucose oxidase-DAB-nickel method in peroxidase histochemistry of the nervous system. Neurosci Lett 1988; 85: 169–171.
Loy DN, Crawford CH, Darnall JB, Burke DA, Onifer SM, Whittemore SR . Temporal progression of angiogenesis and basal lamina deposition after contusive spinal cord injury in the adult rat. J Comp Neurol 2002; 445: 308–324.
Duijvestijn AM, van Goor H, Klatter F, Majoor GD, van Bussel E, van Breda Vriesman PJ . Antibodies defining rat endothelial cells: RECA-1, a pan-endothelial cell-specific monoclonal antibody. Lab Invest 1992; 66: 459–466.
DeLisser HM, Christofidou-Solomidou M, Strieter RM, Burdick MD, Robinson CS, Wexler RS et al. Involvement of endothelial PECAM-1/CD31 in angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 1997; 151: 671–677.
Ulger H, Karabulut AK, Pratten MK . Labelling of rat endothelial cells with antibodies to vWF, RECA-1, PECAM-1, ICAM-1, OX-43 and ZO-1. Anat Histol Embryol 2002; 31: 31–35.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China(2003CB515301) and Grant no. 06MA148 from the PLA Military Medical Research Fund. We are grateful to Ms Xi-Ying Jiao for his assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, XF., Zhao, Y., Zhang, YK. et al. A modified ferric tannate method for visualizing a blood vessel and its usage in the study of spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 47, 852–856 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2009.30
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2009.30
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Beneficial effects of early hemostasis on spinal cord injury in the rat
Spinal Cord (2016)
-
Effect of norepinephrine on spinal cord blood flow and parenchymal hemorrhage size in acute-phase experimental spinal cord injury
European Spine Journal (2014)
-
Protective effects of Batroxobin on spinal cord injury in rats
Neuroscience Bulletin (2013)
-
The Protective Effects of Inosine Against Chemical Hypoxia on Cultured Rat Oligodendrocytes
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2011)