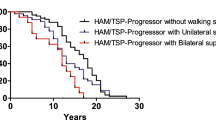
Abstract
Study design:
Cross-sectional study.
Objectives:
To determine the prevalence of falls in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I)-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) patients and possible factors associated to their occurrence.
Setting:
Instituto de Pesquisa Clínica Evandro Chagas, Fundação Oswaldo Cruz (FIOCRUZ) - Brazil.
Methods:
Thirty-six HAM/TSP patients able to walk at least 20 m were assessed by a questionnaire. Data regarding gender, age, duration of disease (DD), HTLV-I proviral load (HPL), frequency of physical activity (FCA), use of walking aids, functional ambulation level, the number of falls and associated injuries in the last year were reviewed. Multiple correspondence analysis was used to group characteristics of this sample according to the fall occurrence.
Results:
The prevalence of falls was 63.9% and we observed injuries in 47.8% of the cases. Four groups were identified in the descriptive analysis. One group was formed by faller individuals, men <60 years, independent ambulation, FCA⩾3 times per week and HPL <6.6 copies per 100 cells (group B). The other one comprised non-faller patients, women ⩾60 years, restricted ambulation, DD ⩾7 years, use of orthosis, FCA 0-1 time per week and HPL ⩾6.6 copies per 100 cells (group D). The others two groups comprised individuals that did not use orthosis (group A) and those that FCA was two times per week and DD <7 years (group C).
Conclusion:
Falls occur in roughly two-thirds of ambulatory HAM/TSP patients and are associated with significant morbidity. Further studies with a larger number of patients are necessarily to identify risk factors in order to elaborate specific programs to prevent falls in this population.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Hlela C, Shepperd S, Khumalo NP, Taylor GP . The prevalence of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 in the general population is unknown. AIDS Rev 2009 Oct-Dec 11: 205–214.
Araujo AQ, de Andrada-Serpa MJ . Tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-I-associated myelopathy in Brazil. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol 1996; 13 (Suppl 1): S33–S37.
Figueiroa FL, Andrade FAS, Crvalho ES, Brites C, Badaro R . HTLV-I associated myelopathy: clinical and epidemiological profile. Braz J Infect Dis 2000; 4: 126–130.
Franzoi AC, Araujo AQ . Disability profile of patients with HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis using the functional independence measure (FIM). Spinal Cord 2005; 43: 236–240.
Franzoi AC, Araujo AQ . Disability and determinants of gait performance in tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-I associated myelopathy (HAM/TSP). Spinal Cord 2007; 45: 64–68.
Lamb SE, Jorstad-Stein EC, Hauer K, Becker C . Development of a common outcome data set for fall injury prevention trials: the prevention of falls network europe consensus. J Am Geriatr Soc 2005; 53: 1618–1622.
Tinetti ME, Speechley M, Ginter SF . Risk factors for falls among elderly persons living in the community. N Engl J Med 1988; 319: 1701–1707.
Dibble LE, Lange M . Predicting falls in individuals with Parkinson disease: a reconsideration of clinical balance measures. J Neurol Phys Ther 2006; 30: 60–67.
Wallace C, Reiber GE, LeMaster J, Smith DG, Sullivan K, Hayes S et al Incidence of falls, risk factors for falls, and fall-related fractures in individuals with diabetes and a prior foot ulcer. Diabetes Care 2002; 25: 1983–1986.
Cattaneo D, De Nuzzo C, Fascia T, Macalli M, Pisoni I, Cardini R . Risks of falls in subjects with multiple sclerosis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2002; 83: 864–867.
Osame M . Human Retrovirology: HLTV. In: Blattner WA (ed.) 1st edn. Raven Press: New York. 1990, 191–197.
Viosca E, Martinez JL, Almagro PL, Gracia A, Gonzalez C . Proposal and validation of a new functional ambulation classification scale for clinical use. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2005; 86: 1234–1238.
Nenadic O . GM. correspondence analysis in R, with two- and three-dimensional graphics: the ca package. J Stat Softw 2007; 20: 1–13.
Greenacre MJ (ed.) Correspondence Analysis in Practice,, 2nd edn. Chapman & Hall/CRC: London. 2007.
Brotherton SS, Krause JS, Nietert PJ . Falls in individuals with incomplete spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2007; 45: 37–40.
Lord SR, Allen GM, Williams P, Gandevia SC . Risk of falling: predictors based on reduced strength in persons previously affected by polio. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2002; 83: 757–763.
Olindo S, Cabre P, Lezin A, Merle H, Saint-Vil M, Signate A et al Natural history of human T-lymphotropic virus 1-associated myelopathy: a 14-year follow-up study. Arch Neurol 2006; 63: 1560–1566.
Brotherton SS, Krause JS, Nietert PJ . A pilot study of factors associated with falls in individuals with incomplete spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med 2007; 30: 243–250.
Acknowledgements
Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Facchinetti, L., Araújo, A., Chequer, G. et al. Falls in patients with HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP). Spinal Cord 51, 222–225 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2012.134
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2012.134
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Signs, meanings and practices of people living with human t-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 or tropical spastic myelopathy
Journal of Patient-Reported Outcomes (2020)
-
Experienced complaints, activity limitations and loss of motor capacities in patients with pure hereditary spastic paraplegia: a web-based survey in the Netherlands
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2020)
-
Effectiveness of virtual reality games for falls, postural oscillations, pain and quality of life of individual HAM/TSP: a randomized, controlled, clinical trial
Journal of NeuroVirology (2020)
-
Neurological manifestations in individuals with HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis in the Amazon
Spinal Cord (2016)