Abstract
Study design:
Retrospective study reporting characteristics and management of septic arthritis of the hip due to pressure sores in spinal cord-injured patients.
Objectives:
To describe clinical and biological data of septic arthritis of the hip and its treating management.
Setting:
The database of the regional SCI referral center, Nantes, France.
Methods:
We retrospectively collected data from 33 cases of septic arthritis of the hip in the medical files of 26 patients.
Results:
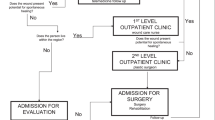
We analyzed 33 cases of septic arthritis of the hip treated in one French referent center for spinal cord-injured patients from January 1988 to December 2009. Most patients had a thoracic complete paraplegia and nearly two-third (17 out of 26) had no systematic follow-up. In 25 out of 33 cases, the septic arthritis of the hip was due to a trochanteric pressure sore. The causal pressure sore was most frequently associated with a persistent drainage. The standard radiological examination led to the diagnosis in 30 cases and, in 7 questionable cases, magnetic resonance imaging was more contributory. Surgery always consisted of a wide carcinological-like excision and of a subtrochanteric proximal femoral resection including both greater and lesser trochanters. A musculocutaneous flap was realized for all cases and the choice of the muscle depended on the localization of the causal pressure sore but also of the remaining choices, as most of the patients had already undergone a prior surgery. An antibiotic treatment was adapted to multiple samples during surgery.
Conclusion:
We do advocate for a one-stage procedure including a subtrochanteric proximal femoral resection and a musculocutaneous flap.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Byrne DW, Salzberg CA . Major risk factor for pressure ulcers in the spinal cord disabled: a literature review. Spinal Cord 1996; 34: 255–263.
Evans GRD, Lewis VL, Manson PN, Loomis M, Vander Kolk CA . Hip joint communication with pressure sore: the refractory wound and the role of Girdlestone arthroplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 1993; 91: 288–294.
Perrouin-Verbe B, Poirier P, Rome J, Touchais S, Le Fourn B, Lejeune F et al. Hip arthritis in spinal cord injuries patients.Colin D, Barrois B, Pélissiér J L'escarre. Masson: Paris. 1998, pp. 176–183
Klein N, Moore Th, Capen D, Green S . Sepsis of the hip in paraplegic patients. J Bone Joint Surg 1988; 70-A: 839–843.
Heilporn A . Psychological factors in the causation of pressure sores: case reports. Paraplegia 1991; 29: 137–139.
Peters JW, Johnson GE . Proximal femurectomy for decubitus ulceration in the spinal cord injury patient. Paraplegia 1990; 28: 55–61.
Lortat-Jacob A, Lortat-Jacob S, Jouanin Th, Beaufils Ph, Coignard S, Held JP et al. Septic arthritis of the hip in paraplegics. Rev Chir Orthop (Paris) 1984; 70: 383–388.
Berlemont M . The treatment of suppurative arthritis of the hip in paraplegia by extensive hip resection. Rev Chir Orthop (Paris) 1985; 71: 377–387.
Klein N, Luster S, Green S, Moore Th, Capen D . Closure of defects from pressure sores requiring proximal femoral resection. Ann Plast Surg 1988; 21: 246–250.
Girdlestone GR . Acute pyogenic arthritis of the hip: an operation giving free access and effective drainage. 1943. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2008; 466: 258–263.
Rubayi S, Pompan D, Garland D . Proximal femoral resection and myocutaneous flap for treatment of pressure ulcers in spinal cord injury patients. Ann Plast Surg 1991; 27: 132–138.
Lawton RL, De Pinto V . Bilateral hip disarticulation in paraplegics with decubitus ulcers. Arch Surg 1987; 122: 1040–1043.
Benito-Ruiz J, Baena-Montilla P, Mena-Yago A, Miguel I, Montanana-Vizcaino J . A complicated trochanteric pressure sore: what is the best surgical management? Case report. Paraplegia 1993; 31: 119–124.
Vancabeke M, Harper L, Penders W, Putz P . Anterior flap for coverage following hip disarticulation for osteomyelitis. Acta Orthop Belg 1999; 65: 223–225.
Correa GI, Calderon WO, Roa RG, Guzman LM, Burnier LA, Danilla SE . Proximal amputation of inferior extremity secondary to recurrent pressure ulcers in patients with spinal cord injuries. Spinal Cord 2008; 46: 135–139.
Acartürk TO . Treatment of large ischial ulcers communicating with the hip joint with proximal femoral resection and reconstruction with a combined vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius and rectus femoris musculocutaneous flap. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2009; 62: 1497–1502.
Sagi A, Meller Y, Kon M, Rosenberg L, Ben-Yakar Y . Bilateral hip resection for closure of trochanteric pressure sores: case report. Paraplegia 1987; 25: 39–43.
Tryggestad KE, Youm T, Koval KJ . Orthopedic management of decubitus ulcers around the proximal femur. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 2006; 35: 316–321.
Minami RT, Hentz VR, Vistnes LM . Use of the vastus lateralis muscle flap for repair of trochanteric pressure sores. Plast Reconstr Surg 1977; 60: 364–368.
Heym B, Rimareix F, Lortat-Jacob A, Nicolas-Chanoine MH . Bacteriological investigation of infected pressure ulcers in spinal cord-injured patients and impact on antibiotic therapy. Spinal Cord 2004; 42: 230–234.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le Fort, M., Rome-Saulnier, J., Lejeune, F. et al. Sepsis of the hip due to pressure sore in spinal cord injured patients: advocacy for a one-stage surgical procedure. Spinal Cord 53, 226–231 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2014.170
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2014.170