Abstract
Study design:
Retrospective chart review.
Objective:
To analyze the role of sonography in detecting heterotopic ossification (HO) following spinal cord injury (SCI).
Setting:
Department of Spinal Cord Injury and Department of General and Trauma Surgery, BG University Hospital Bergmannsheil Bochum, Ruhr University Bochum, Germany.
Methods:
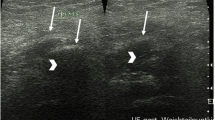
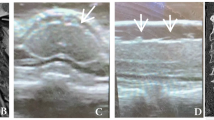
Between January 2003 and December 2013, 217 patients with HO of the hips met the inclusion criteria and were included in the final analyses. The diagnosis of HO was carried out in all cases using our hospital protocol. Primary outcome measure was to calculate the sensitivity of ultrasound screening examination in detecting HO following SCI.
Results:
The diagnosis of HO was confirmed in 217 patients after a mean interval of 64.8 days (range from 8 to 295; s.d.=40.4) via computerized tomography or magnetic resonance imaging scan. In 193 out of 217 patients, suspicious HO signs were noted in the ultrasound screening examination (sensitivity=88.9%).
Conclusions:
The use of ultrasound for screening for HO in SCI patients is reliable and has a high sensitivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Banovac K, Gonzalez F . Evaluation and management of heterotopic ossification in patients with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 1997; 35: 158–162.
Cipriano CA, Pill SG, Keenan MA . Heterotopic ossification following traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2009; 17: 689–697.
Citak M, Suero EM, Backhaus M, Aach M, Godry H, Meindl R et al. Risk factors for heterotopic ossification in patients with spinal cord injury: a case-control study of 264 patients. Spine 2012; 37: 1953–1957.
Wittenberg RH, Peschke U, Botel U . Heterotopic ossification after spinal cord injury. Epidemiology and risk factors. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1992; 74: 215–218.
Estrores IM, Harrington A, Banovac K . C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in patients with heterotopic ossification after spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med 2004; 27: 434–437.
Kim SW, Charter RA, Chai CJ, Kim SK, Kim ES . Serum alkaline phosphatase and inorganic phosphorus values in spinal cord injury patients with heterotopic ossification. Paraplegia 1990; 28: 441–447.
Larson JM, Michalski JP, Collacott EA, Eltorai D, McCombs CC, Madorsky JB . Increased prevalence of HLA-B27 in patients with ectopic ossification following traumatic spinal cord injury. Rheumatol Rehabil 1981; 20: 193–197.
Schurch B, Capaul M, Vallotton MB, Rossier AB . Prostaglandin E2 measurements: their value in the early diagnosis of heterotopic ossification in spinal cord injury patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1997; 78: 687–691.
Sherman AL, Williams J, Patrick L, Banovac K . The value of serum creatine kinase in early diagnosis of heterotopic ossification. J Spinal Cord Med 2003; 26: 227–230.
Singh RS, Craig MC, Katholi CR, Jackson AB, Mountz JM . The predictive value of creatine phosphokinase and alkaline phosphatase in identification of heterotopic ossification in patients after spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2003; 84: 1584–1588.
Citak M, Grasmucke D, Suero EM, Cruciger O, Meindl R, Schildhauer TA et al. The roles of serum alkaline and bone alkaline phosphatase levels in predicting heterotopic ossification following spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2015; 54: 368–370.
Pistarini C, Carlevati S, Contardi A . The echographic diagnosis of neurogenic paraosteoarthropathies in myelosis patients. G Ital Med Lav 1993; 15: 159–163.
Pistarini C, Carlevati S, Contardi A, Cannizzaro G . Use of ultrasonography methods in the diagnosis of neurogenic paraosteoarthropathy in spinal cord injury. Recenti Prog Med 1995; 86: 483–488.
Snoecx M, De Muynck M, Van Laere M . Association between muscle trauma and heterotopic ossification in spinal cord injured patients: reflections on their causal relationship and the diagnostic value of ultrasonography. Paraplegia 1995; 33: 464–468.
Citak M, Grasmucke D, Salber J, Cruciger O, Meindl R, Schildhauer TA et al. Heterotopic ossification mimicking infection in patients with traumatic spinal cord injury. Technol Health Care 2016; 24: 87–91.
Argyropoulou MI, Kostandi E, Kosta P, Zikou AK, Kastani D, Galiatsou E et al. Heterotopic ossification of the knee joint in intensive care unit patients: early diagnosis with magnetic resonance imaging. Crit Care 2006; 10: R152.
Taly AB, Nair KP, Jayakumar PN, Ravishankar D, Kalaivani PL, Indiradevi B et al. Neurogenic heterotopic ossification: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge in neurorehabilitation. Neurol India 2001; 49: 37–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosteius, T., Suero, E., Grasmücke, D. et al. The sensitivity of ultrasound screening examination in detecting heterotopic ossification following spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 55, 71–73 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2016.93
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2016.93
This article is cited by
-
Histology of neurogenic heterotopic ossification and comparison with its radiological expression in acute spinal cord injured patients
Spinal Cord (2025)
-
Pelvic MRI in spinal cord injury patients: incidence of muscle signal change and early heterotopic ossification
Spinal Cord (2021)
-
Heterotopic Ossification After Spinal Cord Injury: Current Clinical Approaches
Current Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Reports (2020)