Abstract
Study design:
Non-randomized study.
Objective:
The mechanism underlying exercise-induced argumentation of natural killer cell cytotoxic activity (NKCA) in humans remains unclear. To address this, NKCA responses were studied during and after exercise in persons with cervical spinal cord injury (CSCI) and dysfunctional sympathetic nervous system.
Setting:
Kibikogen Rehabilitation Center for Employment Injuries.
Methods:
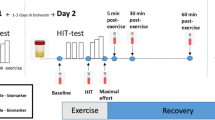
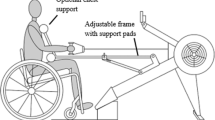
We examined the NKCA responses to 20-min arm-crank ergometer exercise at 60% of maximum oxygen consumption in eight persons with CSCI (between C6 and C7) and six able-bodied subjects. NKCA, adrenaline, and cortisol were measured before, immediately after exercise, 1 h after exercise, and 2 h after exercise.
Results:
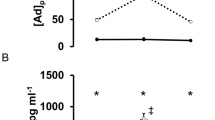
In able-bodied subjects, NKCA increased immediately after exercise (P<0.01) and then decreased to below the pre-exercise level 1 h after exercise, before recovering to the baseline level at 2 h after exercise. Plasma adrenaline concentrations increased significantly immediately after exercise (P<0.01) and returned to the baseline level 1 h after exercise. The plasma cortisol level did not change throughout the study. In contrast, NKCA, plasma concentrations of adrenaline, and cortisol did not change throughout the study in subjects with CSCI.
Conclusion:
In subjects with CSCI, the lack of response in NKCA throughout the experiment is probably mainly due to a dysfunctional sympathetic nervous system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Nash MS . Known and plausible modulators of depressed immune functions following spinal cord injuries. J Spinal Cord Med 2000; 23: 111–120.
Shephard RJ, Rhind S, Shek PN . Exercise and the immune system. Natural killer cells, interleukins and related responses. Sports Med 1994; 18: 340–369.
Hoffman-Goetz L, Pedersen BK . Exercise and the immune system: a model of the stress response? Immunol Today 1994; 15: 382–387.
Nagatomi R . The implication of alterations in leukocyte subset counts on immune function. Exerc Immunol Rev 2006; 12: 54–71.
Nieman DC, Nehlsen-Cannarella SL . The immune response to exercise. Semin Hematol 1994; 31: 166–179.
Furusawa K, Tajima F, Tanaka Y, Ide M, Ogata H . Short-term attenuation of natural killer cell cytotoxic activity in wheelchair marathoners with paraplegia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1998; 79: 1116–1121.
Furusawa K, Tajima F, Umezu Y, Ueta M, Ide M, Mizushima T et al. Activation of natural killer cell function in recreational athletes with paraplegia during a wheeelchair half-marathon race. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2003; 84: 706–711.
Kawashima N, Nakazawa K, Ishii N, Akai M, Yano H . Potential impact of orthotic gait exercise on natural killer cell activities in thoracic level of spinal cord-injured patients. Spinal Cord 2004; 42: 420–424.
Klokker M, Mohr T, Kjaer M, Galbo H, Pedersen BK . The natural killer cell response to exercise in spinal cord injured individuals. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 1998; 79: 106–109.
Ueta M, Furusawa K, Takahashi M, Akatsu Y, Nakamura T, Tajima F . Attenuation of natural killer cell activity during two-hour exercise in individuals with spinal cord injuries. Spinal Cord 2008; 46: 26–32.
Shek PN, Sabiston BH, Buguet A, Radomski MW . Strenuous exercise and immunological changes: a multi-time-point analysis of leukocyte subsets, CD4/CD8 ration, immunoglobulin production and NK cell response. Int J Sports Med 1995; 16: 466–474.
Pedersen BK, Hoffman-Goetz L . Exercise and immune system: regulation, integration and adaptation. Physiol Rev 2000; 80: 1055–1081.
Teasell RW, Arnold JM, Krassioukov A, Delaney GA . Cardiovascular consequences of loss of supraspinal control of the sympathetic nervous system after spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2000; 81: 506–516.
Kjaer M, Pollack SF, Mohr T, Weiss H, Gleim GW, Bach FW et al. Regulation of glucose turnover and hormonal responses during electrical cycling in tetraplegic humans. Am J Physiol 1996; 271: R191–R199.
Timmons BW, Cieslak T . Human natural killer cell subsets and acute exercise: a brief review. Exerc Immunol Rev 2008; 14: 8–23.
Benschop RJ, Oostveen FG, Heijnen CJ, Ballieux RE . Beta 2-adrenergic stimulation causes detachment of natural killer cells from cultured endothelium. Eur J Immunol 1993; 23: 3242–3247.
Benschop RJ, Nijkamp FP, Ballieux RE, Heijnen CJ . The effects of beta-adrenoceptor stimulation on adhesion of human natural killer cells to cultured endothelium. Br J Pharmacol 1994; 113: 1311–1316.
Nagao F, Suzui M, Takeda K, Yagita H, Okumura K . Mobilization of NK cells by exercise: downmodulation of adhesion molecules on NK cells by catecholamines. Am J Physiol Regulatory Integrative Comp Physiol 2000; 279: R1251–R1256.
Shephard RJ . Exercise under hot conditions: a major threat to the immune response? J Sports Med Phys Fitness 2002; 42: 368–378.
Moyna NM, Acker GR, Weber KM, Fulton JR, Robertson RJ, Goss FL et al. Exercise-induced alterations in natural killer cell number and function. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 1996; 74: 227–233.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Drs Hiroyuki Okawa, Atsushi Ikeda, Tomoyuki Ito, and Yoshiki Akatsu for the clinical assistance. We also thank Dr Faiq G Issa for the careful reading and editing of the manuscript. This project was supported by the Japanese National Foundation for Scientific Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamanaka, M., Furusawa, K., Sugiyama, H. et al. Impaired immune response to voluntary arm-crank ergometer exercise in patients with cervical spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 48, 734–739 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2010.13
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2010.13
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hot water immersion induces an acute cytokine response in cervical spinal cord injury
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2015)
-
Wheelchair half-marathon race increases natural killer cell activity in persons with cervical spinal cord injury
Spinal Cord (2012)
-
Does 20-min arm crank ergometer exercise increase plasma interleukin-6 in individuals with cervical spinal cord injury?
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2012)