Abstract
Study design:
Retrospective study.
Objectives:
We present our experience with patients treated with interspinous devices who are affected by neurogenic intermittent claudication (NIC) or lumbar disc herniation (LDH) where the interspinous system has been inserted following microdiscectomy.
Methods:
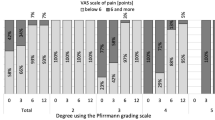
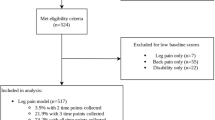
This study included patients (n=100) with NIC secondary to lumbar spinal stenosis (group 1), and patients (n=100) with LDH (group 2) in whom the interspinous device has been implanted following radicular decompression in a period spanning 6 years. The latter have been compared with a homogenous group of patients (n=100) where no interspinous system has been implanted following microdiscectomy (group 3). Clinical findings have been observed preoperatively and 3, 6, 12 months and every year post-operatively using dedicated questionnaires (Zurich Claudication Questionnaire, Visual Analog Scale and Oswestry Disability Index).
Results:
Six years following surgical treatment, 85% of the patients of group 1 presented good improvement of symptoms and 90% of the patients referred satisfaction for surgery. Only few cases needed reoperation. In one case, the device was removed and in two cases, we changed the surgical strategy. Overall, patients of group 2 presented significantly less lumbar disc recurrences compared with group 3 (P<0.05) and better clinical outcome when compared with the same group (P<0.01).
Conclusion:
According to our features, interspinous systems showed significant and clinically meaningful improvements in pain and disability for up to 6 years. Furthermore, interspinous devices have shown better clinical outcome and less lumbar disc recurrences when associated with standard microdiscectomy. These data, however, need further studies and a longer period of follow-up.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Fraser JF, Huang RC, Girardi FP, Cammisa FP Jr . Pathogenesis, presentation, and treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis associated with coronal or sagittal spinal deformities. Neurosurg Focus 2003; 14: e6.
Malmivaara A, Slatis P, Heliovaara M, Sainio P, Kinnunen H, Kankare J et al. Surgical or nonoperative treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis? A randomized controlled trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007; 32: 1–8.
Weinstein JN, Tosteson TD, Lurie JD, Tosteson AN, Blood E, Hanscom B et al. Surgical versus nonsurgical therapy for lumbar spinal stenosis. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 794–810.
Airaksinen O, Herno A, Kaukanen E, Saari T, Sihvonen T, Suomalainen O . Density of lumbar muscles 4 years after decompressive spinal surgery. Eur Spine J 1996; 5: 193–197.
Fox MW, Onofrio BM, Onofrio BM, Hanssen AD . Clinical outcomes and radiological instability following decompressive lumbar laminectomy for degenerative spinal stenosis: a comparison of patients undergoing concomitant arthrodesis versus decompression alone. J Neurosurg 1996; 85: 793–802.
Yone K, Sakou T, Kawauchi Y, Yamaguchi M, Yanase M . Indication of fusion for lumbar spinal stenosis in elderly patients and its significance. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1996; 21: 242–248.
Kim S, Mortaz Hedjri S, Coyte PC, Rampersaud YR . Cost-utility of lumbar decompression with or without fusion for patients with symptomatic degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine J 2012; 12: 44–54.
Anderson PA, Tribus CB, Kitchel SH . Treatment of neurogenic claudication by interspinous decompression: application of the X STOP device in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Neurosurg Spine 2006; 4: 463–471.
Alfieri A, Gazzeri R, Prell J, Scheller C, Rachinger J, Strauss C et al. Role of lumbar interspinous distraction on the neural elements. Neurosurg Rev 2012; 35: 477–484.
Kim KA, McDonald M, Pik JH, Khoueir P, Wang MY . Dynamic intraspinous spacer technology for posterior stabilization: case-control study on the safety, sagittal angulation, and pain outcome at 1-year follow-up evaluation. Neurosurg Focus 2007; 22: E7.
Caserta S, La Maida GA, Misaggi B, Peroni D, Pietrabissa R, Raimondi MT et al. Elastic stabilization alone or combined with rigid fusion in spinal surgery: a biomechanical study and clinical experience based on 82 cases. Eur Spine J 2002; 11 (Suppl 2): S192–S197.
Patil S, Burton M, Storey C, Glenn C, Marino A, Nanda A . Evaluation of interspinous process distraction device (X-STOP) in a representative patient cohort. World Neurosurg 2013; 80: 213–217.
Zucherman JF, Hsu KY, Hartjen CA, Mehalic TF, Implicito DA, Martin MJ et al. A multicenter, prospective, randomized trial evaluating the X STOP interspinous process decompression system for the treatment of neurogenic intermittent claudication: two-year follow-up results. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005; 30: 1351–1358.
Miller LE, Block JE . Interspinous spacer implant in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis: preliminary results of a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Pain Res Treat 2012; 2012: 823509.
Davis RJ, Errico TJ, Bae H, Auerbach JD . Decompression and Coflex interlaminar stabilization compared with decompression and instrumented spinal fusion for spinal stenosis and low-grade degenerative spondylolisthesis: two-year results from the prospective, randomized, multicenter, Food and Drug Administration Investigational Device Exemption trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2013; 38: 1529–1539.
Hobart J, Gilkes C, Adams W, Germon T . Interspinous spacers for lumbar foraminal stenosis: formal trials are justified. Eur Spine J 2013; 22 (Suppl 1): S47–S53.
Stromqvist BH, Berg S, Gerdhem P, Johnsson R, Moller A, Sahlstrand T et al. X-stop versus decompressive surgery for lumbar neurogenic intermittent claudication: randomized controlled trial with 2-year follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2013; 38: 1436–1442.
Kovacs FM, Urrutia G, Alarcon JD . Surgery versus conservative treatment for symptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2011; 36: E1335–E1351.
Moojen WA, Arts MP, Bartels RH, Jacobs WC, Peul WC . Effectiveness of interspinous implant surgery in patients with intermittent neurogenic claudication: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J 2011; 20: 1596–1606.
Moojen WA, Arts MP, Jacobs WC, van Zwet EW, van den Akker-van Marle ME, Koes BW et al. Interspinous process device versus standard conventional surgical decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis: randomized controlled trial. BMJ 2013; 347: f6415.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grasso, G., Giambartino, F. & Iacopino, D. Clinical analysis following lumbar interspinous devices implant: where we are and where we go. Spinal Cord 52, 740–743 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2014.100
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2014.100
This article is cited by
-
Interspinous implants: are the new implants better than the last generation? A review
Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine (2017)
-
Interspinous process stabilization with Rocker via unilateral approach versus X-Stop via bilateral approach for lumbar spinal stenosis: a comparative study
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015)