Abstract
Study design:
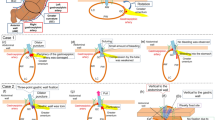
Case reports describing abdominal complications following percutaneous enteral gastric (PEG) tube placement in three tetraplegics.
Objectives:
The aim was to increase provider awareness of PEG tube dislodgement as a complication in tetraplegics.
Setting:
Spinal cord injury center, Veteran's Administration hospital.
Methods:
The charts of three spinal cord injured veterans with tetraplegia were reviewed for clinical presentation and radiographic findings supporting the diagnosis of acute abdominal complications following PEG tube dislodgement.
Results:
PEG tube dislodgement in tetraplegics can present with occult findings and lead to disastrous outcomes if the diagnosis is delayed.
Conclusion:
PEG tube dislodgement should be considered in tetraplegics who develop even subtle abdominal complaints, especially if the injury is complete. Further assessment with computed tomography (CT) scans or fistulograms should be considered to help with decision making.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Kohli H, Bloch R . Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: a community hospital experience. Am Surg 1995; 61: 191–194.
Larson DE, Burton DD, Schroeder KW, DiMagno EP . Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. Indications, success, complications, and mortality in 314 consecutive patients. Gastroenterology 1987; 93: 48–52.
Llaneza PP, Menendez AM, Roberts R, Dunn GD . Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: clinical experience and follow-up. South Med J 1988; 81: 321–324.
Glaesener JJ, Fredebohm M . Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in the rehabilitation of neurological disorders. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 1992; 122: 1600–1605.
Stylianides NA, Date RS, Pursnani KG, Ward JB . Jejunal perforation caused by a feeding jejunostomy tube: a case report. J Med Case Reports 2008; 2: 224.
Levine MS, Scheiner JD, Rubesin SE, Laufer I, Herlinger H . Diagnosis of pneumoperitoneum on supine abdominal radiographs. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1991; 156: 731–735.
Lee BY, Dasilva MC, Ostrander LE, Bond W . Acute abdomen in spinal cord injured patients. In: Lee BY, Ostrander LE (eds). The Spinal Cord Injured Patient, 2nd edn. Demos Medical Publishing: New York, 2002, pp 148–156.
Neumayer LA, Bull DA, Mohr JD, Putnam CW . The acutely affected abdomen in paraplegic spinal cord injury patients. Ann Surg 1990; 212: 561–566.
Miller LS, Staas Jr WE, Herbison GJ . Abdominal problems in patients with spinal cord lesions. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1975; 56: 405–408.
Bar-On Z, Ohry A . The acute abdomen in spinal cord injury individuals. Paraplegia 1995; 33: 704–706.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hess, M., Foo, D. Percutaneous enterogastric tube dislodgement in tetraplegics. Spinal Cord 48, 83–84 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2009.66
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2009.66