Abstract
Study design:
Experimental dog model of spinal cord shortening.
Objectives:
To clarify the relationship between the amount of shortening of the spinal cord and the degree of injury it may induce, and to determine the safe range of the shortening.
Setting:
Xi’an Jiaotong University, China.
Methods:
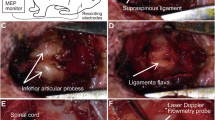
Thirty adult dogs were randomly allocated to five groups. Dogs in Group A (sham operation control) underwent spondylectomy to have two-thirds of the thirteenth thoracic segment (T13) resected, without bone-to-bone contact of the adjacent vertebral bodies. Those in Group B, C, D and E had one-third, half, two-thirds and total of their T13 resected, respectively, with bone-to-bone contact. Somatosensory-evoked potentials (SEP) and spinal cord blood flow (SCBF) were detected. The histopathologic changes of spinal cord tissue were observed by hematoxylin and eosin stain and electron microscope.
Results:
The shortening of the spinal cord < half of a vertebral segment height caused a reversible change of SEP. Whereas, the changes resulted from the shortening of more than two-thirds of a vertebral segment height did not return to the normal level. SCBF increased temporarily when the shortening was within two-thirds of a vertebral segment height; whereas, it decreased progressively when the length of the shortening was equal to one vertebral segment height. More serious hemorrhage occurred as the shortening increased.
Conclusion:
Shortening of half of a vertebral segment height will not induce spinal cord injury (SCI), while that between half and two-thirds of a vertebral segment may lead to incomplete SCI.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Lehmer SM, Keppler L, Buscup RS, Enker P, Miller SD, Steffee AD . Posterior transvertebral osteotomy for adult thoracolumbar kyphosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1994; 19: 2060–2067.
Lenke LG, Sides BA, Koester LA, Hensley M, Blanke KM . Vertebral column resection for the treatment of severe spinal deformity. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010; 468: 687–699.
Manabe S, Tateish A, Abe M, Ohno T . Surgical treatment of metastatic tumor of the spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1989; 14: 41–47.
Padrals JG . Spinal shortening in scoliosis surgery: a case with transitory paraplegia. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1996; 21: 2515–2519.
Suk SI, Kim JH, Kim WJ, Lee SM, Chung ER, Nah KH . Posterior vertebral column resection for sever spinal deformities. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2002; 27: 2374–2382.
Kawahara N, Tomita K, Kobayashi T, Abdel-Wanis ME, Murakami H, Akamaru T . Influence of acute shortening on the spinal cord: an experimental study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005; 30: 613–620.
Modi HN, Suh SW, Hong JY, Yang JH . The effects of spinal cord injury induced by shortening on motor evoked potentials and spinal cord blood flow, an experimental study in swine. J Bone Joint Surg AM 2011; 93: 1781–1789.
Alemdaroglu KB, Atlihan D, Cimen O, Kilinc CY, Iltar S . Morphometric effects of acute shortening of the spine: the kinking and the sliding of the cord, response of the spinal nerves. Eur Spine J 2007; 16: 1451–1457.
Jasper HH . The ten-twenty electrode system of the International Federation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neuro 1958; 10: 371–375.
Oostrom H, Stience PJ, Doornenbal A, Hellebrekers LJ . Nociception-related somatosensory evoked potentials in awake dogs recorded after intra epidermal electrical stimulation. Euro J Pain 2009; 13: 154–160.
Kurosawa M, Toda H, Watanabe O, Budgell B . Contribution of supraspinal and spinal structures to the responses of dorsal spinal cord blood flow to innocuous cutaneous brushing in rats. Auton Neurosci Basic Clin 2007; 136: 96–99.
Rane K, Segerdahl M, Karlsten R . Intrathecal adenosine increases spinal cord blood flow in the rat: measurements with the laser-doppler flowmetry technique. Acta Anaesth Scand 2004; 48: 1249–1255.
Macri S, De Monte A, Greggi T, Parisini P, Zanoni A, Merlini L . Intra-operative spinal cord monitoring in orthopaedics. Spinal Cord 2000; 38: 133–139.
Harakawa I, Yano T, Sakurai T, Nishikimi N, Nimura Y . Measurement of spinal cord blood flow by an inhalation method and intraarterial injection of hydrogen gas. J Vasc Surg 1997; 26: 623–628.
Frerichs KU, Feuerstein GZ . Laser-Doppler-flowmetry: a review of its application for measuring cerebral and spinal cord blood flow. Mol Chem Neuropathol 1990; 12: 55–70.
Martirosyan NL, Feuerstein JS, Theodore N, Cavalcanti DD, Spetzler RF, Preul MC . Blood supply and vascular reactivity of the spinal cord under normal and pathological conditions A review. J Neurosurg Spine 2011; 15: 238–251.
Oyinbo CA . Secondary injury mechanisms in traumatic spinal cord injury: a nugget of this multiply cascade. Acta Neurobiol Exp 2011; 71: 281–299.
Mautes AEM, Weinzier MR, Donovan F, Noble L . Vascular events after spinal cord injury: contribution to secondary pathogenesis. Phys Ther 2000; 80: 673–687.
Sloan TB . Anesthetic effects on electrophysiologic recordings. J Cl Neuroph 1998; 15: 217–226.
Seyal M, Mull B . Mechanisms of signal change during intraoperative somatosensory evoked potential monitoring of spinal cord. J Cl Neuroph 2002; 19: 409–415.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Technology Development Foundation of Shaanxi Province (No.2009K-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, L., Dang, Xq., Lan, Bs. et al. Study on the safe range of shortening of the spinal cord in canine models. Spinal Cord 51, 134–138 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2012.99
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2012.99
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Biomechanical comparison of spinal column shortening - a finite element study
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2022)
-
Safe range of shortening the middle thoracic spine, an experimental study in canine
European Spine Journal (2020)