Abstract
Objective:
The aim of this study was to investigate changes of leptin concentration in plasma in patients with spinal cord injury to come to a single concept by using a Meta-analysis.
Setting:
Systematic Review.
Methods:
Searching relevant articles was performed in Ovid data base, Medline (PubMed) EMBASE, Google Scholar, Cochrane and Scopus up to February 2013. Five articles were selected using two independent reviewers. Analysis were performed using SPSS version 18 and Comparative Meta-analysis software version 2.0.
Results:
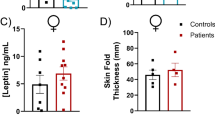
The combined analysis with confidence interval of 95% using comprehensive meta-analysis showed significant higher leptin levels in patients with spinal cord injury in comparison with able bodies (P<0.0001). The effect of spinal lesion level on plasma leptin concentration was also statistically significant (P<0.0001). Body mass index was positively related to plasma leptin concentration in both groups (P<0.0001).
Conclusion:
This Meta analysis approves increased level of leptin in spinal cord injured patients which can be due to fat distribution changes and sympathetic dysfunction in these patients. Our results also showed that patients with higher spinal lesion level have higher plasma leptin concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Brennan AM, Mantzoros CS . Drug Insight: the role of leptin in human physiology and pathophysiology--emerging clinical applications. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2006; 2: 318–327.
Rao MN, Schambelan M, Tai VW, Abrams DI, Khatami H, Havel PJ et al. Assessing the Association between Leptin and Bone Mineral Density in HIV-Infected Men. AIDS Res Treat 2012; 2012: 103072.
Maïmoun L, Puech AM, Manetta J, Badiou S, Paris F, Ohanna F et al. Circulating leptin concentrations can be used as a surrogate marker of fat mass in acute spinal cord injury patients. Metabolism 2004; 53: 989–994.
Bauman WA, Spungen AM, Zhong YG, Mobbs CV . Plasma leptin is directly related to body adiposity in subjects with spinal cord injury. Horm Metab Res 1996; 28: 732–736.
Lee MY, Myers J, Hayes A, Madan S, Froelicher VF, Perkash I et al. C-reactive protein, metabolic syndrome, and insulin resistance in individuals with spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med 2005; 28: 20–25.
Duckworth WC, Jallepalli P, Solomon SS . Glucose intolerance in spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1983; 64: 107–110.
Cragg JJ, Stone JA, Krassioukov AV . Management of cardiovascular disease risk factors in individuals with chronic spinal cord injury: an evidence-based review. J Neurotrauma 2012; 29: 1999–2012.
Wahman K, Nash MS, Lewis JE, Seiger A, Levi R . Increased cardiovascular disease risk in Swedish persons with paraplegia: The Stockholm spinal cord injury study. J Rehabil Med 2010; 42: 489–492.
Huang TS, Wang YH, Chen SY . The relation of serum leptin to body mass index and to serum cortisol in men with spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2000; 81: 1582–1586.
Wang YH, Huang TS, Liang HW, Su TC, Chen SY, Wang TD . Fasting serum levels of adiponectin, ghrelin, and leptin in men with spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2005; 86: 1964–1968.
Thomas T, Burguera B, Melton LJ 3rd, Atkinson EJ, O'Fallon WM, Riggs BL et al. Role of serum leptin, insulin, and estrogen levels as potential mediators of the relationship between fat mass and bone mineral density in men versus women. Bone 2001; 29: 114–120.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG . Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003; 327: 557–560.
Weiss LA, Barrett-Connor E, von Mühlen D, Clark P . Leptin predicts BMD and bone resorption in older women but not older men: the Rancho Bernardo Study. J Bone Miner Res 2006; 21: 758–764.
Buchholz AC, McGillivray CF, Pencharz PB . The use of bioelectric impedance analysis to measure fluid compartments in subjects with chronic paraplegia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2003; 84: 854–861.
Jeon JY, Steadward RD, Wheeler GD, Bell G, McCargar L, Harber V et al. Intact sympathetic nervous system is required for leptin effects on resting metabolic rate in people with spinal cord injury. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 402–407.
Hassink SG, Sheslow DV, de Lancey E, Opentanova I, Considine RV, Caro JF . Serum leptin in children with obesity: Relationship to gender and development. Pediatrics 1996; 98: 201–203.
Ellis KJ, Nicolson MY . Leptin levels and body fatness in children: Effects of gender, ethnicity, and sexual development. Pediatr Res 1997; 42: 484–488.
Zimmet P, Hodge A, Nicolson M, Staten M, de Lancey E, Opentanova I, Considine RV, Caro JF, Moore J et al. Serum leptin concentration, obesity, and insulin resistance in Western Samoans: Cross sectional study. Br Med J 1996; 313: 965–969.
Mantzoros CS, Moschos S, Avramopoulos I, Kaklamani V, Liolios A, Doulgerakis DE et al. Leptin concentrations in relation to body mass index and the tumor necrosis factor-a system in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997; 82: 3408–3413.
Maruyama Y, Mizuguchi M, Yaginuma T, Kusaka M, Yoshida H, Yokoyama K et al. Serum leptin, abdominal obesity and the metabolic syndrome in individuals with chronic spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2008; 46: 494–499.
Spungen AM, Adkins RH, Stewart CA, Wang J, Pierson RN Jr, Waters RL et al. Factors influencing body composition in persons with spinal cord injury: a cross-sectional study. J Appl Physiol 2003; 95: 2398–2407.
Modlesky CM, Bickel CS, Slade JM, Meyer RA, Cureton KJ, Dudley GA . Assessment of skeletal muscle mass in men with spinal cord injury using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and magnetic resonance imaging. J Appl Physiol 2004; 96: 561–565.
Peterson HR, Rothschild M, Weinberg CR, Fell RD, McLeish KR, Pfeifer MA . Body fat and the activity of the autonomic nervous system. N Engl J Med 1988; 318: 1077–1083.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Latifi, S., Koushki, D., Norouzi Javidan, A. et al. Changes of Leptin concentration in plasma in patients with spinal cord injury: A Meta-analysis. Spinal Cord 51, 728–731 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2013.82
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2013.82
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Omega-3 fatty acids in the treatment of spinal cord injury: untapped potential for therapeutic intervention?
Molecular Biology Reports (2022)
-
Biomarkers from Secondary Complications in Spinal Cord Injury
Current Pharmacology Reports (2022)
-
Endocrinological and inflammatory markers in individuals with spinal cord injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders (2022)