Abstract
Study design:
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation study.
Objectives:
The analgesic effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in chronic pain have been the focus of several studies. In particular, rTMS of the premotor cortex/dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (PMC/DLPFC) changes pain perception in healthy subjects and has analgesic effects in acute postoperative pain, as well as in fibromyalgia patients. However, its effect on neuropathic pain in patients with traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI) has not been assessed.
Setting:
Merano (Italy) and Salzburg (Austria).
Methods:
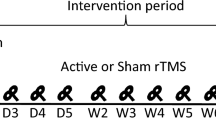
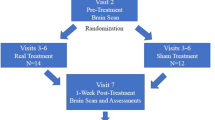
In this study, we performed PMC/DLPFC rTMS in subjects with SCI and neuropathic pain. Twelve subjects with chronic cervical or thoracic SCI were randomized to receive 1250 pulses at 10 Hz rTMS (n=6) or sham rTMS (n=6) treatment for 10 sessions over 2 weeks. The visual analog scale, the sensory and affective pain rating indices of the McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ), the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale and the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale were used to assed pain and mood at baseline (T0), 1 day after the first week of treatment (T1), 1 day (T2), 1 week (T3) and 1 month (T4) after the last intervention.
Results:
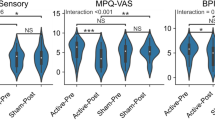
Subjects who received active rTMS had a statistically significant reduction in pain symptoms in comparison with their baseline pain, whereas sham rTMS participants had a non-significant change in daily pain from their baseline pain.
Conclusion:
The findings of this preliminary study in a small patient sample suggest that rTMS of the PMC/DLPFC may be effective in relieving neuropathic pain in SCI patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Hallett M . Transcranial magnetic stimulation: a primer. Neuron 2007; 55: 187–199.
Klein MM, Treister R, Raij T, Pascual-Leone A, Park L, Nurmikko T et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation of the brain: guidelines for pain treatment research. Pain 2015; 156: 1601–1614.
Lefaucheur JP, André-Obadia N, Antal A, Ayache SS, Baeken C, Benninger DH et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS). Clin Neurophysiol 2014; 125: 2150–2206.
Borckardt JJ, Reeves ST, Weinstein M, Smith AR, Shelley N, Kozel FA et al. Significant analgesic effects of one session of postoperative left prefrontal cortex repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation: a replication study. Brain Stimul 2008; 1: 122–127.
Borckardt JJ, Reeves ST, Frohman H, Madan A, Jensen MP, Patterson D et al. Fast left prefrontal rTMS acutely suppresses analgesic effects of perceived controllability on the emotional component of pain experience. Pain 2011; 152: 182–187.
Brighina F, De Tommaso M, Giglia F, Scalia S, Cosentino G, Puma A et al. Modulation of pain perception by transcranial magnetic stimulation of left prefrontal cortex. J Headache Pain 2011; 12: 185–191.
Fierro B, De Tommaso M, Giglia, Giglia G, Palermo A, Brighina F . Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) during capsaicin-induced pain: modulatory effects on motor cortex excitability. Exp Brain Res 2010; 203: 31–38.
Short EB, Borckardt JJ, Anderson BS, Frohman H, Beam W, Reeves ST et al. Ten sessions of adjunctive left prefrontal rTMS significantly reduces fibromyalgia pain: a randomized, controlled pilot study. Pain 2011; 152: 2477–2484.
Lefaucheur JP, Drouot X, Menard-Lefaucheur I, Zerah F, Bendib B, Cesaro P et al. Neurogenic pain relief by repetitive transcranial magnetic cortical stimulation depends on the origin and the site of pain. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2004; 75: 612–657.
Lefaucheur JP, de Andrade DC . Intraoperative neurophysiologic mapping of the central cortical region for epidural electrode placement in the treatment of neuropathic pain by motor cortex stimulation. Brain Stimul 2009; 2: 138–148.
Defrin R, Grunhaus L, Zamir D, Zeilig G . The effect of a series of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulations of the motor cortex on central pain after spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2007; 88: 1574–1580.
Kang BS, Shin HI, Bang MS . Effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over the hand motor cortical area on central pain after spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2009; 90: 1766–1771.
Jetté F, Côté I, Meziane HB, Mercier C . Effect of single-session repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation applied over the hand versus leg motor area on pain after spinal cord injury. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 2013; 27: 636–643.
Tazoe T, Perez MA . Effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on recovery of function after spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2015; 96: S145–S155.
de Andrade DC, Mhalla A, Adam F, Texeira MJ, Bouhassira D . Neuropharmacological basis of rTMS-induced analgesia: the role of endogenous opioids. Pain 2014; 155: 598–605.
Hardy SG . Analgesia elicited by prefrontal stimulation. Brain Res 1985; 339: 281–284.
Hardy SG, Haigler HJ . Prefrontal influences upon the midbrain: a possible route for pain modulation. Brain Res 1985; 339: 285–293.
Lorenz J, Minoshima S, Casey KL . Keeping pain out of mind: the role of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in pain modulation. Brain 2003; 126: 1079–1091.
Nahmias F, Debes C, de Andrade DC, Mhalla A, Bouhassira D . Diffuse analgesic effects of uniloateral repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in healthy volunteers. Pain 2009; 147: 224–232.
Dersh J, Polatin PB, Gatchel RJ . Chronic pain and psychopathology: research findings and theoretical considerations. Psychosom Med 2002; 64: 773–786.
Pincus T, Williams A . Models and measurements of depression in chronic pain. J Psychosom Res 1999; 47: 211–219.
Treede RD, Jensen TS, Campbell JN, Cruccu G, Dostrovsky JO, Griffin JW et al. Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 2008; 70: 1630–1635.
Price DD, McHaffie JG . Effects of heterotopic conditioning stimuli on first and second pain: A psychophysical evaluation in humans. Pain 1988; 34: 245–252.
Dworkin RH, O'Connor AB, Backonja M, Farrar JT, Finnerup NB, Jensen TS et al. Pharmacologic management of neuropathic pain: evidence-based recommendations. Pain 2007; 132: 237–251.
André-Obadia N, Mertens P, Gueguen A, Peyron R, Garcia-Larrea L . Pain relief by rTMS: differential effect of current flow but no specific action on pain subtypes. Neurology 2008; 71: 833–840.
Rossini PM, Burke D, Chen R, Cohen LG, Daskalakis Z, Di Iorio R et al. Non-invasive electrical and magnetic stimulation of the brain, spinal cord, roots and peripheral nerves: basic principles and procedures for routine clinical and research application. An updated report from an I.F.C.N. Committee. Clin Neurophysiol 2015; 126: 1071–1107.
Ahdab R, Ayache SS, Brugieres P, Goujon C, Lefaucheur JP . Comparison of “standard” and “navigated” procedures of TMS coil positioning over motor, premotor and prefrontal targets in patients with chronic pain and depression. Neurophysiol Clin 2010; 40: 27–36.
George MS, Wassermann EM . Rapid-rate transcranial magnetic stimulation and ECT. Convuls Ther 1994; 10: 251–254.
Melzack R . The McGill Pain Questionnaire: major properties and scoring methods. Pain 1975; 1: 277–299.
Hamilton M . A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1960; 23: 56–62.
Hamilton M . The assessment of anxiety states by rating. Br J Med Psychol 1959; 32: 50–55.
Noguchi K, Gel YR, Brunner E, Konietschke F . nparLD: an R software package for the nonparametric analysis of longitudinal data in factorial experiments. J Stat Softw 2012; 50: 1–23.
Yılmaz B, Kesikburun S, Yaşar E, Tan AK . The effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on refractory neuropathic pain in spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med 2014; 37: 397–400.
Apkarian AV, Bushnell MC, Treede RD, Zubieta JK . Human brain mechanisms of pain perception and regulation in health and disease. Eur J Pain 2005; 9: 463–484.
Baron R, Baron Y, Disbrow E, Roberts TP . Brain processing of capsaicin-induced secondary hyperalgesia: a functional MRI study. Neurology 1999; 53: 548–557.
Gustin SM, Wrigley PJ, Siddall PJ, Henderson LA . Brain anatomy changes associated with persistent neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury. Cereb Cortex 2010; 20: 1409–1419.
Stanwell P, Siddall P, Keshava N, Cocuzzo D, Ramadan S, Lin A et al. Neuro magnetic resonance spectroscopy using wavelet decomposition and statistical testing identifies biochemical changes in people with spinal cord injury and pain. Neuroimage 2010; 53: 544–552.
Apkarian AV, Sosa Y, Sonty S, Levy RM, Harden RN, Parrish TB et al. Chronic back pain is associated with decreased prefrontal and thalamic gray matter density. J Neurosci 2004; 24: 10410–10415.
Seminowicz DA, Wideman TH, Naso L, Hatami-Khoroushahi Z, Fallatah S, Ware MA et al. Effective treatment of chronic low back pain in humans reverses abnormal brain anatomy and function. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 7540–7550.
Obermann M, Rodriguez-Raecke R, Naegel S, Holle D, Mueller D, Yoon MS et al. Gray matter volume reduction reflects chronic pain in trigeminal neuralgia. Neuroimage 2013; 74: 352–358.
Yoon EJ, Kim YK, Shin HI, Lee Y, Kim SE . Cortical and white matter alterations in patients with neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury. Brain Res 2013; 2: 64–73.
Petrovic P, Kalso E, Petersson KM, Ingvar M . Placebo and opioid analgesia—imaging a shared neuronal network. Science 2002; 295: 1737–1740.
Paus T, Castro-Alamancos MA, Petrides M . Cortico-cortical connectivity of the human mid-dorsolateral frontal cortex and its modulation by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Eur J Neurosci 2001; 14: 1405–1411.
Strafella AP, Paus T, Barrett J, Dagher A . Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the human prefrontal cortex induces dopamine release in the caudate nucleus. J Neurosci 2001; 21: RC157.
Schweinhardt P, Kalk N, Wartolowska K, Chessell I, Wordsworth P, Tracey I . Investigation into the neural correlates of emotional augmentation of clinical pain. Neuroimage 2008; 40: 759–766.
Avery DH, Holtzheimer PE 3rd, Fawaz W, Russo J, Neumaier J, Dunner DL et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation reduces pain in patients with major depression: a sham-controlled study. J Nerv Ment Dis 2007; 195: 378–381.
Miller EK, Cohen JD . An integrative theory of prefrontal cortex function. Annu Rev Neurosci 2001; 24: 167–202.
Funahashi S . Neuronal mechanisms of executive control by the prefrontal cortex. Neurosci Res 2001; 39: 147–165.
de Oliveira RA, de Andrade DC, Mendonça M, Barros R, Luvisoto T, Myczkowski ML et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the left premotor/dorsolateral prefrontal cortex does not have analgesic effect on central poststroke pain. J Pain 2014; 15: 1271–1281.
Boggio PS, Fregni F, Bermpohl F, Mansur CG, Rosa M, Rumi DO et al. Effect of repetitive TMS and fluoxetine on cognitive function in patients with Parkinson's disease and concurrent depression. Mov Disord 2005; 20: 1178–1184.
Loubinoux I, Kronenberg G, Endres M, Schumann-Bard P, Freret T, Filipkowski RK et al. Post-stroke depression: Mechanisms, translation and therapy. J Cell Mol Med 2012; 16: 1961–1969.
Rumi DO, Gattaz WF, Rigonatti SP, Rosa MA, Fregni F, Rosa MO et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation accelerates the antidepressant effect of amitriptyline in severe depression: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Biol Psychiatry 2005; 57: 162–166.
Fitzgerald PB, Maller JJ, Hoy KE, Thomson R, Daskalakis ZJ . Exploring the optimal site for the localization of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in brain stimulation experiments. Brain Stimul 2009; 2: 234–237.
Chouinard PA, Van Der Werf YD, Leonard G, Paus T . Modulating neural networks with transcranial magnetic stimulation applied over the dorsal premotor and primary motor cortices. J Neurophysiol 2003; 90: 1071–1083.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nardone, R., Höller, Y., Langthaler, P. et al. rTMS of the prefrontal cortex has analgesic effects on neuropathic pain in subjects with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 55, 20–25 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2016.87
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2016.87
This article is cited by
-
Effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on motor ability, neurophysiological changes, mental health, and activities of daily living in spinal cord injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis
European Spine Journal (2026)
-
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Substance Use Disorders and Chronic Pain: a Review of the Evidence and Call for Increased Mechanistic Understanding
Current Addiction Reports (2025)
-
Efficacy of neuromodulation and rehabilitation approaches on pain relief in patients with spinal cord injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Neurological Sciences (2025)
-
Comparative efficacy of common rehabilitation treatments for patients with neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Neurological Sciences (2025)
-
Effect of aerobic exercise program on neuropathic pain and quality of life in person with paraplegia: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Trials (2024)