Abstract
Study design:
This is a cross-sectional study.
Objectives:
The goal of this study was to characterize the diffusion properties across segments of the spinal cord and peak cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) velocities in the stenotic spinal canal, and to determine the correlation between these properties and clinical and electrophysiological parameters in patients with cervical spinal cord injury (SCI).
Setting:
This study was conducted in the University teaching hospital.
Methods:
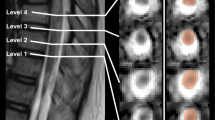
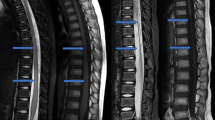
The study involved 17 patients with cervical SCI. The apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and fractional anisotropy (FA) of the spinal cord and peak systolic and diastolic velocities of CSF were measured at the level of maximum compression (region 1) and at the levels above (region 2) and below (region 3) the level of injury with no signal change in conventional magnetic resonance imaging. Neurological and electrophysiological parameters were measured, including American Spinal Injury Association (ASIA) Impairment Scale (AIS), ASIA motor score, ASIA sensory score, Modified Barthel Index, Spinal Cord Independence Measure III (SCIM III), somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEP) and motor evoked potentials (MEP).
Results:
The ADC was significantly higher and the FA was significantly lower in regions 1, 2 and 3 of the SCI patients than in the normal controls (P<0.05 each). FA of the level below correlated with AIS, ASIA sensory score and SCIM III score, and FA of the level above correlated with SSEP latencies and MEP amplitudes (P<0.05 each). The reductions in FA correlated with CSF flow, functional measurements and evoked potentials.
Conclusions:
Diffusion tensor imaging can be used to quantify the proximal and distal extents of spinal cord damage. Reductions in FA were correlated with CSF flow, functional measurements and evoked potentials.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Bakshi R, Thompson AJ, Rocca MA, Pelletier D, Dousset V, Barkhof F et al. MRI in multiple sclerosis: current status and future prospects. Lancet Neurol 2008; 7: 615–625.
Ellingson BM, Ulmer JL, Kurpad SN, Schmit BD . Diffusion tensor MR imaging in chronic spinal cord injury. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2008; 29: 1976–1982.
Hagmann P, Jonasson L, Maeder P, Thiran JP, Wedeen VJ, Meuli R . Understanding diffusion MR imaging techniques: from scalar diffusion-weighted imaging to diffusion tensor imaging and beyond. Radiographics 2006; 26: S205–S223.
Clark CA, Werring DJ . Diffusion tensor imaging in spinal cord: methods and applications – a review. NMR Biomed 2002; 15: 578–586.
Nitz WR, Bradley WG, Watanabe AS, Lee RR, Burgoyne B, O'Sullivan RM et al. Flow dynamics of cerebrospinal fluid: assessment with phase-contrast velocity MR imaging performed with retrospective cardiac gating. Radiology 1992; 183: 395–405.
Haughton VM, Korosec FR, Medow JE, Dolar MT, Iskandar BJ . Peak systolic and diastolic CSF velocity in the foramen magnum in adult patients with Chiari I malformations and in normal control participants. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003; 24: 169–176.
Koç K, Anik Y, Anik I, Cabuk B, Ceylan S . Chiari 1 malformation with syringomyelia: correlation of phase-contrast cine MR imaging and outcome. Turk Neurosurg 2007; 17: 183–192.
Noble LJ, Wrathall JR . Correlative analyses of lesion development and functional status after graded spinal cord contusive injuries in the rat. Exp Neurol 1989; 103: 34–40.
Noble LJ, Wrathall JR . Distribution and time course of protein extravasation in the rat spinal cord after contusive injury. Brain Res 1989; 482: 57–66.
Mautes AE, Weinzierl MR, Donovan F, Noble LJ . Vascular events after spinal cord injury: contribution to secondary pathogenesis. Phys Ther 2000; 80: 673–687.
Cheran S, Shanmuganathan K, Zhuo J, Mirvis SE, Aarabi B, Alexander MT et al. Correlation of MR diffusion tensor imaging parameters with ASIA motor scores in hemorrhagic and nonhemorrhagic acute spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 2011; 28: 1881–1892.
Petersen JA, Wilm BJ, von Meyenburg J, Schubert M, Seifert B, Najafi Y et al. Chronic cervical spinal cord injury: DTI correlates with clinical and electrophysiological measures. J Neurotrauma 2012; 29: 1556–1566.
Ozanne A, Krings T, Facon D, Fillard P, Dumas JL, Alvarez H et al. MR diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tracking in spinal cord arteriovenous malformations: a preliminary study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2007; 28: 1271–1279.
Renoux J, Facon D, Fillard P, Huynh I, Lasjaunias P, Ducreux D . MR diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tracking in inflammatory diseases of the spinal cord. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2006; 27: 1947–1951.
Facon D, Ozanne A, Fillard P, Lepeintre JF, Tournoux-Facon C, Ducreux D . MR diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tracking in spinal cord compression. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2005; 26: 1587–1594.
Tsuchiya K, Katase S, Fujikawa A, Hachiya J, Kanazawa H, Yodo K . Diffusion-weighted MRI of the cervical spinal cord using a single-shot fast spin-echo technique: findings in normal subjects and in myelomalacia. Neuroradiology 2003; 45: 90–94.
Demir A, Ries M, Moonen CT, Vital JM, Dehais J, Arne P et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with apparent diffusion coefficient and apparent diffusion tensor maps in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Radiology 2003; 229: 37–43.
Du Boulay GH . Pulsatile movements in the CSF pathways. Br J Radiol 1966; 39: 255–262.
Gilland O, Chin F, Anderson WB, Nelson JR . A cinemyelographic study of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 1969; 106: 369–375.
Enzmann DR, Pelc NJ . Normal flow patterns of intracranial and spinal cerebrospinal fluid defined with phase-contrast cine MR imaging. Radiology 1991; 178: 467–474.
DeBoy CA, Zhang J, Dike S, Shats I, Jones M, Reich DS et al. High resolution diffusion tensor imaging of axonal damage in focal inflammatory and demyelinating lesions in rat spinal cord. Brain 2007; 130: 2199–2210.
Zhang J, Jones M, DeBoy CA, Reich DS, Farrell JA, Hoffman PN et al. Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging of Wallerian degeneration in rat spinal cord after dorsal root axotomy. J Neurosci 2009; 29: 3160–3171.
Chang Y, Jung TD, Yoo DS, Hyun JK . Diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tractography of patients with cervical spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 2010; 27: 2033–2040.
Armonda RA, Citrin CM, Foley KT, Ellenbogen RG . Quantitative cine-mode magnetic resonance imaging of Chiari I malformations: an analysis of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics. Neurosurgery 1994; 35: 214–223 discussion 223–224.
Enzmann DR, O'Donohue J, Rubin JB, Shuer L, Cogen P, Silverberg G . CSF pulsations within nonneoplastic spinal cord cysts. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1987; 149: 149–157.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology Grant (30–2014–015), Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital and partly supported for 2 years by Pusan National University Research Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SY., Shin, M., Chang, J. et al. Correlation of diffusion tensor imaging and phase-contrast MR with clinical parameters of cervical spinal cord injuries. Spinal Cord 53, 608–614 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2015.57
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2015.57
This article is cited by
-
Characterising spinal cerebrospinal fluid flow in the pig with phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging
Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (2023)
-
Multispectral diffusion-weighted MRI of the instrumented cervical spinal cord: a preliminary study of 5 cases
European Spine Journal (2020)
-
Subject-specific regional measures of water diffusion are associated with impairment in chronic spinal cord injury
Neuroradiology (2017)
-
Relationship between magnetic resonance imaging findings and spinal cord injury in extension injury of the cervical spine
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology (2016)